What Is Paxlovid?
Paxlovid is an oral antiviral pill formulated for the treatment of COVID-19. The drug has been developed by Pfizer pharmaceutical company. The U.S Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for Paxlovid on December 22, 2021.
What Drugs Do Paxlovid Tablets Contain?
Paxlovid is a combination of the following drugs:
-
Nirmatrelvir.
-
Ritonavir.
It is referred to as Ritonavir-boosted Nirmatrelvir, since Ritonavir is coadministered with Nirmatrelvir so that it may increase the concentration of Nirmatrelvir for optimum therapeutic benefit.
The recommended dosage strength of each of these drugs are as follows:
-
Nirmatrelvir: 300 mg.
-
Ritonavir: 100 mg.
What Is Paxlovid Indicated For?
Paxlovid is indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 in adults and pediatric patients.
Specifications:
- Age: 12 years and older.
- Weight: ≥40 kg (nearly 88 pounds).
- Disease Specifications:
- Positive results with direct SARS-CoV-2 testing.
- Patients at high risk of progression to severe COVID-19 (this may include hospitalization and even death).
What Are the Limitations of the Use of Paxlovid?
Paxlovid is not recommended for:
-
Pre-exposure prevention of COVID-19.
-
Post-exposure prevention of COVID-19.
-
Initiation of treatment in severe to critically ill COVID-19 patients requiring hospitalization.
-
Vaccine Substitution: Paxlovid is not a substitute for COVID-19 vaccines. It is recommended to be taken for the adequate prevention of, and reduction in serious COVID-19 outcomes.
How Does Paxlovid Work?
Understanding the mechanism of action of Paxlovid requires an understanding of the mechanisms of action of its components.
-
Nirmatrelvir: Nirmatrelvir is an orally bioavailable protease inhibitor that inhibits the MPROprotease (which is responsible for the replication of viruses). Nirmatrelvir is capable of antiviral activity against all Coronaviruses that infect humans.
-
Ritonavir: Ritonavir is a strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 inhibitor. It is used to boost HIV protease inhibitors and has been found to be equally effective at boosting Nirmatrelvir.
-
Paxlovid (a combination of the protease inhibitor Nirmatrelvir and the pharmacokinetic boosting agent Ritonavir) is considered a SARS-CoV-2 protease inhibitor antiviral. The Nirmatrelvir in Paxlovid blocks the action of SARS-CoV-2-3CL protease. SARS-CoV-2-3CL protease is an enzyme that is necessary for the replication of coronavirus. The coadministration of Ritonavir ensures that the breakdown of Nirmatrelvir in the body is slowed down so that it may remain active in the body for a longer duration and at a higher concentration. This will ensure prolonged activity against the SARS-CoV-2 virus.
How Should Paxlovid Be Taken?
Paxlovid is packaged as three tablets - two 150 mg tablets of Nirmatrelvir (total 300 mg) and one 100 mg tablet of Ritonavir.
Consumption:
-
Frequency: Twice daily.
-
Duration of Consumption: Five days.
-
When to Be Taken: Within 5 days of symptom onset.
-
Route of Administration (Mode of Consumption): Oral.
What Are the Special Considerations Associated With Paxlovid?
-
HIV-1 Infection: When used in patients with uncontrolled or undiagnosed HIV-1 infection, Paxlovid may result in HIV-1 drug resistance.
-
Moderate Renal Impairment: The dosage of Paxlovid should be reduced in patients with moderate renal impairment.
-
Liver Disease: Paxlovid should be prescribed with caution in patients with liver conditions or liver enzyme abnormalities since Ritonavir is capable of causing liver damage.
What Are the Warnings and Contraindications Related to Paxlovid?
Drug Interactions:
-
Paxlovid works by inhibiting enzymes that are known to be responsible for the breakdown of certain drugs. It is therefore not indicated in patients who are already taking such drugs.
-
If the patient is taking drugs that induce these enzymes, the simultaneous administration of Paxlovid may result in the faster breakdown of Nirmatrelvir or Ritonavir. This will lead to a reduced response of the drug.
Disease Contraindications:
Paxlovid is not recommended for use in the following patients:
-
Patients with hypersensitivity to Nirmatrelvir, Ritonavir or any of the other components in Paxlovid.
-
Patients with severe renal (kidney) impairment.
-
Patients with severe liver disease.
What Should Patients Discuss With Doctors Before Beginning Treatment With Paxlovid?
-
Medications: Patients who are taking any sort of medication or drug, including prescription drugs, over-the-counter (OTC) medications, herbal supplements, or recreational drugs, must inform their doctors of the same since Paxlovid can cause drug interaction issues with a number of drugs.
-
Liver Damage: Patients with a history of liver disease should ensure they inform their doctors of their condition and discuss whether or not Paxlovid is a good option for them.
-
Kidney Disease: Patients with kidney disease should let their doctors know about their condition so that the doctor may determine whether or not the drug is a good option for them.
What Are the Side Effects Associated With Paxlovid?
The side effects noted with the use of Paxlovid so far include:
-
Dysgeusia: An altered sense of taste where patients feel that all the food they eat tastes metallic, bitter, sweet, or sour.
-
Hypertension: Increased blood pressure.
-
Diarrhea: Frequent bowel movements that are loose and watery in nature.
-
Myalgia: Mild to severe soreness and pain in a muscle or group of muscles.
Is Paxlovid Safe?
Barring the contraindications and special considerations related to Paxlovid, it may be assumed that this is a relatively safe drug. Further studies and data are required to make an informed decision on the safety of Paxlovid.
Is Paxlovid Effective?
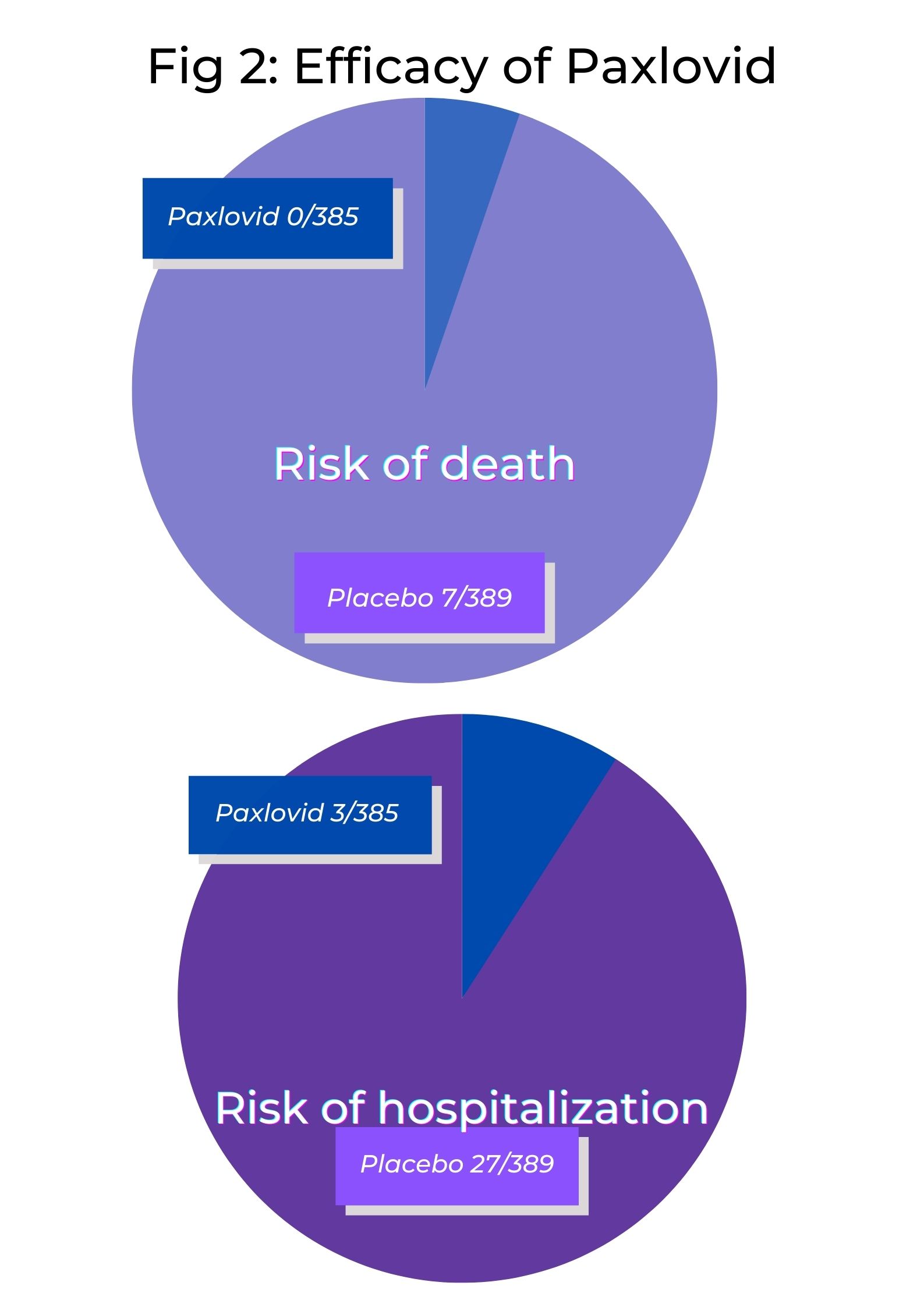
Paxlovid has been found to reduce the risks of hospitalization or death arising due to COVID-19 by 89 % when compared to a placebo. It has been noted that Paxlovid was not associated with any deaths in COVID-19 patients receiving the drug over a period of 28 days, compared to seven deaths (out of 385 patients) in the placebo group. Hospitalization cases were also fewer in the Paxlovid group (3 patients out of 389 were hospitalized) compared to the placebo group (27 cases of hospitalization out of 385 patients).
Placebo: A placebo is an essentially fake treatment. It may be available as a pill, an injection, or even a surgery but has no therapeutic value. Placebos (like sugar pills) are typically used in studies on the effectiveness and safety of new drugs for comparison purposes.
How Should Paxlovid Be Stored and Disposed Of?
-
Tablets of Nirmatrelvir and Ritonavir are supplied in individual blister cavities within the same blister card. The blister cards are child-resistant.
-
The tablets should be stored at a temperature of 20○C to 25○C (68○F to 77○F).
-
The disposal of Paxlovid should be in accordance with local guidelines and medical regulatory bodies. Patients may check with their pharmacists on the best way to dispose of Paxlovid tablets.
What to Do in the Case of Paxlovid Overdose?
There is no antidote for the overdose of Paxlovid. Treatment should consist of monitoring the patient’s vital signs and clinical symptoms while also providing general supportive measures.
What to Do if a Dose of Paxlovid Is Missed?
A missed dose of Paxlovid may be taken within eight hours of the usual dose administration time, followed by the next dose as per the dosing schedule. If more than eight hours pass since the time of the missed dose, the patient must not take the missed dose (as this constitutes double-dosing) and continue with the next dose.
Are There Any Alternatives to Paxlovid?
No adequate or approved alternatives to Paxlovid are currently available for COVID-19 treatment.
Conclusion:
Paxlovid may indicate a positive change for the future of COVID-19, with a definite potential for reduced cases of hospitalizations and deaths, and a reduction in the severity of COVID-19. Results from trials so far have shown that Paxlovid may tentatively be viewed as safe and effective. Doctors and patients alike can hope and look forward to the best results from this revolutionary new drug combination for COVID-19.












