Overview:
Apremilast is an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4) inhibitor, initially manufactured by Celgene Corporation. Amgen Incorporated acquired it in November 2019.
The drug is indicated for the following disorders in adults:
-
Active psoriatic arthritis.
-
Plaque psoriasis in patients eligible for concurrent phototherapy or systemic therapy.
-
Mouth ulcers in Behçet's disease.
Apremilast suppresses the immune system and reduces inflammation. It belongs in the DMARDs (disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs) group of drugs. Although not strictly indicated for rheumatoid arthritis (like most other DMARDs drugs), Apremilast is used in psoriatic arthritis treatment. It may be used alone or in combination with biologic agents in patients who do not show sufficient changes in response to the biologic agents alone.
Apremilast was approved for psoriatic arthritis and plaque psoriasis by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in March 2014 and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in November 2014. FDA approval of Apremilast for oral ulcers in Behçet's disease was obtained in July 2019. The drug has also been approved for use in Behçet's disease (with modifications) in the pediatric population.
The FDA approved a low-cost generic version of Apremilast in 2021, but it is not available in U.S. markets as yet. However, other low-cost generic options have been developed and marketed in countries like India and Bangladesh.
How Does Apremilast Work?
The exact mechanism of action of Apremilast is unclear and incompletely established.
However, it is known that PDE4 influences the cytokine mediators involved in causing disorders like psoriatic arthritis. PDE4 acts as a mediator for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) activity. cAMP is a second messenger responsible for regulating inflammatory mediators. When PDE4 inhibits its action, it can result in the dysregulation of the inflammatory mediators responsible for psoriatic arthritis and plaque psoriasis.
Apremilast is a PDE4 inhibitor - inhibition of PDE4 results in increased intracellular cAMP levels, which in turn suppresses TNF-α, IL-17, and other inflammatory mediators responsible for psoriatic diseases and Behçet's disease. Figure 1 displays a simplified illustration of Apremilast's mechanism of action.

PDE-4:Phosphodiesterase inhibitor-4 is an enzyme present in the immune cells, brain cells, and epithelial cells that regulates inflammatory functions in the body. Inhibition of PDE-4 through several targeted drugs suppresses its overactivity in inflammatory cells, thereby offering treatment for inflammatory conditions.
cAMP:cAMP is a second messenger responsible for regulating inflammatory mediators. It suppresses inflammatory mediator activity.
TNF- α:Tumor necrosis factor - α is an inflammatory cytokine produced during acute inflammation and can lead to cell damage and death.
IL: Interleukins are a group of proteins that regulate immune responses. The interleukins commonly associated with psoriatic conditions include:
-
IL-12.
-
IL-17.
-
IL-22.
-
Il-23.
Uses Of Apremilast
Psoriatic Arthritis: Adult patients who have displayed intolerance to other DMARDs or have shown insignificant responses to these drugs can be prescribed Apremilast alone or in combination with other DMARDs.
Plaque Psoriasis:Adult patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis (chronic) who display intolerance to other therapies, including Methotrexate and Cyclosporin, may be prescribed Apremilast, provided they are also eligible to undergo systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Mouth Ulcers in Behçet’s Disease:Apremilast is also indicated for mouth ulcers in adult patients with Behçet’s disease, who may receive systemic therapy.
Dosage Restrictions
Route of Administration: Oral.
Dosage Form: Diamond-shaped, film-coated tablets.
Available Strengths:
-
10 mg tablet.
-
20 mg tablet.
-
30 mg tablet.
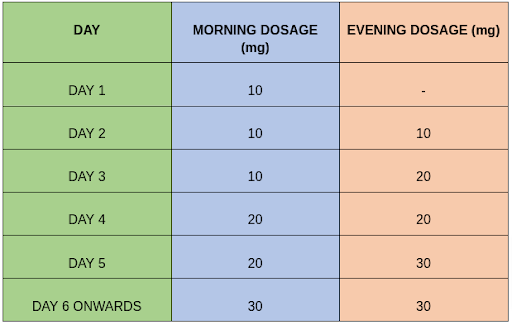
The recommended dosage of Apremilast for psoriatic conditions and Behçet’s disease are titrated with gastrointestinal concerns in mind. The initial dosage titration covers the first five days and begins at 10 mg, followed by 20 mg. From Day 6, the recommended maintenance dosage is 30 mg twice daily.
Special Considerations
Dosage Adjustment:
-
Renal Impairment: For adults with severe renal impairment, the dosage must be adjusted - the dosage is reduced to 30 mg once daily.
-
Elderly Patients: No dose adjustment necessary.
-
Hepatic Impairment: No dose adjustment necessary.
Drug Safety Concerns:
Pediatric Population:While contraindicated in children between 0 years - 17 years of age (owing to a lack of information), Phase II studies have indicated that weight-based dosing of Apremilast can achieve good results, and safety is consistent with that of the expected safety profile in adults. However, these studies require further exploration. Apremilast is contraindicated in children until concrete results are obtained from other large-scale studies.
Warnings and Contraindications
Contraindications:Apremilast is contraindicated in patients who display hypersensitivity to the drug.
Warnings and Precautions: The effects of Apremilast that need to be considered include:
-
Nausea, Vomiting, and Diarrhea: These side effects usually occur during the initial weeks of treatment, particularly in patients over 65 years of age or in those taking medications that can cause volume depletion or hypotension. The dosage must be adjusted or the medicine suspended altogether (in severe cases).
-
Weight Loss: 5 % - 10 % decrease in body weight has been reported in some patients taking Apremilast. Patients on Apremilast need to be monitored regularly for weight loss, and if an unexplained reduction in weight of >10 % occurs, then that needs to be explored so that the drug dosage may be altered, or the drug changed.
-
Depression: Increased depression and depressing thoughts, mood swings, and suicidal behavior have also been associated with Apremilast intake. Patients already suffering from depression need to be cautious when taking the drug.
-
Drug Interactions: Patients already taking Rifampin, Phenytoin, and Carbamazepine may display reduced efficacy of Apremilast due to interactions between the two drugs.
For Patients:
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a long-term skin disease that is mediated by your immune system. The condition causes your skin cells to grow at least ten times faster than is usual - and build up as a result. This build-up of skin cells then appears in the form of red, itchy, and scaly patches on the scalp, trunk, elbows, and knees. Occasionally, the nails and joints may also be affected.
What Is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is an inflammatory condition that affects your large joints. Arthritis itself refers to the swelling and tenderness of joints, leading to stiffness. Psoriatic arthritis usually occurs in those patients who have previously been diagnosed with psoriasis. That is to say, psoriatic arthritis primarily affects people who have psoriasis. However, it has also been reported in patients whose family members are affected with psoriasis.
How Does Psoriatic Arthritis Affect the Body?
Psoriatic arthritis is a lifelong disease, occasionally punctuated with periods of remission. However, the condition worsens with time.
The features of psoriatic arthritis are characterized by the way it affects the joints of your body. It causes painful swelling of the joints and often mimics rheumatoid arthritis in terms of the symptoms displayed.
The signs and symptoms of psoriatic arthritis include:
-
Swelling: Psoriatic arthritis can cause the fingers and toes to swell painfully - giving them a sausage-like appearance. The condition is termed dactylitis.
-
Pain: Given its effects on joints and tendons, psoriatic arthritis can cause severe pain in the foot (where tendons and ligaments are attached to the bones). It can also cause pain in the lower back region due to inflammation of the joints in your spine and pelvis.
-
Inflammation: Apart from inflamed joints, psoriatic arthritis can also cause an inflammatory eye condition called uveitis, which can result in pain and blurry vision and cause vision loss in extreme untreated cases.
-
Nail Changes: The nails may display pitting or may be separated from the nail beds.
-
Arthritis Mutilans: A rare and severe form of psoriatic arthritis called arthritis mutilans may develop in some people. Arthritis mutilans is extremely painful and eventually disables the sufferer by destroying the small bones in the hands. The fingers are particularly affected and become permanently deformed.
How Is Psoriatic Arthritis Treated?
Psoriatic arthritis cannot be cured entirely. Treatment is directed at inflammation control and prevention of disability.
-
DMARDs: The preferred drugs in most cases are the class of drugs called disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
-
Conventional DMARDs such as Methotrexate and Sulfasalazine can slow the progression of the disease and prevent permanent damage.
-
Biologic agents such as Adalimumab and Etanercept can modify the body's biological response by targeting your immune system through a different pathway.
-
Synthetic DMARDs like Tofacitinib may be used when neither conventional nor biologic DMARDs appear to be working.
-
Apremilast: Apremilast is prescribed for mild to moderate psoriatic arthritis that remains unchanged even with conventional DMARD therapy or biologic agents. It suppresses the activity of an enzyme in your body called Phosphodiesterase-4, which is held to be responsible for psoriasis. Your doctor may ask you to take Apremilast alone or in combination with a biologic agent type of DMARD.
-
NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like Ibuprofen and Naproxen may relieve the symptoms of pain and inflammation.
What Is Plaque Psoriasis?
The commonest form of psoriasis, plaque psoriasis, presents as rough, itchy, thick red patches with silvery-white scales. Although patches may also occur in other body parts, the elbows, knees, and scalp are commonly affected.
Why Is Apremilast Prescribed For Plaque Psoriasis?
Apremilast is a potent medication that reduces the redness, scaliness, and thickness of your psoriatic patches. It may be prescribed when other drugs for psoriasis fail to provide relief from the symptoms.
What Is Behcet’s Disease?
Behçet's disease or Behçet's syndrome is an inflammatory disorder of the blood vessels in your body that can cause a variety of apparently unrelated signs and symptoms. These may include:
-
Ulcers and sores in the mouth, skin, eyes, and genital areas.
-
Inflammation of the blood vessels, joints, brain, and nervous system.
-
Issues with the digestive system include bleeding, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Why Take Apremilast For Behcet’s Disease?
Apremilast is recommended as a treatment option for mouth sores in Behçet's disease.
The recommended treatment options for Behçet's disease include Colchicine and other immune-modulating drugs like DMARDs. However, these treatment lines are not always practical. Apremilast can modulate the inflammatory mediators that cause inflammation in Behçet's disease and effectively control mouth ulcers and sores. It may be used in case of failure of other treatment options.
Facts One Should Know About Apremilast
Apremilast usually comes in tablet form and is generally taken twice daily. Your doctor will start with a lower dose and gradually increase the dose over the week. It can be taken even without meals.
How Should You Take Apremilast?
-
Take Apremilast twice daily in the way that is prescribed to you. Read your prescription carefully and contact your physician if you have any questions.
-
The tablets must be swallowed whole and not crushed or broken. Do not chew Apremilast tablets.
-
Never attempt to modify the dosage yourself to see faster or stronger changes - take the drug in precisely the exact dosage prescribed to you, not more or less.
-
If you miss a dose, either take it immediately or skip that dose and proceed with your second dose as scheduled if it is closer to the time of the second dose.
-
Remember that Apremilast will only provide some control over your symptoms. It does not cure the disease. If you see positive results with Apremilast, do not stop the medication. Continue taking Apremilast unless your doctor says otherwise.
What Should You Discuss With Your Doctor Before Beginning Apremilast Therapy?
Your doctor must be made aware of your medical history and relevant personal details that can impact how Apremilast affects your body.
These details may include:
-
Drug History: Your doctor will need a complete and accurate list of all the medication you may be taking in order to determine if drug interactions may occur and cause reactions or reduce the effectiveness of Apremilast. This should also include non-prescription medications, herbal and non-allopathic medications, vitamins, and nutritional supplements.
-
Allergic History: This is particularly relevant in the case of drug allergies. If you are aware of being allergic to Apremilast or any other medications, make sure your doctor is equally aware.
-
Medical History: All medical conditions you may be suffering from need to be mentioned to your doctor. This includes your psychological history - particularly depression.
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: If you are pregnant or breastfeeding or planning for the possibility of either, you need to ensure your doctor knows about it so that they can prescribe accordingly.
-
Weight Considerations: Apremilast has been known to cause weight loss. Discuss this possibility with your doctor and keep an eye on your weight. Arrange to contact your doctor if you notice an unexplained weight loss of over 10 % body weight.
Is Apremilast Safe?
The side effects associated with Apremilast have generally been mild. Patients who terminate their medication usually do so if they develop severe nausea, headache, or diarrhea. Patients who experience depressive episodes or suicidal thoughts and behavior may also be advised to terminate the medication if their life is at risk.
Is Apremilast Effective?
Clinical trials on the effectiveness of Apremilast have shown promising results:
-
Psoriatic Arthritis: 28 % of patients on Apremilast 20 mg and 41 % of patients on Apremilast 30 mg noted over 20 % improvement in their response with Apremilast.
-
Plaque Psoriasis: At least 33.3 % of patients saw around 75 % improvement in plaque psoriasis within 16 weeks of taking Apremilast.
-
Behçet's Disease: Patients with oral ulcers performed far better with Apremilast in terms of reduction in the total number of ulcers.
What Side Effects Can You Expect With Apremilast?
Clinical trials have shown that Apremilast may commonly cause the following side effects:
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Headache.
-
Symptoms of cold (sneezing, runny nose, sore throat).
-
Infections of the respiratory tract.
-
Stomach pain.
-
Weight loss.
-
Suicidal ideation.
Can You Stop Taking Apremilast Without Your Doctor's Say-So and What Happens if You Do?
It is not advisable to stop taking Apremilast without consulting your doctor first. If you are experiencing severe side effects that are difficult to handle, tell the dermatologist about it, and they will either reduce the dosage or prescribe an alternative. Patients who have stopped taking Apremilast have experienced a reversal of its therapeutic effects within five weeks of quitting.
Is Your Age a Factor to Consider When Taking Apremilast?
Evidence from clinical trials differs on this point. While some suggest that there are no differences whatsoever between older and younger patients in terms of their reaction to Apremilast, other studies have noted that people over 65 may show increased incidence and severity of side effects. It is best to consult your doctor and find a solution best suited to your age and medical history.
What Are the Long-term Effects of Taking Apremilast?
There is not much data available on the long-term effects of Apremilast since most clinical trials have been conducted for only as long as a year. Further studies are required to resolve this question.
Are There Any Dietary Restrictions to Consider When Taking Apremilast?
There are no dietary restrictions as such, but you may consult your doctor for advice that may be specific to your nutritional needs or concurrent illnesses.
How Should You Store and Dispose Apremilast?
-
Apremilast should be stored at room temperature and kept away from conditions of moisture, heat, and light.
-
It is best to preserve the tablets in their original container or pack rather than transferring them to another.
-
Ensure that the medicine is kept safely out of the reach of young children and that the container's lid is tightly closed (if available in a container).
-
Disposal: Medicine disposal systems may be specific to your country or locality, and the same is to be followed with Apremilast. Make use of your local medicine take-back program or any available alternatives. Consult the relevant authorities for information on the local medicine disposal system if you are unaware of how it works. Ensure that you do not simply throw the container in waste bins or flush the tablets.
What Can You Do If You Suffer From These Disorders?
There are some things that you can do apart from taking your medication to improve the quality of your life with psoriatic conditions or Behçet's disease:
-
Exercise: Your joints and muscles suffer the most damage with these conditions. Regular, low-stress exercise forms can make a difference and improve your flexibility and mobility. Some forms of exercise that you can try are swimming, tai chi, and yoga.
-
Weight Maintenance: Try to keep excess weight off as it places less stress on your joints and improves the effectiveness of your medication.
-
Give Your Joints a Break: When lifting weights or performing activities that may place some stress on your joints, try to use the whole body to perform these tasks rather than just the joints and muscles of the hand.
-
Limit or Avoid Substance Use: Smoking can increase your chances of developing psoriasis and greater severity of symptoms, while alcohol can diminish the effectiveness of your treatment. Keep your consumption of alcohol limited or avoid it altogether, and work towards giving up smoking to prevent worsening symptoms of psoriasis.
-
Rest: Living with a painful chronic inflammatory disorder can make it hard to work or perform regular daily activities and exercise. Be sure to take adequate rest and not tire yourself out with too many activities.
-
Physical and Occupational Therapy: Physical and occupational therapy may relieve pain and stress to some degree.
-
Massage Therapy: It is also possible to obtain some relief from massage therapy.
What Can You Do in Case of Overdose?
-
Immediately consult your local helpline. If you have local poison helpline services, they should be your first point of contact.
-
If the patient has collapsed or has breathing difficulties or seizures, caretakers or family members must contact local emergency services.
What Else Should You Keep in Mind?
-
Keep in constant touch with your doctor regarding any difficulties you may have when taking the drug.
-
Keep appointments with your doctor promptly, and do not skip any visits.
-
Ensure that your medical and drug history is up-to-date, and carry this information with you when you visit your doctor or when you are out (in case of emergencies).
-
Inform your doctor of any changes in your medications, medical history, or other relevant information.
For Doctors:
Indications:
Psoriatic Arthritis: Apremilast may be prescribed alone or in combination with Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs) in adult patients who have displayed intolerance or inadequate response to previous treatment with DMARD.
Psoriasis: Adult patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis who have displayed intolerance or inadequate response to treatment with drugs such as Cyclosporin, Methotrexate, or Ultraviolet-A light (PUVA).
Behçet's Disease: Apremilast is used to treat adult patients with mouth ulcers associated with Behçet's disease - particularly if previous treatment with immunomodulatory drugs and Colchicine has failed to show adequate response.
Pharmacology
1. Components
Tablet Core: Cellulose, microcrystalline Lactose, monohydrate Croscarmellose, Sodium, Magnesium stearate.
Film-Coating: Poly (vinyl alcohol), Titanium dioxide (E171), Macrogol (3350), Talc, Iron oxide red (E172).
Other:
20 mg tablet: Iron oxide yellow (E172).
30 mg tablet: Iron oxide yellow (E172) and iron oxide black (E172).
2. Mechanism of Action
Clinical Pharmacology
Apremilast is an inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE-4), specific for cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is an oral small-molecule PDE4 inhibitor. The inhibition of PDE4 causes intracellular cAMP molecules to rise. The exact mechanism of action is unclear.
3. Pharmacokinetics
a. Absorption: In oral form, Apremilast is absorbed with an absolute bioavailability of ~73 %.
b. Peak plasma concentration (Cmax): Achieved at ~2.5 hours [median time (Tmax)].
c. Co-administration With Food: No effect on the absorption of Apremilast.
d. Distribution: Human plasma protein binding - 68 %. Mean apparent volume of distribution (Vd) - 87 liters.
e. Metabolism: Apremilast is a major circulating component (45 %) when taken orally. It is well-metabolized in humans. 23 metabolites of Apremilast have been identified in the urine, feces, and plasma.
f. Metabolization Mechanisms:
-
Cytochrome (CYP) oxidative metabolism with subsequent glucuronidation (in vitro mediation relies on CYP3A4, CYP1A2, and CYP2A6.
-
Non-CYP mediated hydrolysis.
g. Elimination:
-
Plasma Clearance: 10 liters/hour (healthy subjects).
-
Elimination Half-life: 6 hours to 9 hours.
-
Radio-labeled Apremilast: After oral administration, radioactivity is recovered in urine (58 %) and feces (39 %).
-
Radioactive Dose Recovered as Apremilast: Urine (3 %), feces (7%).
Special Considerations
Hepatic Impairment: Hepatic impairment does not impact Apremilast pharmacokinetics.
Renal Impairment: Mild to moderate renal impairment does not impact Apremilast pharmacokinetics.
Drug Interactions:
In Vitro Data:
Apremilast does not inhibit:
-
CYP1A2.
-
CYP2A6.
-
CYP2B6.
-
CYP2C8.
-
CYP2C9.
-
CYP2C19.
-
CYP2D6.
-
CYP2E1.
-
CYP3A4.
Apremilast does not induce:
-
CYP1A2.
-
CYP2B6.
-
CYP2C9.
-
CYP2C19.
-
CYP3A4.
Apremilast is a substrate of but does not inhibit P-glycoprotein (P-gp).
It is neither a substrate nor an inhibitor of:
-
Organic anion transporter (OAT) 1.
-
Organic anion transporter (OAT) 3.
-
Organic cation transporter (OCT) 2.
-
Organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1.
-
Organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B3.
-
Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP).
Clinical Trials:
1. Age:
Apremilast 30 mg (single-dose) was administered in young adults (18 years to 55 years) and elderly individuals (65 years to 85 years).
Exposure:
Area under the curve (AUC) or extent of exposure: 13 % higher in the elderly than in the young adult population.
Peak plasma concentration (Cmax):6 % higher in the elderly than in the young adult population.
2. Gender:
Pharmacokinetic trials have been conducted in healthy patients (volunteers).
AUC: 31 % higher for females than males.
Cmax:8 % higher for females than males.
3. Race and Ethnicity:
Pharmacokinetic trials have compared Asian (Chinese and Japanese subjects) males to Caucasian male subjects; trials have also been performed among Hispanic and non-Hispanic Caucasians and African-Americans. Results have shown that Apremilast exposure shows no significant differences and is similar in all these populations.
4. Drug Interaction:
-
Co-administration of Rifampin (CYP450 inducer) (600 mg once daily for 15 days) with Apremilast (30 mg, single dose):
Apremilast AUC reduced by 72 %.
Apremilast Cmax reduced by 43 %.
-
Co-administration of oral contraceptives: No significant interactions.
-
Co-administration of Ketoconazole: No significant interactions.
-
Co-administration of Methotrexate: No significant interactions.
5. Comorbidities:
In patients with severe renal impairment, who were given Apremilast (30 mg single dose):
Apremilast AUC: Increased by 88 %.
Apremilast Cmax: Increased by 42 %.
Disease-specific Trials:
Psoriatic Arthritis: The PALACE 3 trial (Phase 3) evaluated the efficacy and safety of Apremilast in patients with psoriatic arthritis who had received previous therapy with conventional DMARDs or biologic agents.
Study Design:
-
Type of Study: Multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, parallel-group, placebo-controlled trial (Phase 3).
-
Methods: Psoriatic arthritis patients (n=505) were evenly randomized into three groups:
-
Apremilast 20 mg group.
-
Apremilast 30 mg group.
-
Placebo group.
-
Crossover Designs: Crossover was indicated only for those patients on placebo. Those taking Apremilast continued with their dosage for the entire duration of the study.
-
Week 16 Crossover: For placebo patients not showing at least 20 % improvement in swelling and tenderness of joints.
-
Week 24 Crossover: All remaining placebo patients were randomized to Apremilast 20 mg and Apremilast 30 mg groups.
Primary Outcome Measures:Percentage of participants with at least 20 % American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response at Week 16. Response measures included:
-
≥ 20 % improvement in 78 tender joint counts.
-
≥ 20 % improvement in 76 swollen joint counts.
-
≥ 20 % improvement in at least 3 of 5 parameters:
-
Assessment of pain as per patient [100 mm visual analog scale (VAS)].
-
Global assessment of disease activity as per patient (100 mm VAS).
-
Global assessment of disease activity as per physician (100 mm VAS).
-
Self-assessment of physical function as per patient [Health Assessment Questionnaire - Disability Index (HAQ-DI)].
-
C-Reactive Protein (CRP).
Results:
Week 16 (p=0.0295, p<0.0001):
-
Apremilast 20 mg Group: 28 % of patients achieved 20 % improvement in ACR20 response criteria.
-
Apremilast 30 mg Group: 41 % of patients achieved 20 % improvement in ACR20 response criteria.
-
Placebo: 18 % of patients achieved 20 % improvement in ACR20 response criteria.
-
Mean decrease in the Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index score: significantly greater with apremilast 30 mg BD (−0.20) versus placebo (−0.07; p=0.0073).
-
Week 52:
Sustained response of improvements as observed at Week 16, with continued Apremilast treatment.
Adverse Events Profile:
Mild to moderate severity of:
-
Diarrhea.
-
Nausea.
-
Headache.
-
Upper respiratory tract infection.
Plaque Psoriasis: The LIBERATE trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of Apremilast in patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
-
Study Design:
Type of Study:Randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial (Phase IIIb).
-
Methods: Patients (n=250) were randomized to three groups:
-
Apremilast 30 mg BID (n=83).
-
Placebo (n = 84).
-
Etanercept 50 mg QW (n = 83).
-
Crossover Design: Crossover was indicated only for those patients on placebo. Those taking Apremilast continued with their dosage for the entire duration of the study.
Week 104 crossover: All placebo and Etanercept patients switched to Apremilast through Week 104.
Primary Outcome Measures: Percentage of participants with at least 75 % Psoriasis Area Severity Index (PASI) response at Week 16.
-
PASI-75 Response: The percentage of participants who achieved at least 75 % improvement from baseline in PASI score at Week 16.
-
PASI measures the severity of psoriatic disease, including characteristics like erythema, scaliness, and thickness; and the extent of skin surface area involvement.
-
Primary Efficacy Endpoint: Achievement of PASI‐75 at Week 16 with Apremilast vs. placebo. Secondary endpoints: Achievement of PASI‐75 at Week 16 with Etanercept vs. placebo.
-
Improvements in other clinical endpoints for Apremilast or Etanercept vs. placebo at Week 16.
Outcomes Assessment: Through Week 52.
Results:
Week 16:
-
Apremilast 30 mg Group: 39.8 % of patients achieved better PASI‐75 improvement than the placebo group (11.9 %; P < 0.0001).
-
Etanercept Group: 48.2% of patients achieved PASI‐75 (P < 0.0001) vs. placebo group.
-
PASI‐75 response was maintained through Week 52: 47.3% (Apremilast/Apremilast), 49.4% (Etanercept/Apremilast), 47.9% (placebo/Apremilast).
Adverse Event Profile With Apremilast:
-
Nausea.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Upper respiratory tract infection.
-
Headache.
-
Nasopharyngitis.
Oral Ulcers in Behçet's Disease:A Phase 3 trial evaluated the change in the total number of mouth ulcers over 12 weeks, comparing Apremilast with a placebo.
Study Design:
-
Type of Study: Multicenter, randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial (Phase 3).
-
Methods: Patients (n=207) were randomized to three groups:
-
Apremilast 30 mg (n=104).
-
Placebo (n = 103).
-
Crossover Design: None.
Primary Outcome Measures:Area under the curve (AUC) for oral ulcers (total number) during the 12-week placebo-controlled period.
Extension Phase:52 weeks.
Secondary Outcome Measures included:
-
Complete response of oral ulcers.
-
Change in Behçet's Disease Quality of Life score from baseline (0 - 30 range): Higher scores implied diminished quality of life.
-
Change in pain due to oral ulcers (from baseline).
-
Disease activity.
Results:
-
AUC for the total number of oral ulcers (least-squares mean difference, −92.6; 95 % confidence interval [CI], −130.6 to −54.6; P<0.001):
-
Apremilast: 129.5.
-
Placebo: 222.1.
-
Behçet's Disease Quality of Life score (change from baseline)(least-squares mean difference, −3.1 points; 95 % CI, −4.9 to −1.3):
-
Apremilast group: −4.3 points.
-
Placebo group: −1.2 points.
Adverse Event Profile With Apremilast:
-
Nausea.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Headache.
Patient Counseling Information:
Administration Instructions:
-
Take Apremilast as per prescription only.
-
Apremilast may be taken with or without food.
-
Tablets must be swallowed whole and not crushed, chewed, or split.
Complications/Side Effects:
Nausea, Diarrhea, Vomiting:
-
Advise patients of the possibility of side effects such as nausea, diarrhea, vomiting.
-
Patients over 65 years of age must consult their doctors in case of these side effects.
Depression:
-
The emergence of symptoms of depression - to be noted and brought to the doctor's attention.
-
Worsening of previous symptoms of depression - to be noted and brought to the doctor's attention.
-
Suicidal Ideation or behavior - to be noted and brought to the doctor's attention.
Weight Loss:
-
Monitor weight continuously.
-
Unexplained weight loss of over 10 % body weight must be reported to the doctor.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:
-
Inform patients of the potential risks to the fetus if Apremilast is taken during pregnancy, particularly since no complete evidence exists.
-
Patients must tell their doctors if they are pregnant or breastfeeding or if they have plans for the same.
Hypersensitivity:
-
Inform patients that hypersensitivity is a possibility and that they must contact their physician if hypersensitivity is noted.












