Overview:
Romiplostim is a biological medication that can be used in adults and children with immune thrombocytopenia. It is specifically recommended for patients who do not show any improvements with other treatment methods. In addition, the drug can also be used for adults and children who underwent radiation therapy which caused ill effects on their bone marrow. The drug is manufactured from living organisms and is unavailable in biosimilar forms.
It is usually supplied as a powder that can be mixed in a solution. This solution can be injected subcutaneously. The most crucial information about Romiplostim is that it has been approved to increase platelet count caused by idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) and not other medical conditions. In addition, the drug stimulates the bone marrow to form blood platelets. Hence, it is also known as the thrombopoietin receptor agonist.
Information on Drug Development and Approval:
-
The US (United States) FDA (Food and Drug Administration) granted orphan drug designation to Romiplostim in 2003.
-
Finally, the drug was approved by the FDA on 22nd August 2008 as long-term therapy for managing chronic ITP in adults unresponsive to other treatment methods, including corticosteroids, immune globulins, splenectomy, or intravenous immunoglobulins.
Safety and Effectiveness of Romiplostim:
Several clinical studies have found Romiplostim safe and effective in managing ITP and reducing the risk of hemorrhage or bleeding in people diagnosed with ITP. A randomized and placebo-controlled trial was done for 24 weeks. The trial participants included patients who had received treatment for ITP. Romiplostim was administered to these patients to increase the blood platelet count and lower the bleeding risk.
Study Results - The results demonstrate that 88 % of the patients who took Romiplostim had an average blood platelet count of 50,000 during four or six weeks of study. However, 14 % of patients who took the placebo presented the same result.
How Often Should Patients Taking Romiplostim Undergo Laboratory Tests?
One must understand that Romiplostim does not permanently cure ITP or eliminate its cause. Instead, it reduces the risk of bleeding and increases the platelet count. Hence, people receiving Romiplostim therapy must get blood tests done every week. First, the doctor would often recommend the patient undergo a complete blood count, which provides a complete analysis of the levels of all blood cells, including platelets. Next, the doctor will adjust the dosage based on the patient's platelet count. Finally, the doctor might recommend a blood test every month when the patient's weekly platelet count is stable. In addition, the blood test will be recommended every week for a few weeks to ensure that the blood platelet levels are stable.
For Patients
Thrombocytopenia:
Thrombocytopenia is characterized by low blood count or the insufficient production of platelets by the bone marrow. Platelets are blood cells that play a vital role in blood clotting. They clump together and form a platelet plug to control bleeding. Thrombocytopenia is commonly observed in people with autoimmune disease or as a side effect of certain medications. It can affect people of any age group and cause mild or severe symptoms. In rare circumstances, the platelets drop to abnormally low levels resulting in severe internal bleeding. However, the patient must not worry as several treatment options are available.
Symptoms of Thrombocytopenia:
The primary signs and symptoms of thrombocytopenia are listed below:
-
Excess bruising.
-
Presence of multiple pinpoint reddish-purple spots on the superficial layers of the skin.
-
Persistent bleeding from cuts.
-
Gum or nasal bleeding.
-
Presence of blood in stools or urine.
-
Heavy menstrual flow.
-
Fatigue.
-
Enlargement of the spleen.
What Is Romiplostim?
Romiplostim is a prescription medication used to manage ITP in the following:
-
Adults who are diagnosed with ITP and are unresponsive to splenectomy (spleen removal surgery) or other treatment methods.
-
Children one year of age or above and battling with ITP for the past six months. Such children are unresponsive to other treatment procedures.
In addition, the drug can be used to treat newborns exposed to high radiation doses or acute radiation syndrome. However, little information is available regarding the effectiveness of Romiplostim in newborns. The drug cannot be used by people with myelodysplastic syndrome or MDS (a pre-cancerous condition). Romiplostim aims to maintain a person's platelet count to 50,000 per microliter of blood to reduce the risk of bleeding. However, the drug cannot make a person's platelet count normal. Nothing has been known about the safety and effectiveness of the drug in children under one year of age.
What Should the Patient Inform the Doctor Before Taking Romiplostim?
The patient must understand the benefits and risks of the drug before initiating the therapy. In addition, the patient must inform the doctor if they have:
-
Undergone spleen removal surgery.
-
Problems in the bone marrow, including MDS or blood cancer.
-
A blood clot.
-
Chronic liver disease.
-
Bleeding problems.
-
Pregnant or planning for the same. Romiplostim might harm the unborn baby.
-
Breastfed or planning for the same. Romiplostim might pass into the breast milk.
-
Taken prescription, over-the-counter, or herbal supplements or planning to take the same.
How Should the Patient Take Romiplostim?
-
Romiplostim is injected beneath the skin (subcutaneously) once every week.
-
It is administered by the doctor once weekly on exposure to high doses of radiation.
-
The doctor closely evaluates the Romiplostim dosage and platelet count during the therapy.
-
The platelet count will be monitored weekly, followed by the monthly evaluation.
-
The patient must inform the doctor if bleeding or bruising occurs during the therapy.
-
Patients who have missed their Romiplostim schedule can consult the doctor to schedule the next dose.
What Is the Most Important Information the Patient Should Know About Romiplostim?
Romiplostim can cause serious side effects:
-
Worsening of Leukemia or Other Pre-malignant Conditions - Romiplostim is specifically contraindicated in patients with MDS or other pre-cancerous conditions. It should only be used for ITP. Romiplostim can worsen the symptoms and cause acute leukemia in patients with MDS who consume the drug. In addition, it increases the risk of death due to leukemia.
-
Higher Chances of Blood Clots - The risk of blood clot formation is higher in patients whose platelet count becomes high during Romiplostim therapy. The complications become severe to the extent that blood clots migrate to the lungs, increasing the risk of heart attack or stroke. People with chronic liver disease must remain cautious as blood clot formation in the liver can cause liver damage.
-
Bone Marrow Problems - Romiplostim can increase reticulin levels in the bone marrow resulting in the formation of abnormal blood cells. Hence, patients with bone marrow problems must consult their doctors to avoid complications.
What Are the Side Effects of Romiplostim?
Romiplostim can cause serious side effects in a patient.
-
Dizziness.
-
Joint pain.
-
Speech difficulties.
-
Sleeping problems.
-
Muscle weakness or tenderness.
-
Pain in the legs or arms.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Indigestion.
-
Shoulder pain.
-
Bronchitis (inflammation of bronchioles).
-
Sinusitis (inflammation of sinuses).
-
Diarrhea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Cough.
-
Upper respiratory tract infections.
-
Pain in the mouth or pharynx.
The following side effects are seen in children one year of age or above:
-
Bruising.
-
Upper respiratory tract infections.
-
Pain in the mouth or pharynx.
For Doctors
Indications and Usage:
Immune Thrombocytopenia Patients:
Romiplostim is indicated for managing thrombocytopenia in the following:
-
Adults with ITP who show no significant improvements after treatment via other methods.
-
Pediatric patients with ITP for over six months had an insufficient response to immunoglobulins or splenectomy.
Hematopoietic Syndrome Patients:
Romiplostim can be used in adults and children with acute exposure to myelosuppressive doses of radiation.
Dosage and Administration:
Patients With Immune Thrombocytopenia:
The doctor must recommend the lowest dose of Romiplostim to maintain a platelet count of 50,000 per liter to reduce the risk of bleeding. The drug dose can be adjusted based on the patient's complete blood count (CBC) report. The prescribed dose might have a small volume (0.15 mL). Hence, it should be administered only with the syringe that contains 0.01 mL graduations. Discontinue Romiplostim if the platelet count does not elevate even after four weeks at the maximum daily dose of 10 mcg per kg. The doctor must obtain the CBC report every two weeks to analyze the blood's health.
Adult Patients With ITP:
The initial dose of Romiplostim is 1 mcg per kg. The patient's body weight must be considered before initiating the therapy. The drug dose must be adjusted for adults:
-
Platelet Count Less Than 50 X 10^9/L - Increase the dose by 1 mcg per kg.
-
Platelet Count Between 200 X 10^9 to 400 X 10^9/L - Decrease the dose by 1 mcg per kg.
-
Platelet Count More Than 400 X 10^9/L - Assess the patient's count weekly and start the therapy only after the count drops to 200 x 10^9/L.
Pediatric Patients With ITP:
The initial dose of Romiplostim is 1 mcg per kg. The child's body weight must be considered before initiating the therapy. In addition, the child's weight must be reassessed every 12 weeks. The drug dose must be adjusted for children:
-
Platelet Count Less Than 50 X 10^9/L - Increase the dose by 1 mcg per kg.
-
Platelet Count Between 200 X 10^9 to 400 X 10^9/L for Two Consecutive Weeks - Decrease the dose by 1 mcg per kg.
-
Platelet Count More Than 400 X 10^9/L - Assess the patient's count weekly and start the therapy only after the count drops to 200 x 10^9/L.
Patients With Hematopeotic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome:
For Adults and Children:
The recommended dosage of Romiplostim is 10 mcg per kg subcutaneously. The drug must be given immediately after suspected radiation exposure. The drug can be administered in such a situation, irrespective of CBC reports. The doctor must calculate the patient's absorbed radiation dose before giving the drug.
Preparation and Administration:
The doctor must follow the preparation and administration instructions to avoid errors. Romiplostim is administered subcutaneously using an aseptic technique. The drug is supplied in a single-dose sterile vial free of preservatives. The powder must be reconstituted and administered by a syringe. The calculation of the patient dose is done as follows:
Patient Dose (mcg) = Prescribed dose (mcg per kg) x weight (kg).
The table below describes the reconstitution and dilution of Romiplostim according to the vial content:
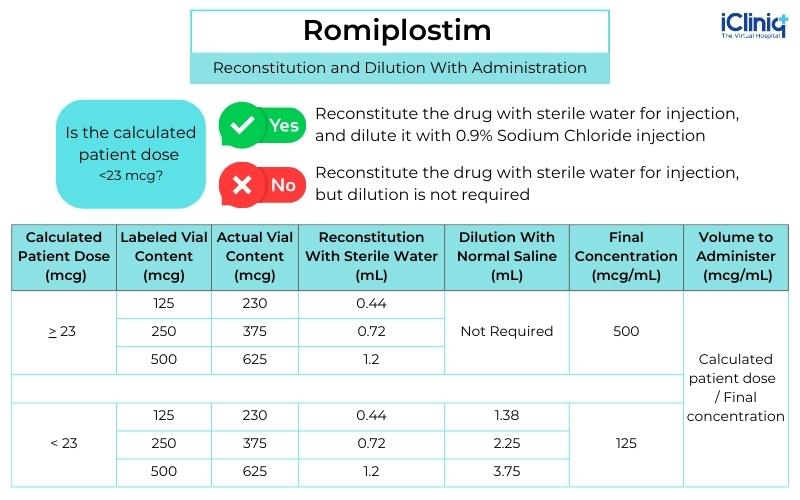
Swirl the vial and invert it to reconstitute the drug. However, avoid shaking it vigorously. The discoloration of the drug occurs in less than two minutes. The reconstituted solution appears clear and colorless. Hence, one must visually inspect the solution for discoloration or particulate matter. Discard the drug immediately if it contains particulate matter. Romiplostim must be reconstituted with sterile water for injection at the concentration of 500 mcg per mL. Avoid reconstituting the drug with bacteriostatic water for injection. For patients taking less than 23 mcg of the drug, additional dilution with 0.9 % Sodium chloride injection is required.
Administration of Prepared Romiplostim Solution:
Romiplostim should only be administered using a syringe with 0.01 mL graduations. The doctor must ensure that the syringe contains the exact dose.
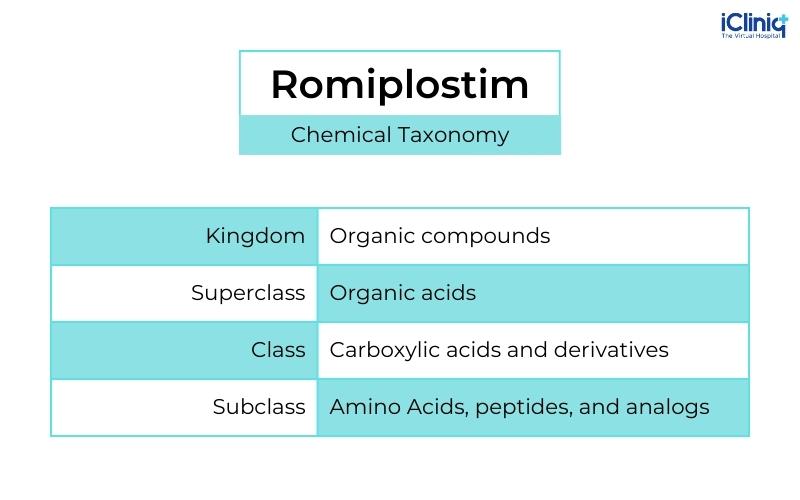
Chemical Taxonomy of Romiplostim:
Storage of Reconstituted Solution:
Reconstitute Romiplostim with Sterile Water for Injection, which has not been diluted and can remain in the vial at 25 degrees Celsius. The drug can be refrigerated from 2 to 8 degrees Celsius for 24 hours after reconstitution. The reconstituted water can be held in the syringe for four hours. However, protect the solution from sunlight and avoid shaking it.
Storage of Diluted Solution:
The drug reconstituted with sodium chloride injection can be dispensed in the syringe at 25 degrees Celsius in the original vial for not more than four hours before administration. Avoid shaking and protect the product from sunlight.
Dosage Forms and Strength:
Romiplostim is a lyophilized, sterile, or solid white powder available in 125 mcg, 250 mcg, or 500 mcg vials.
Warnings and Precautions:
-
Progression of Myelodysplastic Syndrome - The progression of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute myelogenous leukemia has been noticed in trials with Romiplostim. A randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled trial was done in adults with severe thrombocytopenia and low or intermediate-risk MDS. The trial was done for 58 weeks with a five-year long-term follow-up. Patients were randomized to Romiplostim or a placebo. The trial results demonstrated that 11.09 % of patients who took the placebo demonstrated worsening symptoms, whereas 11 % had disease progression after taking Romiplostim.
-
Thrombotic Complications - Thrombotic or thromboembolic complications occur due to elevated blood platelet count. However, no evidence exists to establish the relationship between maximum platelet count and the risk of thrombotic complications. Portal vein thrombosis has been reported in patients with chronic liver disease. People without myelosuppression on radiation exposure must avoid taking Romiplostim to avoid thrombotic complications.
-
Loss of Response to Romiplostim - Hyperresponsiveness or loss of response to Romiplostim is one of the situations. Hence, the patient's blood samples must be examined regularly to rule out other complications.
What Are Some of the Adverse Reactions of Romiplostim?
The following adverse reactions were reported during clinical trials and after the launch of Romiplostim in the market:
-
Myalgia.
-
Shoulder pain.
-
Pain in extremities.
-
Dizziness.
-
Paresthesia.
-
Insomnia.
-
Dyspepsia.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Ear infection.
-
Upper respiratory tract infections.
-
Sinusitis.
-
Gastroenteritis.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Pain in the mouth or pharynx.
-
Skin rashes.
-
Purpura.
-
Urticaria.
-
Contusion.
-
Peripheral swelling.
-
Pyrexia.
-
Anaphylaxis.
-
Erythromelalgia.
Description:
Romiplostim is primarily a thrombopoietin receptor agonist (TPO-RA). The drug belongs to the category of the TPO mimetic class, which is an Fc peptide fusion protein or peptibody. The molecule contains two identical single-chain subunits. Each chain contains human immunoglobulin IgG1 of the Fc domain. The chains are covalently linked at the C-terminus to thrombopoietin receptor binding domains. It does not have an amino acid sequence homologous to endogenous TPO. Romiplostim is synthesized by recombinant DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) technology in Escherichia coli (E.coli). It is a sterile, lyophilized, and white powder for subcutaneous injection.
Clinical Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action:
Romiplostim increases platelet production by binding and stimulating TPO receptors. This mechanism is analogous to endogenous TPO.
Pharmacodynamics:
Clinical studies demonstrate that Romiplostim causes a dose-dependent increase in platelet count. When a single subcutaneous dose of Romiplostim 1 to 10 mcg per kg was given in patients with ITP, the peak platelet count was 1.3 to 15 times greater than the baseline platelet counts over a period of two to three weeks. Seven out of eight patients who received six weekly doses of Romiplostim 1 mcg per kg had platelet counts above 50 x 10^9. In addition, the platelet count increased from 4.7 to 7.3 above baseline values with a single dose of 10 mcg per kg dose of Romiplostim.
Pharmacokinetics:
Patients With Immune Thrombocytopenia:
An extension study was done in adults with ITP who received weekly therapy of Romiplostim subcutaneously. According to the study, Romiplostim in the dose range of 3 to 15 mcg per kg had peak serum concentrations about seven to 50 hours after the dose. The half values of Romiplostim are in the range of one to 34 days. However, variations were observed in the serum concentrations, which did not correlate with the administered dose.
Non-Clinical Toxicology (Potential Adverse Effects of Drug):
-
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility: Nothing has been known about the carcinogenic potential of Romiplostim. The mutagenic potential of the drug has not been evaluated in humans. In addition, Romiplostim had no clinically significant effects on animal fertility.
Use in Specific Populations:
Pregnancy:
Romiplostim might cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant female. However, there is insufficient data regarding Romiplostim use in pregnant females and the risk of birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse fetal or maternal outcomes. In addition, animal studies reveal that Romiplostim can cross the placenta, causing adverse reactions like thrombocytosis or postimplantation loss.
Lactation:
There are no data about the presence of Romiplostim in human milk or its effects on the baby or milk secretion. Immunoglobulin G is present in human milk. However, lactating females must be counseled to avoid breastfeeding during Romiplostim therapy.
Pediatric Use:
Two randomized and placebo-controlled studies have been done in children one year of age or above for six months to establish Romiplostim's safety, effectiveness, and pharmacokinetics. However, nothing has been known about the safety and efficacy of the drug in patients below one year of age. In addition, efficacy studies have not been conducted on children with myelodysplastic syndrome and acute radiation exposure.
Geriatric Use:
Of the 271 patients who received Romiplostim, 20 % were above 55, whereas 10 % were above 75. However, no clinically significant differences were noted between young and old patients in placebo-controlled studies. Hence, dose adjustments must be made cautiously in elderly patients to avoid complications.
Clinical Trial:
Adults With Immune Thrombocytopenia:
The safety and efficacy of Romiplostim were observed in two randomized placebo-controlled studies. During the studies, patients with a platelet count greater than or equal to 30 x 10^9 were randomized to Romiplostim or a placebo for 24 weeks. The median time for both studies was 2.1 years and eight years, respectively. The first study evaluated patients who had not undergone splenectomy, whereas the other evaluated patients who had undergone splenectomy. According to the trial results, profuse bleeding was reported in 6 % of patients who took Romiplostim, whereas 10 % of those who took the placebo.












