Overview:
Aspirin is a prescription medicine that belongs to the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory class of drugs. Aspirin is acetylsalicylic acid. This drug is rapidly converted to salicylic acid in the body, which is responsible for most of the actions. Other actions are the result of the acetylation of specific macromolecules, including COX. It is one of the oldest analgesic-antiinflammatory drugs and is still frequently used.
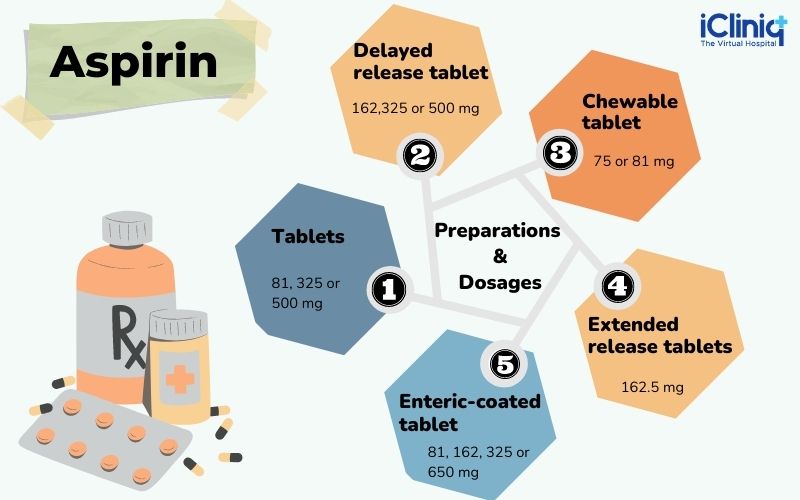
It helps to relieve pain, fever, rheumatoid arthritis, acute rheumatic fever, prevent colon cancer, etc. This drug is available in systemic injections, topical creams, and some of them are oral tablets, extended-release capsules, delayed-release tablets, chewing tablets, enteric-coated tablets, etc.
Composition:
This tablet contains,
-
Active Ingredient:Aspirin.
-
Inactive Ingredients:
a. Carnauba wax.
b. Corn starch.
c. Hypromellose.
d. Powdered cellulose.
e. Triacetin.
Drug Group:
Aspirin comes under the class of drugs called non-opioid analgesics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. It is a salicylate derivative that belongs to nonselective COX inhibitors, a traditional NSAID form. This drug stops the body from producing substances that cause fever, pain, and inflammation.
What Is Aspirin Used For?
The uses of Aspirin are as follows,
-
Analgesic - Relieves mild to moderate pain or pain associated with,
- Inflammation.
- Muscles and joints (osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis).
- Integumentary structures (epidermis, dermis, hypodermis, etc.).
- Headache (migraine).
- Backache.
- Dysmenorrhoea.
- Neuralgias.
- Dentistry: It helps to relieve pain following procedures such as,
a) Impaction.
b) Open extraction.
c) Pulpitis.
d) Traumatic occlusions, etc.
- Less effective in ischemic or visceral pain.
2. Antipyretic - Relieves fever of most origin (except heat stroke).
3. Anti-Inflammatory - It provides symptomatic relief only. For example:
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis – Decreases pain, swelling, morning stiffness, and inflammatory damage.
- Acute Rheumatic Fever – This is the first line of drugs for acute rheumatic fever. It provides symptomatic relief in 1-3 days, and the duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks. It decreases pain, swelling, heat, redness, fever, immobility, and prevents further joint involvement.
4. Antiplatelet Use - Prevents clot formation in post-MI (myocardial infarction) and stroke patients.
5. Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension - Decrease incidence of hypertension and prevent pre-eclampsia in patients with high BP (blood pressure).
6. It helps in the closure of ductus arteriosus and avoids surgery.
7. Prevention of colon cancer.
8. In familial colonic polyposis, it gives symptomatic relief and suppresses polyp formation.
9. Treat Bartter syndrome (genetic disorder with special defects in kidney function).
10. Beneficial in prostaglandins mediated diarrhea.
11. To prevent flushing associated with Nicotinic acid ingestion which is due to PGD2 released in the skin.
12. Topical salicylates are used as a keratolytic, counter-irritant, antiseptic, and fungistatic.
How Does Aspirin Work?
The enzyme cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 is responsible for the production of prostaglandin (PG). Prostaglandins are irritating substances that have broad activity in pain and inflammation, that is, headaches, pain upon injections, etc.
Aspirin irreversibly inhibits the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX); that is, both COX–1 and 2 present both in the periphery and central nervous system (CNS), thereby inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins.
Onset Of Action:
Aspirin is well absorbed orally. It is metabolized in the liver, and some are hydrolyzed into salicylates in the gut wall. It is excreted via urine (60 to 100%), feces, sweat, and saliva. The onset of action is 30 minutes, and it starts to inhibit platelet function within 60 minutes. It has 80 to 100% of oral bioavailability and 80 to 90% of protein binding capacity.
Expiry Date:
Avoid taking this medicine after it expires. Aspirin does not work and may lead to serious side effects when used beyond the expiry date. So before taking medicine, verify the expiry date printed on the back of the pack or ask the pharmacist or doctor in case of any doubts.
What Is the Dosage and Administration of Aspirin?
a) Preparations and Dosages -
Aspirin is available in a number of dosages and formulations. These are mentioned as follows:
- Tablet
- Delayed release tablet.
- Chewable tablet.
- Extended release tablet.
- Enteric coated tablet.
b) Adult Dosage:
.jpg)
c) Child Dosage:

How to Use Aspirin?
-
When you are going to self-treat, you should read all directions on the package label before usage; when the doctor has prescribed the medicine, you should take it as directed by the doctor.
-
Take the medication by mouth with a glass full of water.
-
When you experience stomach upset on taking this medication, you can take it with milk, food, or an antacid.
-
Aspirin medication should be swallowed as a whole and should not be crushed, chewed, or broken before usage because the special coating on the tablet will be broken and may increase the side effects.
-
When you have any doubts or questions, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Missed Dose:
It is important to take the missed dose as soon as you remember it, but if it is almost time for the next dose, you can skip the missed dose and start continuing with the regular dosing schedule. In order to compensate for a missed one, do not take a double dose.
What Are the Drug Warnings and Precautions?
-
Before using, inform your doctor or pharmacist if you have been allergic to this medicine or salicylates or other NSAIDs. This drug contains inactive ingredients, which may cause allergic reactions or any other problems. So, it is always better to speak to the doctor or pharmacist to know more information.
-
Avoid increasing the dose by yourself or taking this medication more often than directed by the pharmacist or doctor because the dosage depends on age, response to the treatment, and medical condition.
-
Before using Aspirin, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist about your medical history (present and previous), especially of,
4. Children below 18 years should not take Aspirin if they recently had chickenpox, flu, or received a vaccine.
5. Aspirin is not recommended during pregnancy to relieve pain or fever. Before taking this medication, women of childbearing age should talk to the doctor as it may cause problems when planning to get pregnant, harm an unborn baby, and create problems during delivery. Aspirin is not recommended from 20 weeks of pregnancy until delivery.
6. It is said that this medication passes into breast milk, so consult with your doctor before taking this medicine while breastfeeding.
What Are the Side Effects of Aspirin?
1. GIT (Gastrointestinal Tract):
It can cause,
-
Peptic ulcer.
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Epigastric pain.
-
Erosions.
-
Gastritis.
-
Esophagitis.
-
Stomach bleeding.
-
Gastric mucosal damage.
-
Increased occult blood loss in stools.
2. Hypersensitivity or Anaphylactoid or Idiosyncratic Reactions:
It occurs less frequently but can be serious when it occurs, such as,
-
Rashes.
-
Urticaria.
-
Rhinorrhea.
-
Photosensitization.
-
Precipitation of asthma.
-
Angioedema.
-
Fixed drug eruptions.
-
Anaphylaxis, etc.
3. Antiplatelet Action:
-
Bleeding from GIT.
-
Bleeding from the skin.
-
Bleeding from the nose.
-
Serious intracranial bleeding.
4. Labor and Pregnancy:
-
If used near or during labor, it can result in premature closure of ductus arteriosus.
-
It can prolong labor.
-
More significant postpartum blood loss.
5. Kidney:
-
Edema.
-
Nephropathy.
-
Hyperkalemia.
6. CVS (Cardiovascular System):
-
Edema.
-
Rise in blood pressure.
-
Rarely CHF (congestive heart failure).
7. Liver:
Liver damage can occur, especially in children treated for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
8. CNS (Central Nervous System):
-
Dizziness.
-
Confusion.
-
Tinnitus.
-
Vertigo.
9. When used as an anti-inflammatory dose for prolonged periods, it causes,
-
Headache.
-
Dizziness.
-
Tinnitus.
-
Vertigo.
-
Reversible impairment of hearing and vision.
-
Excitement.
-
Mental confusion.
-
Electrolyte imbalance.
All these could be reversed when the drug is stopped.
10. Acute Salicylate Poisoning:
It can result in acute salicylate poisoning, which is seen more in children. The symptoms are,
-
Vomiting.
-
Dehydration with acidosis.
-
Bleeding.
-
Electrolyte imbalance.
-
Hallucination.
-
Convulsion.
-
Coma.
-
Respiratory depression.
-
Death.
What Are the Drug Interactions of Aspirin?
-
Drug interactions may change the mechanism and effectiveness of the drug; also, they increase the risk of serious side effects. So, it is better to inform your doctor about all the prescription, nonprescription and herbal drugs you are taking.
-
You should not stop or change the dosage of the drug by yourself; always ask your doctor's approval before changing the dosage of the drug.
-
Ask for any doubts to your doctor or pharmacist about using the products safely.
-
Aspirin displaces the following drugs from the binding sites on plasma proteins, such as,
-
Warfarin.
-
Naproxen.
-
Sulfonylureas.
-
Phenytoin.
-
Methotrexate.
-
Also, the toxicity of these drugs may occur.
5. Its antiplatelet action increases the risk of bleeding in patients on oral anticoagulants.
6. Aspirin at analgesic doses inhibits tubular secretion of uric acid and antagonizes uricosuric action of probenecid. Tubular secretion of Methotrexate also gets interfered.
7.Aspirin blunts diuretic action of Furosemide and Thiazides.
8.It reduces the potassium-conserving action of Spironolactone.
9. Competition between Canrenone (the active metabolite of Spironolactone) and Aspirin for active transport in proximal tubules has been demonstrated.
10. Aspirin reduces protein-bound iodine levels by displacement of Thyroxine, but hypothyroidism does not occur.
11. Dichlorphenamide and Mifepristone can severely interact with Aspirin. The serious interactions of Aspirin are,
-
Captopril.
-
Benazepril.
-
Fosinopril.
-
Ketorolac.
-
Enalapril.
-
Ketorolac intranasal.
-
Lisinopril.
-
Mumps, measles, rubella, and varicella vaccine live.
-
Methotrexate.
-
Ibuprofen.
-
Moexipril.
-
Quinapril.
-
Ramipril.
-
Ticlopidine.
-
Probenecid.
-
Trandolapril.
-
Perindopril.
-
Varicella virus vaccine live.
12. Always inform the doctor or pharmacist about the other products you are taking, as some medications such as anti-platelets and blood thinners can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with other drugs.
13. Check all the prescription and nonprescription labels carefully because most of the medications contain pain relievers or fever reducers. So, there will be an increase in the risk of side effects when taken together.
14. Suppose when the doctor has directed to take low-dose Aspirin to prevent heart attack or stroke; in that case, continue taking the Aspirin unless the doctor instructs. For more details, speak to the doctor or pharmacist.
15.Always keep a list of all the products you are taking and share it with the doctor or pharmacist to reduce the risk of serious drug interactions.
What Are the Common Brand or Trade Names of Aspirin?
The common brand names of Aspirin are,
-
Easprin.
-
Aspergum.
-
Aspirtab.
-
Genacote.
-
Bayer.
-
Ecotrin.
-
Halfprin.
-
Ecpirin.
-
Ascriptin.
-
Entercote.
-
Norwich Aspirin.
-
Ninoprin.













