Overview:
Guaiphesesin is a plant product that enhances bronchial secretion and mucociliary function while being secreted by tracheobronchial glands. Guaiphenesin belongs to the class, expectorant (mucokinetics). It increases bronchial secretion or reduces its viscosity, thus facilitating its removal by coughing.
This drug helps to treat cough, common cold, and other breathing illnesses by thinning the mucus and clearing the congestion as it is a bronchial secretion enhancer. Ask your doctor about the ways to relieve the symptoms of cough and cold because steam inhalation and proper hydration may be more helpful in clearing airway mucus. A variety of expectorants in combination with antihistamines and antitussives are marketed without proof of efficacy, so before planning to take a drug consult a doctor and do not self-medicate.
Composition:
This tablet contains,
-
Active Ingredient: Guaifenesin.
-
Inactive Ingredients:
-
Caramel.
-
Sodium Benzoate.
-
Sodium Citrate.
-
Saccharin Sodium.
-
Glycerin.
-
Citric Acid.
-
Flavor.
-
Propylene Glycol.
-
Sorbitol Solution.
Drug Group:
Guaifenesin belongs to the group of drugs called expectorants (mucokinetics). Guaifenesin makes the mucus thin and clears the air passages by loosening up the mucus, making it easier to cough and breathe. The other drugs that belong to the group expectorants are,
1. Bronchial Secretion Enhancers:
-
Sodium or Potassium citrate.
-
Potassium iodide.
-
Balsam of Tolu.
-
Vasaka.
-
Ammonium chloride.
2. Mucolytics:
-
Bromhexine.
-
Ambroxol.
-
Acetylcysteine.
-
Carbocisteine.
What Is Guaifenesin Used For?
Guaifenesin is used for,
1. Coughs.
-
It is used in dry coughs that occur due to irritation above the larynx.
-
It makes the cough productive and less tiring.
-
It is used in chronic coughs.
2. Congestion caused by,
-
Common cold.
-
Bronchitis.
-
Breathing illnesses.
3. Used only on doctors instructions for,
-
Long-term breathing problems such as,
-
Chronic bronchitis.
-
Emphysema.
How Does Guaifenesin Work?
Guaifenesin works by thinning the mucus and clearing the airways, thus helping to breathe easier. These drugs work by increasing the volume (by stimulating the bronchial secretory cells) or decreasing the viscosity of the respiratory secretions and facilitating their removal by ciliary action and coughing.
Onset Of Action:
Guaifenesin generally starts working within 30 minutes and reaches its peak plasma concentration within an hour of taking the drug. The duration of action is 4 to 6 hours, so it is meant to be taken every four hours or every 12 hours (extended-release tablets) a day.
Habit-Forming:
Guaifenesin contains a narcotic cough medicine that may be habit-forming, and misuse of this medicine leads to addiction, overdose, and death. So do not take this medicine for more than a week unless prescribed by the doctor.
Expiry Date:
Avoid taking this medicine after it expires. You can verify the expiry date printed on the back of the pack before taking the medicine.
What Is the Dosage and Administration of Guaifenesin?
Dosage and administration of Guaifenesin depends on the following,
-
Age.
-
Medical condition.
-
Response to treatment.
Preparations and Doses:
The available forms of Guaifenesin for both adult and children are,
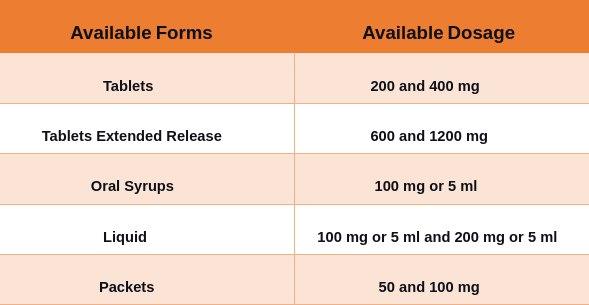
Guaifenesin Usual Dosage:
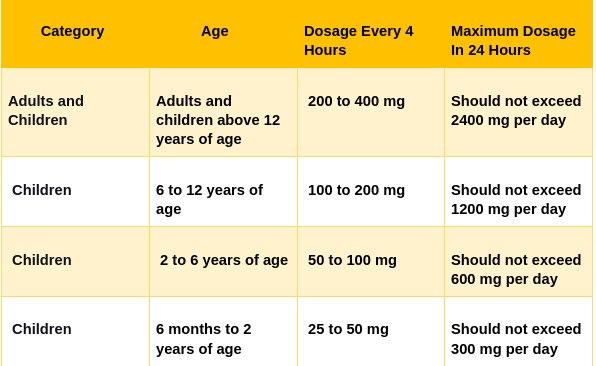
Guaifenesin Dosage for Extended-Release Tablets:
Extended-release tablets should be swallowed as a whole, and they should not be chewed or crushed.

How to Use Guaifenesin?
1. Used Orally - This drug is taken orally, with or without food, for every four hours as directed by the doctor.
2. Tablet Form - This tablet has a bitter taste and should be swallowed as a whole, and should not be chewed or crushed.
3. Liquid Form - On using the liquid form of medicine, always measure it with a dosing syringe or medicine cup, and if you do not have any of these dose-measuring devices, ask your pharmacist for one.
4. Powder Form - On using the powder packets, empty the packet and place it on the tongue, and do not chew to avoid a bitter taste.
5. Instruction on Self-Medication: Before using the medicine or self-treating, read the label carefully and ask your pharmacist for any doubts.
6. Water - Drink plenty of fluids to break the mucus and clear congestion.
Missed Dose:
Usually, Guaifenesin is taken as needed, and in case if your doctor has instructed you to take it regularly, the missed dose can be taken as soon as you remember it. But if it is time for the next dose, you do not want to take the missed dose, and you can continue with your regular dosing schedule. Also, do not take a double dose in order to compensate for a missed one.
What Are the Drug Warnings and Precautions?
1. Tell your doctor if you have been previously allergic to this medicine or the ingredients present in the drug because this product contains inactive ingredients, which can cause other problems and allergic reactions.
2. Tell your physician or pharmacist about your previous and present medical history, especially of,
-
Cough with blood.
-
Smokers cough.
-
A large amount of mucus.
3. Be aware of taking Guaifenesin because it most often comes in combinations, so check the brand name and other constituents present in the label.
4. When you are self-medicating and the chronic or persistent cough does not improve within a week, seek a doctor.
5. Caution is needed when you take liquid forms of Guaifenesin, especially on diabetes or liver diseases because liquid forms contain sugar and alcohol, so ask the pharmacist or the doctor about the product's safety.
6. The liquid forms and powder packets may contain Phenylalanine or Aspartame, so talk to your doctor before using it if you have phenylketonuria (PKU) or any other conditions that require restrictions to Aspartame or Phenylalanine.
7. Pregnancy - Although benefits outweigh the risks in pregnancy, use Guaifenesin only if it is absolutely necessary and consult a doctor before use.
8. Breastfeeding - Caution is needed during lactation because it is unknown whether it is excreted in breast milk.
9. Before surgery - Tell your doctor all the prescription and nonprescription medications you are taking and do not take Guaifenesin light, considering it only as a cold tablet, because every tablet is unique and can interact with surgical procedures.
10. It is not advisable to take more than 6 doses per day, and dosage depends on the causative factor.
11. Get immediate medical attention when your cough is associated with,
-
Severe sore throat.
-
Rashes.
-
Persistent headache.
What Are the Side Effects of Guaifenesin?
-
Common Side effects:
Guaifenesin causes some common side effects, and they usually go away as the body starts to adjust to this medicine during the treatment and do not require separate medical attention. Also, you can ask your physician how to prevent or reduce these side effects. The most common side effects of Guaifenesin are,
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Dizziness.
-
Stomach pain.
-
Headache.
-
Decreased uric acid levels.
-
Drowsiness.
-
Serious Side effects:
On taking this drug, when you come across any of the following symptoms, seek emergency medical attention.
-
Trouble breathing.
-
Severe drowsiness.
-
Allergic reactions (rare) such as,
-
Swelling of the face.
-
Rashes.
-
Swelling of the tongue and throat.
-
Also, Guaifenesin is reported to have side effects in kidneys, like stone formation.
The above-mentioned adverse effects are not all possible side effects, and others may occur. If you notice these symptoms, stop the drug and get medical attention.
What Are the Drug Interactions of Guaifenesin?
1. Certain drugs can change their effect when it interacts with other drugs or herbal products, increasing the risk of serious side effects and causing the medications to not work properly.
2. These drug interactions are not common, and the doctor or pharmacist prevents the interactions by close monitoring.
3. Diabetic patients - If you are diabetic and given Guaifenesin by the doctor or pharmacist, do not stop or change the drug because they will be aware of any possible drug interactions and monitor you for them.
4. Guaifenesin does not have any severe, mild, or moderate interactions with other drugs. Even though this drug does not have serious interactions with other drugs, tell your doctor or pharmacist about all the prescription, nonprescription and herbal tablets you are taking.
5. Guaifenesin is available with and without prescription so check your labels to ensure you are not taking more than one Guaifenesin product.
6. Always keep a list of all the medications you are having, and share with your doctor or pharmacist to know health questions or concerns.
What Are the Common Brand or Trade Names of Guaifenesin?
The common brand or trade names of Guaifenesin are,
-
Adult Tussin.
-
Mucinex.
-
Children’s Mucinex.
-
Good Neighbor Pharmacy Tussin.
-
Organidin NR.
-
Siltussin SA.
-
Tussin Chest.
-
Leader Mucus Relief.
-
Diabetic Tussin Expectorant.
-
Iophen NR.
-
Liqufruta.
-
Robitussin Chest Congestion.
-
Wal Tussin.
-
Bronchoril.
-
Mucus Relief.
-
Sunmark Tussin.
-
Kids-EEZE.
-
Bidex 400.
-
Children’s Mucus Relief.
-
MucaPlex.
-
Topcare Mucus Relief.
-
Equate Tussin.
-
Refenesen Chest Congestion Relief.












