Introduction
The first-choice medication is statins to lower high blood cholesterol, a risk factor for cardiovascular disease (CVD) occurrences in both those with and without a history of heart disease. Statins are recognized for reducing cardiovascular events and death rates in people with coronary artery disease or who are at high risk of acquiring cardiovascular disease. Statins provide advantages such as reducing thrombus (clot) formation, inflammation, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. By inhibiting the 3-hydroxy-methylglutaryl coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase enzyme, statins reduce the blood's level of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Giving statins to patients who have coronary artery disease and high blood cholesterol levels lowers the risk of serious cardiovascular events. Moreover, rigorous statin therapy has better therapeutic advantages than conventional treatment.
What Are Statins?
Hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMG-CoA) inhibitors, also known as statins, are one of the most regularly prescribed medication classes worldwide. Presently, there are six statin medications available:
-
Pitavastatin.
-
Rosuvastatin.
-
Atorvastatin.
-
Simvastatin.
-
Pravastatin.
-
Fluvastatin.
HMG-CoA, a rate-limiting step in cholesterol production, is inhibited by statins. Statin therapy has been proven to be successful in the following ways:
-
Lowering triglyceride (fat) levels by 10 percent to 20 percent.
-
Lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels by 20 percent to 50 percent.
-
Increasing high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels by five percent to ten percent in serum.
What Are the Recommendations for the Use of Statin Therapy in Cardiovascular Diseases?
-
Score A: For people aged 40 to 75 with at least one cardiovascular risk factor such as dyslipidemia (imbalance of lipids), diabetes, hypertension, or smoking and a ten-year cardiovascular disease risk estimate of ten percent or higher.
-
Score B: People with one or more cardiovascular risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, hypertension, or dyslipidemia and an estimated ten-year CVD risk of 7.5 percent to less than ten percent, persons between the ages of 40 and 75 should discreetly administer a statin.
The cholesterol levels and other cardiovascular (cardiovascular) disease risk factors will determine whether there is a need to take a statin. Before recommending a statin, the doctor will take into account all of the risk factors for heart attacks and strokes.
-
Cholesterol Overall - The average person should strive to maintain a total cholesterol level of less than 200 mg/dL, or 5.2 mmol/L.
-
Cholesterol in Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL) - Under 100 mg/dL, or 2.6 mmol/L, is the target level for this "bad" cholesterol. Aim much lower (below 70 mg/dL, or 1.8 mmol/L) if there is a history of heart attacks or are at very high risk of having one or having a stroke. The long-term risk of a heart attack or stroke is the most significant factor that will be considered when deciding whether to treat with statins. Unless the LDL is higher than 190 mg/dL (4.92 mmol/L), there will be no need for a statin if the risk is very low.
What Are the Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases?
The risk factors for heart disease and stroke, besides cholesterol, include:
-
Smoking.
-
Lack of exercise.
-
Age.
-
Diabetes.
-
Obesity or excess weight.
-
High blood pressure.
-
Family history of heart disease, especially if it occurred in male relatives before the age of 55 or in female relatives before the age of 65.
-
Clogged arteries in arms, legs, or neck (peripheral artery disease).
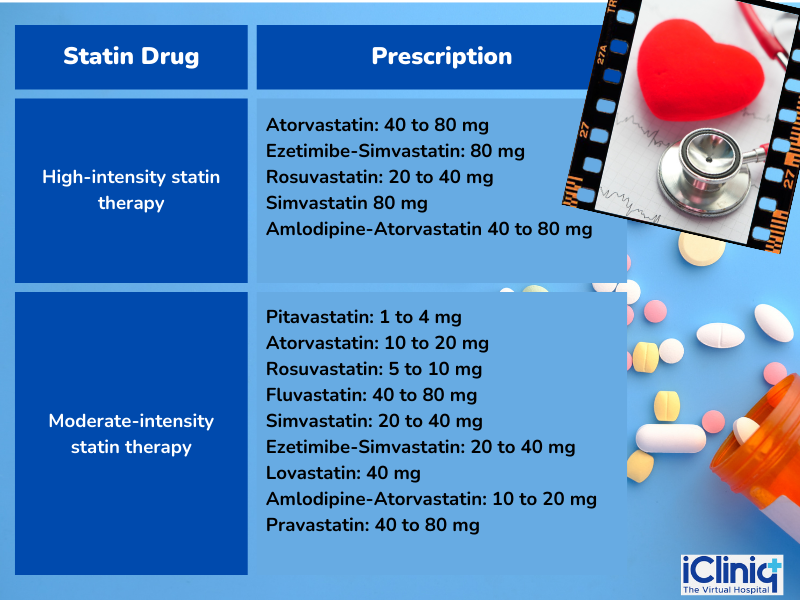
What Are the Types of Statins Employed in Managing Cardiovascular Diseases?
What Are the Adverse Effects of Statin Therapy?
The adverse effects of statin therapy are as follows:
-
Cancer.
-
Pulmonary disease.
-
Liver disease.
-
Brain hemorrhage.
Other rare side effects include the following:
-
Type 2 Diabetes or Elevated Blood Sugar - Statins may slightly raise the blood glucose levels which can cause type 2 diabetes. The advantages of taking a statin may, however, exceed the risks. Statin use significantly lowers the risk of heart attacks in diabetics.
-
Liver Injury - The use of statins can occasionally elevate liver enzyme levels. If the rise is slight, one can keep taking the medication.
-
Injury to Muscle Cells - Extremely rarely, taking high doses of statins can lead to the breakdown of muscle cells and the release of myoglobin into the bloodstream. Kidney damage and excruciating muscle pain may result from this.
How to Prevent Cardiovascular Diseases?
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is still essential to preventing heart disease. Whether there is a need for statins or not, making lifestyle changes is essential for lowering the chance of developing heart disease. The following measures can be taken to prevent heart disease:
-
Stop smoking.
-
Keep a healthy weight.
-
Consume a diet high in fresh produce, whole grains, seafood, and vegetables that are low in sodium, trans fats, saturated fats, and processed carbohydrates.
-
Increase physical activity.
Statins may be a possibility, but despite making healthy lifestyle modifications, cholesterol remains high, especially the bad type.
Conclusion
Statins decrease cholesterol and function by obstructing a component that the body requires to produce cholesterol. Statins also lower the risk of heart diseases and strokes, lessen the risk of some blood clots, and assist in stabilizing the plaques on blood vessel walls. Statins are very safe and effective drugs for both avoiding and managing coronary artery disease, irrespective of cholesterol levels. However, there is also a need to keep an eye on the adverse effects, which can occasionally include liver malfunction and muscular pains (myalgias). There is some evidence that statins may raise the chance of developing diabetes, although the advantages of reducing cardiovascular disease typically outweigh that risk. To determine whether statins are useful in people with severe chronic diseases such as chronic renal failure or heart failure, more research is required. In clinical practice, statins should be recommended to all patients with coronary artery disease unless the patient exhibits problems such as rhabdomyolysis (damaged muscle disease) or high liver enzymes.












