Introduction:
Generally, the food we eat is converted to energy by chemical reactions in the body. The carbohydrates and fatty acids are broken down by various enzymes in the body to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Metabolic myopathy happens due to a lack of enzymes that are required in ATP synthesis. This article reviews the different types of metabolic myopathies, their diagnosis, and their management.
What Are Metabolic Myopathies?
Metabolic myopathies are hereditary disorders that disturb the body's energy production process. Therefore, the energy supply to muscles is blocked and does not coordinate well with the bones and joints during the body’s movements.
Usually, it is classified as
-
Myopathies that show exercise-related symptoms: Muscle pain and cramps occur after transient exercise or extended physical activities.
-
Myopathies with fixed symptoms: The patient complains of muscle weakness and is linked with underlying systemic conditions.
What Are the Types of Metabolic Myopathies?
-
Glycogen Storage Disorder (Glycogenosis): The carbohydrate (glucose) in the food is processed into glycogen and is stored in the liver and skeletal muscles. During any physical activity, the glycogen is broken down to produce ATP. Any changes (mutation) in the genes involved in the synthesis or degradation of glycogen leads to a glycogen storage disorder.
-
Lipid Storage Disorder: The fat in the food that we eat is converted to fatty acids, and it provides energy during minimal exercise or fasting. The fatty acids are transferred to mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell), where it is broken down to produce energy. The short-chain fatty acids pass freely into mitochondria, whereas the long-chain fatty acids bind with carnitine to get into mitochondria. The process of fatty acid transformation is controlled by CPT (carnitine palmitoyltransferase) I and II enzymes. A specific genetic mutation that causes CPT I and II enzyme deficiency gives rise to lipid storage disorders.
-
Mitochondrial Disorder: The mitochondria in the cell do various functions like fat, protein metabolism, and energy production. Various genes are involved in the functioning of mitochondria. Thus, mitochondrial disorder occurs due to the mutation of genes responsible for normal mitochondrial functioning and is passed from parents to offspring.
What Are the Various Glycogen Storage Disorders?
The glycogen storage disorders that arise from several enzyme deficiencies are listed.
Type I: Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency.
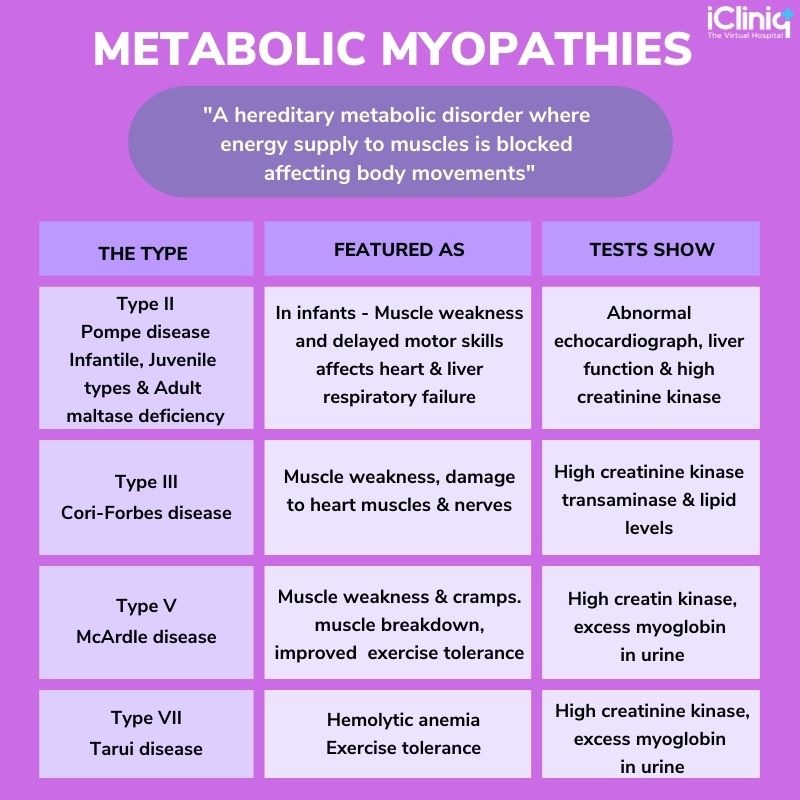
Type II: Pompe disease due to acid-maltase deficiency.
Type III: Cori-Forbes disease; debrancher enzyme deficiency.
Type IV: Anderson disease; brancher enzyme deficiency.
Type V: McArdle disease: muscle phosphorylase deficiency.
Type VI: Liver phosphorylase deficiency.
Type VII: Tarui disease; phosphofructokinase deficiency.
Type VIII: Phosphorylase b kinase deficiency.
Type IX: Phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency.
Type X: Phosphoglycerate mutase deficiency.
Type XII: Lactate dehydrogenase deficiency.
Type XII: Aldolase A deficiency.
The characteristic features of a few glycogen storage disorders on clinical and laboratory examinations are discussed below:
What Are the Features of Lipid Storage Disorders?
1) Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase (CPT) Deficiency: The CPT, I, and II enzymes are required for fatty acid metabolism. In childhood, the lipid disorder is severe and mild in adults. The characteristic features include muscle weakness or stiffness and pain. The symptoms occur in episodes and last for several weeks.
The following factors trigger the attacks -
-
Severe exercise.
-
Exposure to cold.
-
Drugs such as Ibuprofen, Diazepam, etc.
-
Infection.
-
High fat intake.
2) Myoadenylate Deaminase Deficiency (MADD): It is another form of lipid storage disorder, and it causes muscle pain, weakness, stiffness, cramps, and exercise intolerance. Laboratory investigations show increased levels of serum creatine kinase and lactate.
What Are the Types of Mitochondrial Disorders?
Mostly all mitochondrial disorders possess symptoms like exercise intolerance due to fatigue from mild exercise. But, the classic features of glycogenosis, like muscle stiffness and cramps, are not present. Certain mitochondrial syndromes are listed below -
-
Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (KSS): The symptoms and signs develop before the age of 20, and it includes pigmentary retinopathy (a degenerative disorder of the retina), extraocular muscle weakness, and ataxia (lack of coordination).
-
MELAS: Mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and stroke-like epilepsy syndrome (MELAS) affect the brain, muscles, and nervous system. It is genetically transferred to offspring from their mothers.
How Are Metabolic Myopathies Diagnosed?
-
Laboratory Examination - On blood investigation, decreased red blood cells and low creatine kinase is observed.
-
Muscle Biopsy - A sample of muscle tissue is surgically removed for investigation. Mitochondrial disease like KSS shows ragged blue fibers on staining.
-
Genetic Testing - It is done to determine the mutation of genes responsible for causing specific enzyme deficiency.
How to Treat Metabolic Myopathies?
There is no effective treatment available for metabolic myopathies. However, the following measures help in relieving the symptoms.
-
Low-fat diet: Intake of foods rich in carbohydrates, vegetables, and fruits and less fat are found to be helpful.
-
Avoid severe or prolonged exercise.
-
Vitamin supplements are also suggested to improve energy production.
-
Enzyme replacement therapy: intravenous administration of deficient enzymes is done to relieve the patient from symptoms like fatigue, muscle pain, etc.
-
Physical training: A therapist provides special training to get relief from muscle pain. They also aid in doing mild exercise to manage body weight.
Conclusion:
Every muscle in the body requires energy to be active and function well. Metabolic myopathies are a rare genetic disorder that disturbs energy production, and muscles become weak. A detailed clinical and laboratory investigation is necessary to identify the exact type of metabolic myopathy and differentiate it from other genetic disorders. It also provides a clear view of deciding the treatment plan.












