Introduction
When a medical treatment necessitates limited resources such as manpower, infrastructure, equipment, and so on, the decision to get the treatment becomes critical. Surgery is one such treatment that requires critical decision-making by the patients and their families. The medical or healthcare sector is incomplete without surgical procedures and is a challenge for many countries worldwide because of limited resources.
When deciding to undergo surgical treatment, many factors play an important role. The success rate of the treatment, recovery time, etc., are a few of them. However, for those living in low-resource settings and remote areas where healthcare facilities are difficult to avail, it becomes challenging to undergo a surgical procedure. As a result, many patients lose their lives after postponing the surgery or even completely denying it. Furthermore, crises such as the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic further add to the hardships, reallocating the limited resources and postponing non-urgent treatments and surgeries so that healthcare professionals can treat only COVID-19-affected patients.
What Is Elective Surgery?
Elective or optional surgery is a medically necessary treatment that is not urgent or preplanned and can be delayed or postponed for a minimum of 24 hours. It is usually performed under anesthesia.
What Are Elective Surgery Examples?
Gallbladder elective surgery, elective cosmetic surgery, elective colorectal surgery, elective ortho surgery, etc., are examples of elective surgery.
What Are the Categories of Elective Surgery?
Based on the clinical assessment of the patient, there are three categories:
-
Category 1 Urgent: A patient with the most urgent need of surgery will be treated first. The clinical condition of the patient has the potential to become worse further and may become an emergency. Surgery is performed within 30 days. For example, heart surgery, heart valve replacement, etc.
-
Category 2 Semi-Urgent: The patient’s clinical condition is less likely to become an emergency or worsen further. It improves the quality of a patient’s life and does not require urgent treatment. The patient may experience pain and discomfort because of the ill condition. Surgery is performed within 90 days. For example, colposcopy, spine fracture with no neurological symptoms, etc.
-
Category 3 Non-Urgent: The patient’s clinical condition is unlikely to become an emergency or worsen further. The patient may experience pain and discomfort. Surgery is performed within 365 days. For example, cosmetic surgery without indications, diagnostic knee arthroscopy, etc.
What Is Elective Major Surgery?
It is a type of elective surgery involving tissue trauma, a high risk of infection, a long recovery time, and a serious medical condition or disease that could be life-threatening. For example, hernia surgery, kidney stone removal, etc.
What Is Elective Minor Surgery?
It is a type of elective surgery that is minimally invasive with a low risk of infection and a shorter recovery time. For example, dental implants, cataract surgery, etc.
What Is the Most Common Elective Surgery?
The few most common elective surgeries are the following:
-
Cosmetic surgery.
-
Cleft lip repair.
-
Dental implants.
-
Cataract surgery.
-
Bariatric (weight loss) surgery.
Why Is Elective Surgery Necessary?
-
To improve the overall health of the patient.
-
To improve quality of life.
-
To relieve pain, discomfort, and disability.
-
To treat health conditions that require surgical treatment.
-
To avoid further risks of infection and complications.
How To Know if a Surgery Is Considered Elective or Not?
Surgery can be eligible for one patient but may not be elective for another patient. For example, getting a dental implant to replace a lost tooth may be elective for a patient who wants a perfect smile. In contrast, for another patient, it could be non-elective or necessary to restore functional abilities to chew food properly.
Surgery is elective if-
-
It is done based on the patient's choice without any underlying serious medical condition.
-
It is not performed urgently or in an emergency.
What Are the Consequences of Delaying Elective Surgery?
Below are the possible consequences of delaying or postponing an elective surgery:
-
Some diseases could be "time-sensitive," which means if the elective surgery is not done on time, it may worsen the health condition or symptoms and quality of life and increase risks further.
-
It may result in an emergency case and unnecessary complications.
-
It may impair the physical functioning of the patient.
-
It may deteriorate mental health, such as increased anxiety, stress, etc.
-
Patients may become socially inactive and less productive.
How to Prepare for Elective Surgery?
Preparing for elective surgery depends on the severity of the medical condition, type of surgery, type of anesthesia, and many other factors. In general, the patient should:
-
Stop taking food and water for a specific time before surgery.
-
Wear loose-fitting clothes.
-
Avoid wearing jewelry and other valuables.
-
Undergo a few tests such as blood tests, X-rays, etc.
-
Stop smoking and alcohol consumption.
-
Stop taking medications that affect blood flow, such as aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs. Aspirin results in increased bleeding after the surgical procedure; therefore, the patient should stop taking aspirin seven to ten days before elective surgery. It is important to discuss these medications with the doctor.
Why Is Elective Surgery Postponed?
A pharmacological treatment must be considered before deciding to go for elective surgery as the only option or best option for the treatment. In addition, there could be various factors for postponing an elective surgery:
-
High or low blood pressure.
-
Uncontrolled diabetes.
-
Abnormal electrolyte levels in the blood, such as potassium.
-
Unstable vital signs such as increased pulse rate or heart rate.
-
Presence of infectious problems. For example, elective surgery of a patient with tuberculosis should be delayed until there is no infection.
-
The old age of the patient. If the success rate of the surgery is low or the associated post-surgery side effects are high, considering the patient's old age, then it may be delayed.
Should One Postpone Elective Surgery After COVID-19 Positive Test?
Yes. The elective surgery should be postponed if the patient is tested positive for COVID-19. The surgery is not planned further until the patient recovers completely from the COVID-19 symptoms.
How Long After COVID-19 Can One Have Elective Surgery?
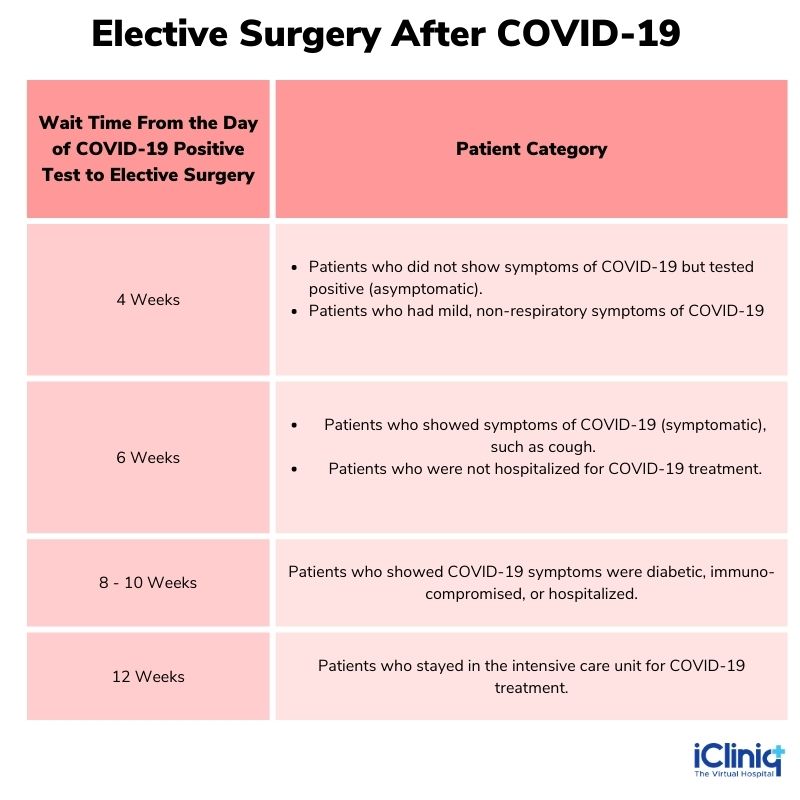
Conclusion
When deciding on elective surgery, the patient's overall health and other patient-related factors must be considered. Elective surgery can be safe if proper precautions are taken. However, a non-urgent or less urgent surgical treatment may become an emergency if ignored. Therefore, asking the right question to the doctor and making an informed decision is always advisable.













