What Is Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction (SD) refers to any reduction in sexual desire, arousal, or frequency of intercourse; or a delay in or inability to achieve orgasm.
Do Psychotropic Drugs Cause Sexual Dysfunction?
Patients on long-term antipsychotic and antidepressant therapy often experience sexual dysfunction. Although quite common, sexual dysfunction arising from psychotropic treatment often goes unrecognized or unacknowledged by physicians. This may lead to non-compliance, where patients discontinue their medication without informing their physician or refuse to continue treatment. Sexual dysfunction occurs with greater severity in males than females - it is also tolerated less well by males. It has been linked with a poorer quality of life and a negative attitude towards therapy.
How Do Psychotropic Drugs Cause Sexual Dysfunction?
The mechanisms that induce sexual dysfunction in patients taking psychotropic drugs are unclear. Suggested mechanisms include disturbances in the following areas:
-
Sexual interest (libido).
-
Sexual arousal (including vaginal lubrication in women and erection in men).
-
Orgasm (and other endocrine disorders).
Sexual dysfunction may occur in as many as 70 % of patients with major depression, often manifesting as a lack of libido. While libido has been known to improve with the treatment of depression, there is also the converse possibility of antidepressants resulting in other adverse effects on sexual function. A proportional link has also been noted between the severity of psychotic symptoms and sexual dysfunction.
What Are the Symptoms of Sexual Dysfunction Due to Psychotropic Drugs?
In men on antidepressant therapy, sexual desire and orgasms are most affected. Women, on the other hand, display arousal dysfunction more commonly. The severity and type of symptoms experienced may vary depending on the dosage.
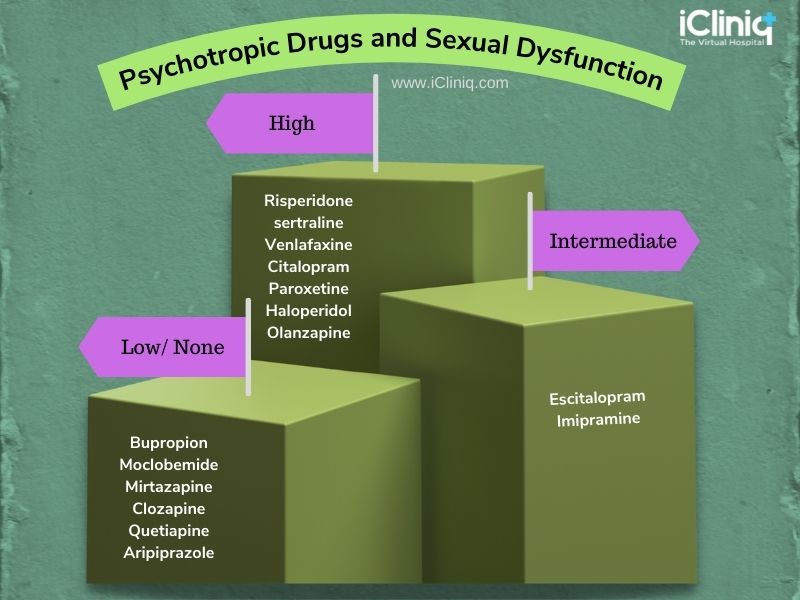
Which Psychotropic Drugs Are Responsible for SD?
Depending on the drug being taken, symptoms of sexual dysfunction may vary from high to intermediate or low.
What Are Some Other Causes for Sexual Dysfunction?
Sexual dysfunction in patients with depression and other psychological illnesses may also occur due to:
-
Inadequate treatment of psychological illness.
-
Other physical and chronic diseases.
-
Stress and emotional factors like relationship problems and job anxiety.
-
Psychosocial factors (including performance anxiety).
-
Hormone deficiencies.
-
Other Medication:
-
Antacids like Cimetidine.
-
Oral contraceptives or estrogen replacement therapy in women.
Should Patients and Physicians Discuss Sexual Dysfunction?
While it is assumed that most patients would be embarrassed about discussing sexual dysfunction with their physician, evidence has indicated otherwise. Physicians who broach the subject with their patients may find that they are open to discussion. Although patients may share their sexual issues with their doctors, the possible connection between their sex life and depression or medication may go unnoticed. That is why it is essential that patients share relevant details and that physicians ensure that to obtain a thorough medical history. Sensitive questioning could result in open conversation and help the physician and patient arrive at an optimal solution. Constant reassurance and close monitoring of the patient would provide relief while ensuring that patients stay on track with their medication.
How Can Sexual Dysfunction From Psychotropic Drugs Be Managed?
Sexual dysfunction management in patients taking antidepressants or antipsychotics is not an easy task. Therefore, it is essential that before beginning treatment for depression, any existing sexual dysfunction be diagnosed and acknowledged, along with its cause. Doctors should warn patients of the possibility of developing sexual dysfunction with psychotropic medication and consider their needs when prescribing. Once patients begin to take psychotropic medication, doctors may assess any subsequent development of sexual dysfunction by having their patients fill out a questionnaire. This will help them determine changes in sexual function, types of problems experienced, and tolerability.
Some of the questionnaires that may be used include:
-
Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX).
-
Changes in Sexual Functioning Questionaire (CSFQ).
-
Sex Effects Scale (SexFX).
-
Derogatis Interview for Sexual Functioning (DISF, DISF-SR).
-
Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI).
-
Psychotropic-Related Sexual Dysfunction Questionaire (PRSexDQ).
If sexual dysfunction (as a result of psychotropic medication) is diagnosed, doctors may pursue several avenues of management such as:
-
Dose Reduction of the Antidepressant: This would improve libido while still maintaining antidepressant effects.
-
Using Alternative Drugs.
-
Medication Holidays: Taking a break from drug therapy for short intervals (1-2 days) may be beneficial, but is subject to the doctor’s approval. Patients are not encouraged to attempt medication holidays on their own.
-
Drug Reversal: Addition of a drug that reverses these effects.
-
Targeted Medication: Drugs such as Sildenafil and Tadalafil may help treat sexual dysfunction - they can be given in combination with psychotropic medication.
Patients can also try timing their sexual activity to suit their needs. Medication could be taken after intercourse, thus reducing sexual side effects. However, this would depend on individual routines, patient comfort, symptoms, and side effects.
What Are Some Alternative Ways to Manage SD?
When all else fails, it may be worth considering alternative ways to deal with sexual dysfunction:
-
Psychotherapy.
-
Nutritional supplements.
-
Acupuncture.
-
Doing activities together with a partner to prepare for intercourse or finding new ways to enhance pleasure and stimulation.
However, it must be kept in mind that alternative therapy is not a substitute for medically-prescribed therapy and should only be considered a last resort.
How to Communicate With Partners?
Sexual dysfunction is not easy to deal with and may result in severe performance anxiety, leading to fractured relationships with sexual partners.
-
Communication Is Critical: Communicating with one’s partner is essential - this would require mature reflection, adequate time, and patience from both partners. The first step is to acknowledge the difficulties and feelings experienced by both partners.
-
Ask For Help: Couples may also consider seeing a therapist or counselor if they tend to fight often.
-
Lead With Honesty: Being honest about how either partner feels and mindful about how this honesty is accepted and reciprocated would result in a balanced, helpful conversation.
-
Do It Together: Confronting challenges and conflicts together will empower couples to work to better their relationship.
Conclusion:
Psychological illness and concurrent sexual dysfunction may seem like a scary dual challenge, but it does not have to be an insurmountable one. Trusting one’s physician, partner, and oneself to make the best choices and overcome the challenge together will make life easier.













