Introduction:
Radiological imaging is vital for providing a confirmatory diagnosis and rendering timely treatment. The prime goal of an imaging procedure is to achieve the best quality images with high precision so that an accurate diagnosis can be made. It is also essential to have a supportive patient to achieve this goal, along with an exceptionally trained radiologist. Diagnostic procedures are relatively easy when performed in adults; however, it is challenging with the pediatric population. The prime reason for this is the inability of children to comprehend the importance of the situation.
Why Are Diagnostic Procedures Challenging in the Pediatric Population?
Most children are anxious and scared when taken to a health care center. This anxiety stems from various reasons. They are as mentioned below:
-
Unfamiliar Environment: The procedure room may not be familiar, resulting in fear of the unknown.
-
Trauma or Illness: Children may be crying and are often unable to remain still due to the pain and discomfort from the disease.
-
Fear of Separation: Infants and toddlers fear being separated from their parents.
-
Fear of Pain: Older kids fear that the procedure will be immensely painful.
-
Fear of Needles: Infants, toddlers, and even older kids have an intense fear of needles or any sharp objects, thinking that it would be extremely painful.
-
Fear of the Procedure: Children may not have an idea about the procedure or the outcome, and hence this uncertainty may result in fear of the procedure.
Why Is It Necessary to Keep the Kids Still During a Diagnostic Procedure?
The main aim of an imaging procedure is to achieve a high-quality image. In order to accomplish this, most medical imaging procedures require patients to remain still. Any movement while imaging may result in blurring of the images or cause motion artifacts. Hence, this could lead to repeat imaging resulting in increased radiation exposure which may be risky for the pediatric population as they are more radiosensitive and vulnerable to radiation-induced damage. Hence it is essential to keep children still while taking images and practice radiation safety protocols while imaging the pediatric patients.
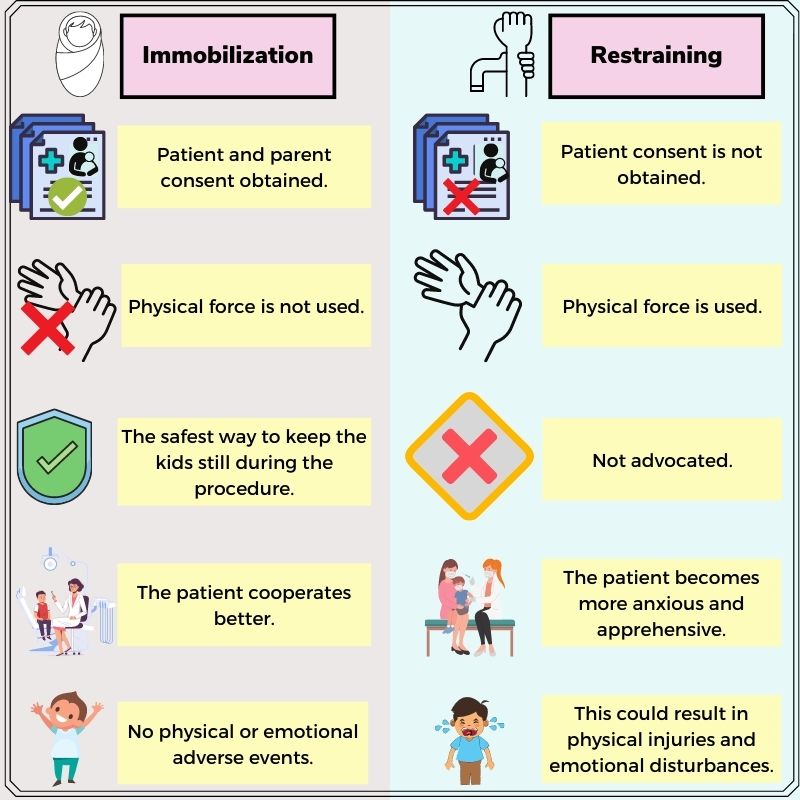
What Is the Difference Between Immobilization and Restraint?
Various techniques can be used to keep children still during the diagnostic procedures. These techniques should ensure that children do not experience any negative incidents disturbing them emotionally or physically. Immobilizing a child forcefully may result in some injuries, further increasing their anxiety and the chances of unsuccessful imaging. The techniques should aim to restrict patient movement by following paramount safety protocols, thereby obtaining accurate images with no adverse events.
These techniques can be broadly termed immobilization or restraining methods. Both the terms, though, serve the same purpose yet have a broad distinction in the means of usage. Immobilization means to hold a child still with their consent. It is the safest way to restrict the movement of the child as it ensures better cooperation with no damaging incidents. Using physical force without the consent of children to keep them still is known as restraining. Restraining can prove devastating, making the child more apprehensive and may induce post-traumatic stress.
What Are the Different Immobilization Techniques?
The different immobilization techniques are as given below:
Physical
-
The physical immobilization technique refers to manual help in keeping the child still during the diagnostic procedure.
-
The radiologist or other staff members may be asked to hold the child still.
-
The parent can also help by holding the hands or legs to prevent any movement.
-
Instructions will be given to the parent on how to hold the child still without disrupting the procedure or obscuring the imaging part.
-
Parental holding is the most effective way of immobilization in toddlers and young kids, as this method helps gain trust and confidence in kids.
-
However, an anxious parent may prove ineffective.
Mechanical
Mechanical immobilization uses specific equipment or tools to keep kids still. They are as follows:
-
Sandbags or Sponges: Sandbags or sponges can be used to keep the arms or legs steady. The heaviness of the sandbag prevents any movement.
-
Swaddling: This method is very effective in infants and babies. They can be wrapped comfortably in a swaddle cloth, which keeps them from moving. The swaddle can also help comfort the baby and may help them fall asleep.
-
Pacifier: A pacifier can be used in babies. They help the babies calm down and even fall asleep.
-
Velcro Straps: Velcro tapes or bands are often attached to the examination table or a board. Once the child lies down, the Velcro tape is closely pulled over them, keeping them still during the procedure. These Velcro tapes keep the child still and prevent them from falling down the table during the examination.
-
Pigg-O-Stat: It is a device most commonly used to make the child sit erect for a chest X-ray. This device consists of a small seat on which the child sits. Two plastic arms are present above the seat that fits closely around the hips and help the child to keep their arms above the head.
-
Perspex Paddles: These immobilization devices are used for the extremities.
Chemical
-
At times, no amount of understanding or verbal interaction may calm an apprehensive child.
-
The child may receive a sedative or general anesthesia in such a situation.
-
The sedative may help the child fall asleep, and the procedure can be carried out without any difficulty.
-
If required, general anesthesia may also be given.
-
Both procedures are safe when carried out under excellent observation and trained personnel.
-
Infants can be breastfed to sleep. Babies can be offered sucrose solution to make them comfortable and cooperative during certain procedures.
Psychological
-
Psychological immobilization involves the use of communication to distract the children.
-
Distraction diverts the mind from the procedure or the pain, thus ensuring the child is still during the process.
-
Effective verbal communication can prove helpful in gaining the confidence of the child.
-
The child may be allowed to carry their favorite toy, books, blanket, or any personal item that can prove to be a resourceful source of distraction.
What Preparations Can Be Done to Reduce Anxiety in Children Before the Procedure?
Preparing the child well ahead helps facilitate the procedure, and the child copes well during the process.
-
Parents need to understand the procedure and its benefits for their children. Parents should remain calm and support themselves as the child can quickly sense the anxiety in parents.
-
For toddlers and preschoolers, explain the procedure in simple words. Explain to them the importance of the test. Be honest with them, as most of them cope well with a thorough understanding of the situation. However, avoid frightening terms.
-
For older kids, talk about the procedure and use simple words. Again, pretend play can help them understand the process.
-
The preparation of the child should depend on their age, maturity, and understanding level.
Conclusion:
Pediatric diagnostic imaging is considered tough and challenging due to various factors such as the age of the child, their ability to cooperate, their level of understanding, radiation dosage, and the precision of the image. While working with pediatric patients, the radiologist should keep in mind that along with precise diagnosis, the communication and emotional needs of the children should also be prioritized. The simplest form of immobilization should always be preferred, and it should be ensured that the child does not endure any adverse events.












