Overview:
Fluoroquinolones are a class of antibiotics with a broad spectrum of action and are used to treat various bacterial infections, specifically urinary tract infections and respiratory tract infections. The antibiotics in this class include Ciprofloxacin, Levofloxacin, Ofloxacin, Gemifloxacin, Norfloxacin, and Moxifloxacin. These drugs are commonly available in oral tablets, eye or ear drops, and injections (a doctor can only administer them). Fluoroquinolones have a bactericidal action (kills the infection-causing bacteria). Avoid using the drugs in this class if there is a previous history of allergy to the drugs or any of their components. Seek medical help if unusual symptoms develop following administration.
Drug Group:
Fluoroquinolones are the class of antibiotics that come under the broad classification of antimicrobials. They are further divided into two groups:
-
Older Fluoroquinolones: Ofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin, and Norfloxacin.
-
Newer Fluoroquinolones: Moxifloxacin, Levofloxacin, and Gemifloxacin.
The newer Fluoroquinolones have a considerably strong effect against infections caused by bacterial species of Streptococci and some anaerobic bacteria.
Do not use Fluoroquinolones or any drug without talking to a healthcare professional first.
What Are Fluoroquinolones Used For?
Fluoroquinolones are the commonly used antibiotics for infections of the respiratory tract and urinary tract, mainly:
-
Acute sinusitis (inflammation of the sinus).
-
Acute bronchitis (inflammation of the lungs).
-
Urinary tract infections.
-
Bacterial diarrhea (frequent loose or watery stools).
However, it is also used to treat individuals who are not responding to other antibiotics (as confirmed by the doctor).
Fluoroquinolones are ineffective against infections caused by viruses or other helminthic infections. Avoid unnecessary usage of antibiotics unless prescribed by a doctor, as it may lead to the development of resistance (antibiotics may become ineffective in the future).
How Do Fluoroquinolones Work?
The general mechanism by which Fluoroquinolones act is by inhibiting the enzyme DNA gyrase.
Enzymes are biological catalysts that carry out various reactions in the body. DNA gyrase is an enzyme that is involved in the replication of DNA (genetic material). Now, replication is crucial for the survival of the bacteria, and by inhibiting this enzyme, replication is stopped or hindered. This will block DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) synthesis, ultimately leading to the death of the disease-causing bacteria.
Onset of Action:
The onset and duration of action are different for the different antibiotics under this class. However, here are some general considerations:
-
Absorption: Upon oral administration, the absorption (reaching of the drug into the blood circulation) of Fluoroquinolones is greatly reduced in the presence of food containing magnesium, calcium, iron, and zinc.
-
Excretion: Most Fluoroquinolones are excreted in the urine.
Habit-Forming:
There have been no reports of a habit-forming tendency in people taking Fluoroquinolones.
Expiry Date:
Avoid taking this medicine after it expires. The date of expiry will be provided on the back of the pack.
What Is the Dosage of Fluoroquinolones?
For bacterial infections, the doctor will start with a standard dose and increase or decrease it based on the response to the therapy given. Make sure that the doctor is notified of how well the drug works and if any side effects are experienced.
The general dosing is as follows:
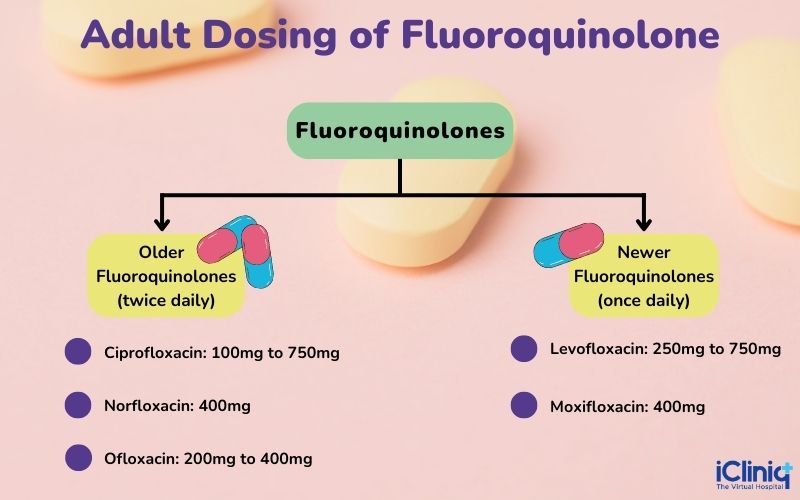
-
The once-daily dosing is followed for the extended-release tablets of Ciprofloxacin.
-
Fluoroquinolones are not recommended for use in children as it has been reported to cause problems in bone development in animal studies.
-
For the elderly and individuals with liver and kidney diseases, dose adjustment is required and will be based on various other considerations. The doctor will prescribe this. Follow the instructions carefully.
How to Use Fluoroquinolones?
Fluoroquinolones are available as tablets, eye/ear drops, suspensions, and injections.
Tablets:
-
It is preferable to take these drugs with a full glass of water. Increasing the water intake can help reduce some of the side effects of Ciprofloxacin and Norfloxacin.
-
Avoid taking Enoxacin and Norfloxacin on an empty stomach. Others may be taken on an empty stomach or with meals.
-
Do not take Ciprofloxacin with calcium-containing food or drinks (dairy products, juices).
Eye or Ear Drops:
Use as instructed by the doctor.
General Instructions:
-
Take the medications at regular intervals as instructed.
-
Even if the patient starts to feel better after a few days, continue taking the medication for the full course of therapy to help clear up the infection completely. The symptoms can come back if the medication is stopped abruptly.
Missed Dose:
Take the missed dose of this medication as soon as it is recalled. This will make it easier to maintain a steady level of medication in the blood or urine. If the next dose is close, skip the missed one and resume the regular dosing regimen. Avoid doubling doses.
Overdose:
In case of overdose and usual symptoms arise, seek emergency help or contact the poison control center immediately.
What Are the Contraindications of Fluoroquinolones?
The use of Fluoroquinolones is contraindicated (use strictly unadvised due to harmful effects of the drug) in the following conditions:
-
History of photosensitivity (sensitivity towards light).
-
Known hypersensitivity to drugs or their components.
-
Pregnancy.
What Are the Drug Warnings and Precautions?
Inform the doctor if there is a history of any of the following conditions:
-
Allergy: Inform if there is a previous history of allergy to the drugs or any of their components.
-
Pregnancy: Avoid use in pregnancy, as the drugs of this class can adversely affect the fetus. Talk to the doctor if the patient is pregnant or intends to get pregnant.
-
Breastfeeding: Fluoroquinolones pass through the breast milk. Hence, use is restricted for nursing mothers.
-
Infants and Children: Not recommended for treating infections in children under 18 years of age.
-
Heart Diseases: Inform the physician if there is a history of irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
-
Tendonitis: It is the inflammation of tendons. Fluoroquinolones can worsen this condition.
-
Diabetes: Fluoroquinolones can cause alterations in blood sugar levels. Monitoring is required while in therapy.
-
Seizures: Fluoroquinolones can worsen seizure conditions. Talk to the doctor before starting the medication.
-
Liver or Kidney Diseases: Dose adjustment may be required.
-
Myasthenia Gravis: This is a muscle disorder. Fluoroquinolones can worsen this condition and can cause weakness in the lung muscles. Avoid usage.
Note: Fluoroquinolones, especially Sparfloxacin, have been reported to cause increased sensitivity to sunlight, and even short-term exposure can result in itching, sunburns, rashes, or discoloration. While on therapy with this drug, ensure that:
-
Exposure to direct sunlight is reduced to the maximum.
-
Sunblock creams are applied, or protective clothing is worn.
-
Avoid tanning booths or sunlamps.
What Are the Side Effects of Fluoroquinolones?
The common side effects of Fluoroquinolones are as follows:
-
Abdominal discomfort.
-
Mild diarrhea.
-
Dizziness.
-
Anxiety.
-
Difficulty sleeping.
-
Vaginal pain and discharge.
-
Mood swings.
-
Shortness of breath.
These symptoms are minor and will go away on their own. However, if they become severe or more persistent, seek medical help.
Some serious side effects include
-
Loss of consciousness or irregular heartbeat (Sparfloxacin, Lomefloxacin).
-
Bloating.
-
Headache.
-
Blurred vision.
-
An allergic reaction includes symptoms like swelling of the face, and mouth, extreme rash, and itching.
Report any signs of these severe side effects to the doctor or a healthcare professional and seek medical help immediately.
What Are the Interactions of Fluoroquinolones?
Most drugs interact with other drugs, food, beverages, or supplements. These interactions can result in unwanted side effects. The common interactions of Fluoroquinolones are as listed:
1. With Other Drugs:
-
Aminophylline.
-
Theophylline.
-
Ciprofloxacin.
-
Norfloxacin.
-
Amiodarone.
-
Bepridil.
-
Cisapride.
-
Erythromycin.
-
Pentamidine.
-
Caffeine.
-
Chlorpromazine.
-
Procainamide.
-
Phenytoin.
-
Quinidine.
-
Sotalol.
-
Terfenadine.
-
Antidepressants.
-
Warfarin.
-
Antacids.
-
Iron supplements.
-
Sucralfate.
This list does not cover all the drug interactions. It may be specific for each drug. Check with the doctor or pharmacist for details on the interacting drugs.
2. With Alcohol: Fluoroquinolones do not interact with alcohol. However, concomitant intake of alcohol may increase the incidence of side effects like nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain. Drinking in moderation is preferred while on this therapy.
3. With Food: Avoid food containing calcium, iron, zinc, magnesium, and aluminum.












