Why Are Calcium Supplements Needed?
Calcium is an essential nutrient for our body. It helps build bones and regulate muscle contractions. Inadequate calcium in our diet can cause conditions like rickets in children and osteoporosis in older people. Calcium supplements can be taken to balance the calcium content in the blood. These are available in multiple ionic calcium concentrations like acetate, citrate, carbonate, phosphate, lactate, and gluconate. Calcium carbonate has the maximum elemental calcium content, is cheap, and is the first choice. They should be prescribed with caution considering varying factors like tolerability, the amount required by the body, cost, interactions with other medications, available forms, and absorbability.
An average calcium requirement for an adult is 1000 mg to 1200 mg per day. Calcium supplements are usually given to those who have difficulty getting enough dietary calcium, like people who follow a vegan diet, have lactose intolerance or digestive diseases, or receive long-term corticosteroid treatment.
Who Can Take Calcium Supplements?
The drug is taken by individuals unable to get the required amount of calcium from their diet or those with special needs for calcium like in pregnancy, nursing women, and children.
-
Pregnant Women: The increased uptake of calcium in pregnancy helps in developing the bones and teeth and improves the developing nervous and muscular system of the fetus. In addition, the drug reduces the risk of pre-eclampsia (a pregnancy complication) by controlling high blood pressure.
-
Women in the Peri and Post-Menopause: Calcium supplements are recommended in women nearing their menopause. This limits the risk of osteoporosis and prevents bone loss. Vitamin D intake helps reverse bone softening due to low calcium intake.
-
Hypocalcemia and Hypothyroidism: Calcium supplements are most commonly used for the treatment and prevention of low calcium levels in the blood (hypocalcemia), and muscle cramps. Calcium supplements are also indicated in hypocalcemic rickets and hypothyroidism.
-
Premenstrual Syndrome: This also reduces mood swings, bloating, and pain associated with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
-
Digestive Problems: The supplements are used to relieve heartburn and indigestion. Calcium Carbonate is used as an antacid to relieve upset stomach and neutralizes the acid secretions in the stomach.
-
Renal Failure: Taking Calcium supplements is effective in controlling high phosphate levels in the blood in kidney failure patients. It also reduces the blood pressure in these patients.
-
Adjunct with Other Medications: Medicines like Rifampicin, anti-seizure drugs, loop diuretics, Corticosteroids, and Chloroquine require concurrent calcium supplements.
How Do Calcium Supplements Work?
Calcium is absorbed either by the active transport process in the duodenum and jejunum or by intracellular passive transport proceeding along the entire intestine. Vitamin D increases the absorption of calcium, protects, and relaxes the muscles and nerves.
In heartburn and an upset stomach, Calcium carbonate increases gastrointestinal tract motility. The calcium carbonate acts as a buffer and neutralizes the gastric acid contents of the stomach. This helps to reduce the damage caused to the mucosal lining of the stomach and duodenum. The calcium ions enhance the peristalsis of the esophagus to the stomach and thus decreases the symptoms of heartburn.It is also taken for constipation treatment.
In kidney diseases, calcium acts as a phosphate binder and is indicated in the use of hyperphosphatemia.
Calcium supplements work within hours or weeks of intake. Calcium absorption takes place in the small intestine. The amount of calcium absorbed varies with age, the highest level of absorption occurring in infancy, early puberty, and during the last two trimesters of pregnancy. There is a marked decrease in calcium absorption in old age and post-menopause.
What Is the Recommended Daily Intake of Calcium?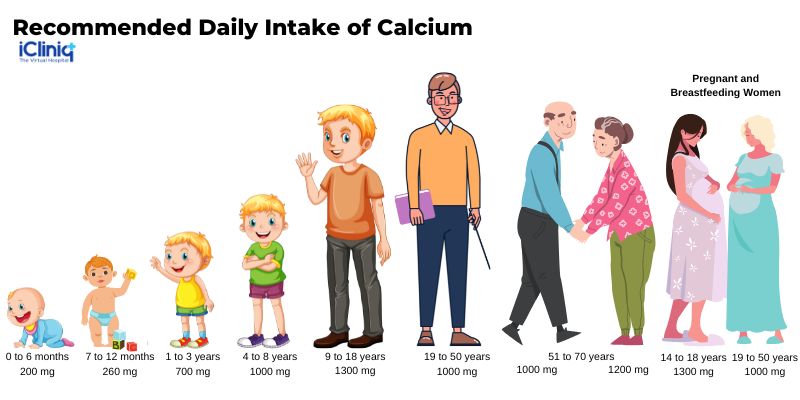
Calcium supplements are available online in the form of tablets, chewable, oral suspension, or powder. The most commonly administered supplements are calcium carbonate and calcium citrate and are available as over-the-counter medicines. They can be given in combination with vitamins and other minerals.
The intake of calcium supplements must be spread throughout the day for better absorption and fewer side effects. It should not exceed 500 mg at one time.
How to Use Calcium Supplements?
-
For Pregnancy and Lactating Women - The absorption and bioavailability of oral calcium carbonate depend on the gastric acids in the stomach and therefore need to be taken with food. However, calcium citrate is readily absorbed with or without food.
-
Always take calcium supplements in small doses, and the doses should be divided equally throughout the day. This enhances the systemic absorption of the supplements.
-
For the intravenous route, calcium gluconate is used to regulate the low serum calcium in cases of seizures, tetany, or cardiac arrhythmias and correct acute hypocalcemia.
-
Oral suspensions should be taken as advised by the doctor. Measure the appropriate amount. Shake the bottle well before use.
-
Chewable tablets must be first chewed well and then swallowed.
-
Keep a minimum of one-hour interval in between different medicines.
In the case you miss the dose, take it as soon as possible. Do not take two tablets together as it may increase the side effects.
What Are the Precautions to Be Taken Before Administering the Supplements?
If you have any of the following, consult your doctor:
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding - Dosage should be altered accordingly in pregnant and lactating mothers. Take the supplements as prescribed to avoid unpleasant side effects.
-
Allergies - Inform the doctor if you are allergic to calcium or other drugs.
-
Hypercalcemia - Increased calcium supplements can cause hypercalcemia symptoms like increased heart rhythm.
-
Prostate Cancer- Calcium supplements along with a high intake of calcium-rich dairy products may increase the risk of prostate cancer. If you are in the risk group for prostate cancer, inform your doctor beforehand.
-
Heart Diseases - The intake of calcium supplements may increase the risk of heart diseases including stroke and heart attack. If you have any personal or family history of heart diseases, consult with your doctor before starting calcium supplements.
-
Kidney Stones - Consuming more than 2000 mg per day can increase the risk of kidney stones. Consult with your doctor for the same. Drink an adequate amount of water.Intake of inessential amounts of calcium supplements is not recommended.
-
Smoking - There is less calcium absorption in people who smoke. Refrain yourself from smoking if calcium supplements are medicated.
-
Alcohol - Excessive alcohol can interfere with calcium balance and may worsen liver damage. Avoid alcohol intake when on calcium supplements.
-
Children - The doctor should adjust the amount of calcium-containing foods when calcium supplements are taken to avoid hypercalcemia.
-
Self-Medication - Although the medicines are available over-the-counter, it is always recommended to consult the doctor before taking them.
What Are the Side Effects of Calcium Supplements?
Calcium is relatively safe when used in the recommended dose of 1000 mg to 1200 mg per day.
The common side effects are
-
Constipation.
-
Severe diarrhea.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Flatulence.
-
Bloating.
When taken with Vitamin D, there can be severe side effects like
-
Irregular heartbeat.
-
Weakness.
-
Drowsiness.
-
Dry mouth.
-
Feeling tired.
-
Increased thirst.
Mild symptoms may last for a few days. If it persists for a longer time, consult your doctor. Inform the doctor of the severe symptoms immediately.
What Are the Common Interactions of Calcium Supplements?
Calcium supplements interact with other drugs, foods, and supplements. While taking calcium supplements, the following foods and drugs should be consumed with caution:
With Medicines:
Moderate Interactions -
Quinolone.
Tetracycline.
Bisphosphonates.
Digoxin.
Levothyroxine.
Sotalol.
Verapamil.
Thiazides.
Severe Interactions -
Indapamide
Microzide.
Nifedipine.
Ceftriaxone.
With Food:
- Spinach, rhubarb-like food rich in oxalic acid, or foods containing phytic acid (bran and whole grain) decreases calcium absorption.
- Soda and caffeinated drinks like coffee may interfere with calcium absorption.
- High salt foods reduce calcium absorption and increase the excretion of calcium in the urine.
With Diseases:
Sarcoidosis - Calcium supplements can cause a risk of hypercalcemia in patients with sarcoidosis.
Multiple Myeloma - Bone damage associated with multiple myeloma results in too much release of calcium into the blood. If calcium supplements are taken in those cases, it might cause hypercalcemia.
Kidney Diseases - Calcium supplements can increase the risk of kidney failure.
Conclusion:
Calcium supplements are recommended only if you have trouble getting enough calcium from your diet. Balanced calcium content in blood ensures the strengthening of bones at all ages. These should however be taken with caution in order to avoid overdose that might lead to hypercalcemia. The dose should be chosen correctly after consulting with the doctor.












