Overview:
Dupilumab Is a monoclonal antibody used for a skin disease known as atopic dermatitis, which causes dry skin with itchiness and can sometimes develop red, scaly rashes. Dupilumab is used with or without topical corticosteroids. It is used in atopic dermatitis when other topical therapies with corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are either ineffective or not advisable.
Dupilumab was approved by the FDA (United States Food and Drug Administration) in March 2017 as an injectable form for treating moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. On October 20, 2021, it was also added as a maintenance treatment option in patients with moderate to severe asthma aged between 6 years and 11 years. Dupilumab comes in a 300 mg/2 mL solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe.
How Does Dupilumab Work?
Dupilumab Is an interleukin-4 (IL-4) receptor alpha antagonist. It is a human monoclonal (similar) antibody of the immunoglobulin G4 subclass, which inhibits Interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13) signaling by binding to the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit.
Dupilumab works with two receptors:
-
Type I receptor inhibits IL-4 signaling.
-
Type II receptor inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 signaling.
By blocking the IL-4 receptor alpha subunit, Dupilumab inhibits IL-4 and IL-13 cytokines-induced responses and inhibits the release of proinflammatory cytokines, immunoglobulin E, and chemokines (which can cause inflammation).
What Are IL-4 and IL-13?
Interleukin (IL) are proteins made in response to external pathogens and other antigens, which help regulate inflammatory and immune responses. Inflammatory responses are reactions of tissue when injured by any microorganism like bacteria, toxins, heat, or trauma. The cells release chemicals such as histamine, prostaglandins, and bradykinin, which may cause blood vessels to leak fluids into the tissue and cause swelling and irritation. Whereas immune response is the defense system of the body against bacteria, viruses, or any other foreign body. Initially, it was thought to be produced by leukocytes alone, but later it was found to be produced by many other body cells. Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 are cytokines that together regulate many aspects of allergic inflammation. They have significant roles in regulating the responses of lymphocytes, non-hematopoietic cells, and myeloid cells.
What Are the Uses of Dupilumab?
-
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): In cases of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children above six years, Dupilumab is prescribed. It is advised only when other medications cannot be recommended or their eczema has not responded to other medicines.
-
Asthma: As approved by FDA on October 20, 2021, Dupilumab is prescribed in moderate to severe cases of asthma in adults and children between 6 to 11 years. The asthma symptoms are shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, and chest tightness.
-
Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: It is a condition in which there is a continuous runny nose with nasal congestion or sinus swelling along with optional symptoms of reduced sense of smell or pain and pressure in the face. Dupilumab injection is advised in those adults whose symptoms are not cured with other medicines.
Dosage:
Dupilumab is available as 300/2 mL solution in a prefilled single-dose syringe.
-
Initial Dose: 600 mg (two 300 mg/2 mL injections in different injection sites).
-
Second Dose: 300 mg/2 mL every other week.
Note:The syringes are single-use, so they should be disposed of after one use.
Warning:
The side effects of the Dupilumab injection can vary from mild to severe:
-
Mild Side Effects: Some of the initial effects could be:
-
Redness at the site of infection, along with pain.
-
Mouth or lip sores.
-
Pain in the throat.
-
Moderate Side Effects: These side effects sometimes need doctors' assistance and even emergency medical treatment.
-
Eye problems include eye pain, pink or red eye (s), blurred vision, conjunctivitis, swollen eyelids, or even a vision change. These signs could worsen eventually.
-
Shortness of breath, fever, and chest pain.
-
Numbness in arms or legs or feeling of pins and needles.
-
Severe Side Effects: If the patient witnesses any of these signs, the administration of Dupilumab injection should be stopped, and the doctor should be consulted:
-
Swollen lymph nodes and difficulty in swallowing or breathing.
-
Feeling of dizziness or fainting.
-
Feeling of tightness in the chest.
-
Swelling of face, eyelids, throat, or tongue.
-
Itching or rashes on the body.
-
Firm, flat, hot, and red skin lumps, which are painful.
-
Fever.
For Patients:
What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
It is a type of eczema which is not common. It is characterized by dry and itchy skin, which can leave red scars on the face, arms and legs. Most cases are noticed in children; however, adults are also affected in a large number. The rashes are temporarily appearing and may reappear. In most cases, the first signs of eczema appear before the age of 5 years.
What Body Parts Are Affected by Atopic Dermatitis?
-
Red rashes, which are very itchy, are found on the back of the neck, knees, and creases of elbows. Eventually, the rashes may develop on the face, wrists, and forearms. There is also the presence of small bumps and flaky stains on these body parts.
-
The itchiness is usually more aggressive at night, and the skin becomes thick, dark, and scarred after scratching.
-
Scratching can lead to red bumps filled with pus or clear fluid.
-
Cracked skin can hurt and bleed sometimes.
-
Creased skin under the eyes and on the palms.
-
Darker skin under the eyes.
What Is the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis?
The medications for atopic dermatitis when Dupilumab is not used are
1) Oral Medications:
-
Mycophenolate.
-
Prednisone.
-
Cyclosporin.
-
Methotrexate.
2) Topical Medications to Apply to the Infected Area:
-
Fluocinonide.
-
Mometasone.
-
Hydrocortisone.
-
Tacrolimus.
3) Phototherapy:
-
Ultraviolet light therapy.
More About the Drug:
Before Starting Dupilumab:
When and Why Switch to Dupilumab?
As mentioned earlier in the article, Dupilumab is prescribed for three significant conditions: atopic dermatitis, asthma, and rhinosinusitis with polyps. The indications of use for these conditions are listed below:
-
Dupilumab for Atopic Dermatitis: Dupilumab is approved by FDA to treat moderate to severe cases of eczema (atopic dermatitis) that are not responding to topical medications such as ointment or creams or in cases when topical medications cannot be prescribed. Dupilumab can also be administered in children who are six years and above.
-
Dupilumab for Asthma: It can be prescribed in cases of eosinophilic asthma or oral corticosteroid-dependent asthma. Children, more than 12 years of age with asthma can use Dupilumab. However, Dupilumab should not be used to treat asthma attacks. In cases of an asthma attack, a "rescue inhaler" should always be used.
-
Dupilumab For Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: In cases of chronic rhinosinusitis, there is an increased number of eosinophil cells in the nasal and sinus cavities. These eosinophil cells increase the swelling in the nasal region. Dupilumab helps to reduce this swelling and relieve symptoms of rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp. Other medications for the infection are also administered along with Dupilumab.
How Does Dupilumab Work for Diseases?
The immune system causes inflammation, rash, and red, flaky skin in atopic dermatitis. Dupilumab blocks the two proteins which cause inflammation and thus reduces the inflammation, relieving symptoms and clearing the skin.
How Long Does It Take To Work?
Dupilumab starts to work after the first injection; however, it may take a few weeks before the symptoms improve. In clinical trials, it was observed that more than approximately 36 % of adults with eczema were relieved from itching in 16 weeks or less of administration. In children aged between 12 to 17 years, almost 37 % had relief. Dupilumab treatment should be continued for at least 16 weeks.
What Are the Things to Inform the Doctor Before Taking Dupilumab?
Before using Dupilumab, the following information is essential to share with the doctor:
-
Under treatment or suspected to have a parasitic (helminthic) infection.
-
Suffering from some eye problems.
-
Suppose any vaccination is scheduled, as receiving a 'live vaccine' is not recommended during treatment or before taking Dupilumab. Live vaccines include measles, mumps, rubella, smallpox, and rotavirus.
-
Pregnant or planning to conceive.
-
Breastfeeding or can breastfeed in the coming time.
-
Medicine currently on, including corticosteroids, herbal supplements, or vitamins.
-
Suffering from or recent history of any health issue. History of herpes infection should be informed.
Starting Dupilumab:
How to Take Dupilumab?
Dupilumab is available in injection form. It comes in single-dose prefilled syringes or pens in 200 mg/1.14 mL or 300 mg/2 mL.
For eczema, the first dose is generally administered as a loading dose (a higher dose of medication given at the start of treatment). After this loading dose, one maintenance dose is administered every other week. These maintenance doses help maintain the same amount of medicine in the body so that its effect is not altered.
The Dupilumab injection is given subcutaneously (under the skin) into the thigh or abdomen (avoiding 2 inches from the navel). It can also be administered in the upper arm. The site of injection should be changed for every dose.
NOTE: Never administer the injection into bruised, tender, damaged, or scarred skin.
Process of Injection of Medicine:
-
The syringe should be kept in a cool environment, best in the refrigerator. Before administration, it should be removed from the refrigerator and allowed to reach room temperature (for around 45minutes).
-
The syringe should be inspected well for any discoloration or particulate matter before injecting.
What to Do if the Dose Is Missed?
If a person misses a dose of Dupilumab, it should be administered within seven days, and the original schedule should be resumed. If the dose is missed for seven days, the next dose should be injected according to the original schedule.
How to Store a Dupilumab Syringe?
It should be kept at 2-9 degrees Celsius in the original packaging to prevent exposure to light. If the syringe has to be stored at room temperature, it should not exceed 25 degrees Celsius and maximum for 14 days.
What Are the Common Side Effects?
The more common side effects of Dupilumab are:
-
Injection Site Reaction: It includes pain, swelling, redness, and itching around the injection areas. The symptoms can last for a few days after an injection is given.
-
Herpes Infections: Cold sores (oral herpes) are the most common herpes infection during Dupilumab therapy. It occurs in cases that already have herpes in their body.
-
Throat pain and difficulty in swallowing.
-
Dry or itchy eyes and eyelid inflammation is also noticed in some cases.
-
Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva (eye). The eye color turns pink.
-
Gastritis: Inflammation of the mucosal lining of the stomach.
-
Increase in the number of eosinophilic cells (white blood cells that help fight the infection).
-
Trouble sleeping (insomnia).
Avoid Self-Medication:
Dupilumab should not be taken without a doctor's prescription, as it can cause severe side effects. The adequate dose of injection and administration schedule is prepared according to the disease status (here, atopic dermatitis). So any wrong administration can lead to other reactions or overdose in the body.
Staying on the Drug:
Following factors should be considered during the Dupilumab injection course:
-
Topical corticosteroids like betamethasone or triamcinolone can be simultaneously used with Dupilumab injections for atopic dermatitis.
-
Live Vaccine Avoidance: vaccines inject a small number of viruses into our bodies related to a particular disorder. Since Dupilumab may weakens the immune system, a live vaccine can cause infections. Therefore live vaccines should be avoided before and during the Dupilumab course. Some of the live vaccines are
-
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR).
-
Smallpox and chickenpox.
-
Intranasal flu.
-
Yellow fever.
-
Rotavirus.
-
Typhoid.
For Doctors:
Indication:
Dupilumab is indicated in moderate to severe atopic dermatitis (eczema) cases in adults and children above six years ago. In cases of eczema unresponsive to topical medications or in cases where topical medications are contraindicated, Dupilumab is prescribed. Dupilumab is also advised in moderate to severe cases of asthma in adults and children aged 12 years or above. It can also be prescribed in cases of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps as a maintenance dose.
Pharmacology: Mechanism of Action:
Dupilumab is an immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) monoclonal antibody that blocks the interleukin-4 (IL-4) and interleukin-13 (IL-13). It blocks the type 1 and 2 receptors of IL-4 and type receptors of IL-13. IL-4 and IL-13 are associated with inflammatory signals and the release of inflammatory cytokines. Blocking these two leads to a reduction of inflammation in the body. Reducing the inflammatory chemokines and cytokines reduces the symptoms of atopic dermatitis, asthma, and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps.
Pharmacokinetics:
After the first dose, the steady-state dosing is achieved within 16 weeks of the drug injection course. The bioavailability of Dupilumab varies from 61 % to 64 % in all diseases. Since Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody of IgG4 (immunoglobulin G4), its degradation pathway is similar to Ig4 protein. It degrades into small peptides.
The pattern of pharmacokinetics is nonlinear for Dupilumab. It means that an increase in dose may not show a linear increase in response.
Absorption:
The absorption of the first dose of 600 mg or 400 mg of Dupilumab takes a maximum of 3 to 7 days. After this, another dose of 75 to 600 mg is administered, after which the bioavailability reaches 61 % to 64 % for atopic dermatitis.
Metabolism:
Being a monoclonal antibody, Dupilumab does not undergo hepatic metabolism. It undergoes nonspecific degeneration into smaller peptides and amino acids and is observed with endogenous IgG (immunoglobulin G).
Route of Elimination:
As it is a monoclonal antibody that does not undergo hepatic metabolism, elimination is also not through the renal pathway. It is stated that Dupilumab was eliminated through parallel linear and nonlinear pathways.
-
When the drug is in higher concentration, it is primarily cleared through a nonsaturable proteolytic pathway.
-
At lower concentration, Dupilumab undergoes a nonlinear saturable interleukin-4 Alpha target mediated elimination.
Precaution:
-
Allergic Reactions: Dupilumab should is avoided in cases of its hypersensitivity. These allergic reactions can be rashes, hives, and trouble breathing.
-
Parasitic Infection: In cases of parasitic infection such as tapeworm, it should be treated before taking dupilumab.
-
Eye Conditions: Dupilumab worsens existing eye conditions or causes a new one.
-
Asthma Attacks: Dupilumab should not be used for an asthma attack or if there is a breathing issue. It can reduce symptoms of asthma but not an asthma attack.
Drug Forms and Strengths:
Dupilumab is sold in a single-dose prefilled syringe or pen. Each box contains two syringes. The Dupilumab is available in two doses.
-
200 mg/1.14 mL.
-
300 mg/2 mL.
Doses in Adults:The first dose is taken in the two injections of300 mg/2mLeach. A total of 600 mg is administered as the first dose. After this, 300 mg/2mL is administered every week.
Doses in Children: The Dupilumab dose in children between 6-17 years is based on body weight.

Drug Interactions:
Dupilumab can interacts with other medicines, which can cause different effects. Some drug interactions could enhance drug effects, and some drugs could create side effects. However, Dupilumab does not interact with many other medicines as it is metabolized inside cells and not in the liver.
-
Live Vaccines: Any live vaccine should be avoided before or during the administration of Dupilumab. As live vaccines contain a small number of viruses for the body to develop antibodies for future interactions and Dupilumab suppresses the immune system, these live viruses can infect the body. Some of the live vaccines are
-
Intranasal flu.
-
Smallpox and chickenpox.
-
Rotavirus and typhoid virus.
-
-
Corticosteroid Medications: Some steroid medications, such as Prednisone, can cause swelling of the blood vessels when taken along with Dupilumab in cases of asthma. Other symptoms can also be noticed, such as rash, fever, shortness of breath, or chest pain. However, Prednisone should not be stopped abruptly. Stopping corticosteroids suddenly can cause symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Slowly the doses should be reduced and then stopped.
-
Herbal Supplements: No herbal supplements have been observed to interact with Dupilumab. However, consulting a doctor before starting Dupilumab along with herbal supplements is advised.
Results of Clinical Trials:
The study was conducted in ten countries between December 2014 to January 2016 with 962 total participants. Out of 962 participants, 708 were randomized, and 707 were treated in the study. The participants were divided into three groups:
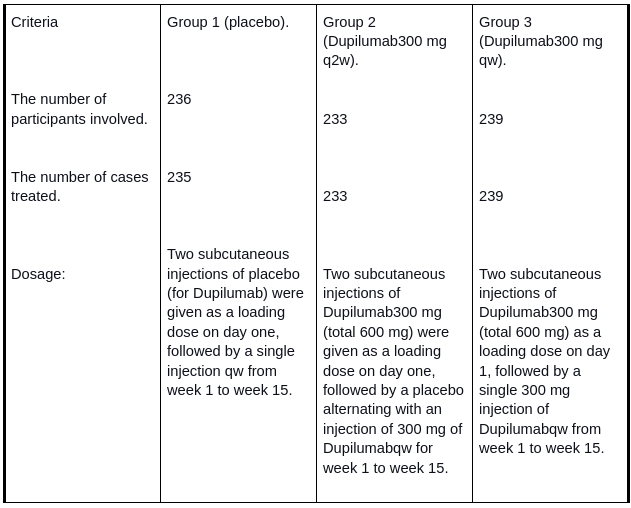
Results:

Note: EASI (Eczema area and severity index) score is used to measure the severity and extent of atopic dermatitis and measured erythema, infiltration, excoriation, and lichenification on four anatomic regions of the body- upper and lower extremities, head, and trunk.
IGA (Investigator’s Global Assessment): This scale is used to determine the severity of atopic dermatitis and clinical response to treatment on a 5- point scale.
-
0- clear.
-
1- almost clear.
-
2- mild.
-
3- moderate.
-
4- severe.
Dupilumab and Pregnancy:
It was seen that atopic dermatitis accounted for approximately 36 to 49 % of all cases of gestational dermatoses (any skin defect or lesion on the skin). Pregnancy can be a trigger factor for atopic dermatitis and can worsen in the second or third trimester. Topical and systemic therapies are limited during preconception, pregnancy, and lactation.
According to the limited clinical data available, it was observed that there were no complications or effects of Dupilumab on pregnancy. Neither the mother nor the fetus had any adverse effects due to the drug.
Dupilumab and Breastfeeding:
Though Dupilumab is not well studied for use while breastfeeding, it is assumed that it will not pass through breast milk as it is a large protein. Even if it goes into breastmilk, it is unlikely to be absorbed by the infant's gastrointestinal tract.
Dupilumab Geriatric Patients:
Studies propose that cases of Dupilumab in elderly patients showed a lower percentage of conjunctivitis than younger adults and provided great control over itching.












