What Are Sepsis and Shock in Neonates?
Due to vagueness and delayed diagnosis, there are many diseases that stay untreated and increase the mortality ratio. Also, infants are more susceptible to catching an infection than adults because of their developing immune systems or birth-related defects. During the intrauterine phase of the fetus, the pathology of the placenta and fetus is almost ambiguous. As a result, there are chances of sepsis for at least 90 days from birth. Neonatal sepsis is caused by E.coli bacterial infection leading to life-threatening situations in newborns. For the next ten days, newborns are kept under observation as there are chances of secondary infection or septic shock that leads to organ failure. Neonatal sepsis is a bacterial infection that usually occurs in the first three months after birth by Escherichia coli, Listeria, and group B streptococcus bacterias. Even with the advancement in medicine, the proper definition of sepsis has not been defined for neonates due to immature organ development and the unreliability of changing the vitals of newborns. According to WHO, with over 130 million children being born, there are at least 4 million deaths, of which almost 36 % of deaths are from infection. Many preterm babies die within seven days of birth due to infection. Sepsis usually results in cytokines release, causing inflammation and a decrease in cardiac activity resulting in multi-organ failure. Sepsis further progressed to severe sepsis, ending with septic shock.
Shock is a pathological as well as a physiological state where tissue perfusion is seen, followed by cardiovascular dysfunction. Shock is the condition where owing to a system failure, and the bloodstream is unable to maintain adequate oxygen levels. However, if sepsis is treated adequately on time, there are chances to prevent complications related to septic shock in neonates.
What Are the Causes Of Sepsis and Septic Shock?
There are many factors that affect prenatal and postnatal sepsis in neonates. For instance -
-
Factors Related to Mother:
-
Mother’s age.
-
Premature and prolonged rupture of membrane (PROM).
-
Meconium staining.
-
Lack of nutrition.
-
Infection during pregnancy.
-
The birth canal has a bacterial infection.
-
Infection in uterus or placental tissue.
-
Chorioamnionitis - Infected amniotic fluid.
-
Immunocompromised mother.
-
-
Neonatal:
-
Gestational age.
-
Vascular catheterization for a long time.
-
Prolonged internal monitoring.
-
Group B streptococcal growth rectovaginal.
-
Decrease in baseline serum.
-
Postnatal nutrition.
-
Increased proinflammatory cytokines.
-
Prolonged hospitalization.
-
What Are the Signs and Symptoms?
It is comparatively difficult to distinguish sepsis in newborns as the signs they show are relatively different from older babies. However, the signs that newborns with sepsis show are:
-
Elevated body temperature.
-
Shortness of breath (apnea).
-
Diarrhea.
-
Unstable vitals.
-
Reduced appetite.
-
Seizures.
-
Low blood sugar.
-
Inflammation of the abdomen.
-
Vomiting.
-
Constant crying and restlessness.
-
Pale yellow skin and eyes (jaundice).
-
Multi-organ failure.
-
Bradycardia.
How to Diagnose Sepsis in Newborns?
Diagnostic measures for sepsis in newborns are:
- Complete Blood Count: A blood sample is taken before the antimicrobial therapy to determine if the bacterial infection is there in the bloodstream.
- Urine Culture: Sometimes, a catheter or suprapubic tap sample is obtained from the bladder.
- Spinal Tap (Lumbar Puncture): For infectious diseases like meningitis, a small needle is inserted into the spinal cord to take the spinal fluid sample to test for any infections.
- Swab Cultures: The sample is taken from the groin, eyes, ears, throat, rectum, or umbilicus to check for bacterial growth.
- C-reactive Protein: CRP level increases within 6-8 hours if the newborn has an infection in the body, and it elevates to the highest level within the next 24 hours. With this nonspecific marker, the certainty of inflammation of any internal organ can be ruled out.
- Chest X-Ray: To see images of an internal organ, tissues, or bones for infection.
What Are the Complications Associated With Sepsis in Neonates?
-
Respiratory Distress Syndrome: When newborn babies do not have enough surfactant in the lungs, it results in unstable respiratory vitals.
-
Apnea: It is a sleep disorder where breathing abruptly starts and stops.
-
Hyperthyroidism: When the thyroid gland produces too much thyroxine hormone.
-
Meningitis: When the fluid and membrane surrounding the brain swell, it is known as meningitis.
-
Intraventricular Hemorrhage: Commonly seen in premature babies with bleeding in the fluid-filled cavities such as the brain.
-
Seizure: Abrupt electrical activity inside the brain that lasts for a few seconds or minutes.
-
Cerebral Palsy: Cerebral palsy is a congenital disorder of brain development.
-
Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE): It is a type of brain dysfunction due to insufficient oxygen or blood flow to the brain.
-
Organ Dysfunction: It is an inflammatory reaction to a condition like sepsis, which requires immediate hospitalization.
-
Pneumonia: When air sacs in both lungs are infected, it causes fatal conditions like pneumonia.
-
Hypoglycemia: Abrupt drop in blood sugar level is called hypoglycemia.
-
Death: Due to severe sepsis, multi-organ failure is possible, and that can result in death.
How to Treat Sepsis in Newborns?
According to the guidelines of the American College of Critical Care medicine, stopping the further development of septic shock and preventing other complications within the first 60 minutes are very crucial. There are four phases to be considered during therapy. They are:
- Resuscitation phase.
- Optimization phase.
- Stabilization phase.
- Evacuation phase.
As soon as the diagnosis suggests sepsis in newborns, they are admitted to the NICU for the following aggressive treatment.
-
Volume Replacement: In case of septic shock, intravenous fluid replacement of electrolytes, total body water, or nutritions are done.
-
Mechanical Ventilation: In case of septic shock and respiratory distress, this is required to maintain oxygenation and tissue perfusion.
-
Intravenous Antibiotics: Newborns are unable to take antibiotics orally, and in newborns younger than four weeks with severe symptoms, this line of treatment is given along with other treatments. Also, before this treatment, a blood culture is taken to rule out the type of infection.
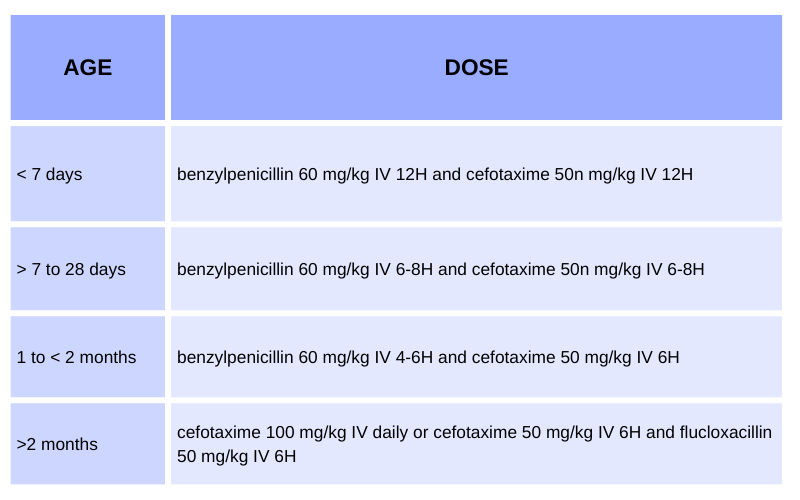
Conclusion
Neonatal septic shock is a fatal condition with high mortality and morbidity rate if not treated promptly. Owing to pathological and physiological responses and underdeveloped immune systems, preterm babies are at the highest risk. It is very important for doctors to maintain a sterile environment for mother and baby during birth in order to prevent sepsis. Additionally, parents should religiously follow up after their discharge from the hospital. However, in the case of the prenatal condition, it is more important to diagnose and treat sepsis as early as possible. Even though there are many treatment options available, there is still scope for the advancement and research in antimicrobial therapy and supportive care.













