What Is a Pulmonary Nodule?
A pulmonary or lung nodule indicates the presence of suspicious growth in one or both lungs. There may be one or several nodules in each lung. Having a pulmonary nodule definitely brings the suspicion of lung cancer. But pulmonary nodules can either be benign or malignant. If a lung nodule is benign, it does not indicate cancer, while in rare cases, it might be a sign of lung cancer. Lung nodules are generally three or less than three centimeters in diameter. They could be easily pinpointed on imaging scans like x-rays and CT (computed tomography) scans. The doctor usually addresses the abnormal lung growth as a coin lesion, shadow, or spot on the lung.
How to Rule Out Lung Cancer if You Have a Pulmonary Nodule?
As lung nodules are widespread, they could be easily identified in half of the population during their routine chest x-rays and CT scans. In addition, it has been reported that lung nodules are usually benign except for 5 % of the population. Benign pulmonary nodules can occur due to various factors such as infections and scarring. When healthcare professionals diagnose a pulmonary nodule, they might refer for some additional tests to rule out lung cancer.
What Are the Causes of Pulmonary Nodules?
Pulmonary nodules can develop due to an infection or inflammation of the lung tissue, which results in the clumping of the cells, the granuloma. Gradually, the granuloma calcifies and hardens within the lung to form a benign pulmonary nodule. There are two types of benign pulmonary nodules, they are:
-
Hamartomas - It is one of the most common types of benign pulmonary nodules. They are composed of abnormal amounts of normal tissues like fat, cartilage, connective tissue, and muscle. Mostly they are found on the outer surface of the lung connective tissue and some on the airways leading to the lungs. They do not press against the surrounding tissues and are limited only to the particular area. It is said that hamartomas are more common in males between the age of 50 to 70 than females. Rarely, on chest x-rays, it could appear as fluffy wool or popcorn in addition to the coin-like round growth. These coin-like round growths on chest x-rays are usually less than three centimeters in diameter.
-
Bronchial Adenomas - The other common type of benign pulmonary nodule is bronchial adenoma. They grow in the,
-
Airways of the lungs.
-
Mucous glands.
-
Ducts of the trachea.
The other causes of benign pulmonary nodules are;
-
Air pollutants or irritants.
-
Fungal infections (histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, etc.).
-
Scar tissues.
-
Respiratory system infections like tuberculosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), etc.
-
Autoimmune diseases like sarcoidosis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.
Pulmonary nodules can be cancerous, and malignant pulmonary nodules are usually large. Large lung nodules, such as 30 millimeters or more, are more likely to be cancerous. The abnormal growth of cells in the lung is known as neoplasm. Some examples of malignant neoplasms are carcinoid tumors and lung cancer, and the benign neoplasm may include neurofibromas.
Who Is at Risk of Developing Pulmonary Nodules?
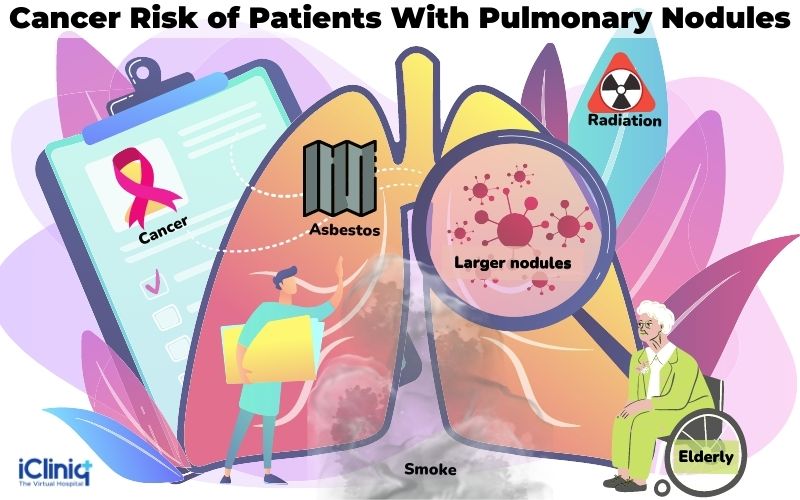
No specific population group is at more risk of developing pulmonary nodules. However, the following factors will increase the risk of a pulmonary nodule getting converted into cancer. They are:
-
Elderly people.
-
Having a larger nodule.
-
Previous or current smokers.
-
Family history of cancer.
-
Handling asbestos in the past.
-
Had exposure to radon or other secondhand smoke.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary Nodules?
Benign pulmonary nodules do not pose any symptoms, and they usually do not impede over the surrounding tissues. In the case of large or cancerous nodules, the tissue growth may press against the airway, resulting in cough, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. Over time, the person may develop the signs of early-stage lung cancer, like:
-
Discomfort in the chest.
-
Coughing up blood.
-
Wheezing.
-
Tiredness.
-
Hoarseness of voice.
-
Loss of appetite.
-
Sudden, unexplained weight loss.
-
Recurring respiratory infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia.
Consult the doctor when you have pulmonary nodules and experience above mentioned symptoms.
How Are Pulmonary Nodules Diagnosed?
Lung nodules may be identified during the imaging test taken for any other purpose or while preparing for other procedures. If you have a lung nodule, you might have active surveillance and be asked to get another CT scan after 6 to 12 months. During the 2-year surveillance, if the nodule remains the same, then they are not likely to become cancerous, and you can discontinue taking CT scans. If the nodule enlarges and becomes 13 millimeters or more, the doctor may advise further tests.
-
Bronchoscopy: The healthcare provider will sedate the patient and insert a bronchoscope down the throat into the lung. This instrument helps to cut a sample of tissue from the nodule. The retrieved tissue sample is sent to the laboratory to analyze the presence of abnormal cells.
-
CT Scan-Guided Biopsy: If the pulmonary nodule exists on the outer part of the lung, then a CT scan-guided biopsy might be needed. The physician might use the CT images to guide a thin needle into the lung. The tissue taken for biopsy with the help of a thin needle is sent to the laboratory, where examination for abnormal cells is done.
-
Positron Emission Tomography Scan (PET): An imaging device and injectable radioactive chemical is used to detect the diseased cells in the lungs.
What Are the Treatment Options for Pulmonary Nodules?
Usually, non-cancerous pulmonary nodules do not require treatment. If you have an infection or inflammation, you may need medications, such as:
-
Antibiotics.
-
Antifungals.
Surgical treatment is required when the pulmonary nodule turns cancerous or causes troubles. The surgical procedures carried out in patients with cancerous and non-cancerous pulmonary nodules are:
-
Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS): At the time of the procedure, small instruments and thoracoscope are inserted through the small incisions. Thoracoscope is a camera that the physician uses to look at the images to remove the nodule.
-
Thoracotomy: The surgeon might extract the pulmonary nodule by thoracotomy, that is, below the shoulder blade, and between the ribs to reach the lungs. After surgery, a tube drains excess fluid from your chest for several days.
Conclusion:
Pulmonary nodules are not always cancerous. Malignant and sometimes non-cancerous pulmonary nodules may press against the airway and cause complete or partial blockage in some people. In these cases, surgery might be required to clear the pathway for better breathing. Avoid or reduce cigarette smoking, exposure to irritants, and asbestosis to protect the lungs from pulmonary nodules. When you experience any abnormal symptoms, do not hesitate and reach out to your doctor to assess the severity of the condition and plan the right course of treatment.












