Overview
Tezepelumab is a human monoclonal antibody that blocks thymic stromal lymphopoietin, an epithelial cell-derived cytokine implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma. It is used as an adjunct therapy in the maintenance phase of asthma.
What Are the Indications and Limitations of Tezepelumab?
-
It is usually recommended in adult asthmatic patients.
-
It is also used to treat young children aged 12 years and above with severe asthma.
-
It should not be used for status asthmaticus patients.
-
It is not advised for acute bronchospasm relief.
What Is the Recommended Dosage of Tezepelumab and How Is It Administered?
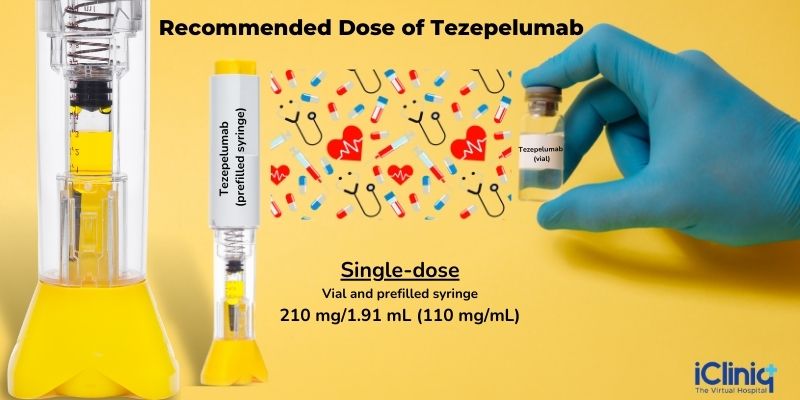
Glass Vial - The recommended dosage of Tezepelumab is 210 mg/1.91 mL solution.
Prefilled Syringe - It contains a single dose of Tezepelumab 210 mg/1.91 mL (110 mg/mL).
-
It is administered through a subcutaneous route once every four weeks.
-
It is injected in the thigh, arm, or near the abdomen.
-
It should be avoided in damaged skin areas like bruises or erythematous skin.
-
For a single-dose pre-filled syringe, the needle cover should not be removed until ready to inject. Avoid touching the needle safety guard.
-
Hold the body of the syringe and remove it from the tray.
-
Avoid using plungers. Do not remove the entrapment of air bubbles before injecting.
-
Remove the cover only during administration. A small amount of liquid near the needle tip is present.
-
The needle is directed at a 45° angulation into the subcutaneous tissue.
-
The medication is injected fully in between the needle guard activation.
-
After administration of the dose, apply pressure and remove the needle.
How Is Tezepelumab Prepared Before the Administration Through the Subcutaneous Route?
-
Tezepelumab is administered by a medical professional. One pre-filled syringe contains one dose of Tezepelumab.
-
It is kept in the refrigerator. It is administered after allowing it to cool to room temperature for an hour.
-
It should not be kept inside the refrigerator after taking it out.
-
It should be used within a month after taking it from the refrigerator.
-
There will be a slight discoloration after taking it out from the refrigerator.
-
Dispose of the needle in an appropriate container.
What Are the Contraindications of Tezepelumab?
-
Hypersensitivity Reactions - Some patients get adverse effects like hypersensitivity, rashes in the skin, and conjunctivitis in the eyes. It occurs after a few hours of administration. Some patients get these reactions after many days. Your medical professional decides whether to continue or discontinue the Tezepelumab drug depending on the benefits and adverse effects of the individual patient.
-
Acute Asthma Symptoms - Tezepelumab should not be prescribed for acute asthma or acute exacerbations. Patients should consult an asthma specialist if asthma cannot be controlled.
-
The Risk Associated While Stopping Corticosteroids - Drastic reduction of systemic or inhaled corticosteroids can result in adverse effects. To avoid withdrawal symptoms, consult your medical professional and reduce the dosage gradually.
-
Parasitic Infection - It is also known as helminth infections. Patients diagnosed with helminth infections were not included in the clinical trials. So the influence of Tezepelumab in patients with helminth infections is still under research. Many medical professionals prescribe other medications for helminth infections. If the patient did not respond the medications are discontinued and treated with Tezepelumab.
-
Live Attenuated Vaccines - Interaction of Tezepelumab and live attenuated vaccines are not evaluated. However, live attenuated vaccines should not be administered to patients taking Tezepelumab.
Clinical Trial Experience:
The external conditions vary for each drug in clinical trials. So it cannot be compared directly. A study was conducted among 665 adults and children above 12 years of age with asthma. They were administered Tezepelumab 210 mg once daily through a subcutaneous route for approximately four weeks. Placebo-controlled trials were continued for about 52 weeks. The patients reported with pharyngitis due to bacterial or viral infection, arthralgia, and back pain. Also, 3.3 % of patients had swelling, pain, or erythema near the injection site.
Immunogenicity:
Therapeutic proteins of Tezepelumab are highly potential for immunogenicity. The antibodies are detected for sensitivity and specificity. The incidence of neutralizing antibodies is influenced by various factors such as methodology, handling of collected samples, time in which the sample is collected, medications for another systemic disease, and other underlying medical conditions.
Another study conducted among 601 patients detected anti-drug antibodies. The study period was about 48 to 52 weeks. Some patients developed emergent antibodies in response to the treatment, while few had neutralizing antibodies. The titer values appear low and did not significantly impact the efficacy, pharmacokinetics, or pharmacodynamics of the drug.
Drug Interactions - A study was not conducted about the interaction between Tezepelumab and other medications.
Use of Tezepelumab in Specific Populations
It includes pregnancy, fetal risk, lactation, pediatric, and geriatric use;
-
Pregnancy - Available data is not sufficient to determine the risk associated with pregnant women. Studies evaluate the risk of congenital defects, miscarriage, abortion, or adverse reactions during maternity. Monoclonal antibodies were detected during the third trimester. A study was conducted on monkeys to evaluate the harmful effects of Tezepelumab during the pre and post-natal development of the fetus. So an intravenous administration of Tezepelumab 168 times more than the recommended dosage of 210 mg was performed. But there were no abrupt reactions. In the United States, 2 % to 4 % and 15 % to 20 % of pregnant women were observed with congenital defects and miscarriage, respectively. Administering Tezepelumab before the third trimester may result in potential side effects. So the medical professional should prescribe Tezepelumab in the third trimester only if the mother requires medical attention for asthma exacerbation.
-
Fetal Risk - Pregnant women with asthma must be carefully monitored, and the management is done accordingly. If the dosage of Tezepelumab goes beyond the optimal level, it results in preeclampsia and gestational-related disorders in the mother. It also causes prematurity and low birth weight in babies. A study was conducted on pregnant monkeys administered with Tezepelumab from GD20 to GD22 during organogenesis once a week. It continued till the third trimester. The maternal intravenous doses were increased up to 300 mg/kg/week. No developmental disorders were observed in the infants up to 6.5 months of age. Since the Tezepelumab drug can cross the placenta, the serum concentration of the drug was 0.5 to 6.7-fold higher in fetuses than in maternal monkeys. The molecular weight of Tezepelumab is more than 147,000 Da. Therefore, when administered an overdose, there is a chance of Tezepelumab crossing the placenta and affecting the fetus.
-
Lactation - The available data are insufficient to determine the presence of Tezepelumab in human milk during milk production or breastfeeding the infants. Tezepelumab-ekko was observed in breastfeeding monkeys following the administration of the Tezepelumab drug. Developmental and health benefits of breastfed milk are related to the requirement of Tezepelumab for the management of asthma in mothers, adverse reactions in the breastfed infant, or other underlying medical conditions in mothers. A study on monkeys to determine prenatal and postnatal development in monkeys indicated 0.5 % Tezepelumab in the serum after intravenous administration. It was continued up to 300 mg/kg/week (168 times higher than the required dose in humans). So there is a mismatch in the presence of Tezepelumab-ekko in the monkey's milk compared to the human's milk. The effect of Tezepelumab on breastfed infants, lactation, and maternal IgG is yet to be studied. However, the mother's emergency requirement of Tezepelumab is considered a vital factor along with the potential side effects on infants.
-
Pediatric Use - Safety and efficacy of Tezepelumab to manage severe asthma in children 12 years and above were studied in 82 patients ranging from 12 to 17 years. They were administered with 210 mg Tezepelumab through a subcutaneous route once every month. The placebo effect and the improvement of asthma exacerbation were studied specifically. However, the pharmacodynamics in pediatric patients were similar to studies conducted in other populations. The safety and efficacy of Tezepelumab in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age were not determined. When compared to placebo, the asthma exacerbation is improved in the patients who were studied in NAVIGATOR after a year. FEV1 (0.17 L; 95 % CI -0.01,0.35) with a ratio of 0.7; 95 % CI 0.3,1.5) were observed in the pediatric patients with exacerbation.
-
Geriatric Use - About 665 elderly patients prone to asthma are treated with Tezepelumab during the clinical study. Among them, 18 % of the patients, or 119 patients, were older than 65 years of age.
For Doctors:
Description:
Tezepelumab is an immunoglobulin G2 gamma. It is activated in the Chinese hamster ovary cells using recombinant DNA technology. The molecular weight of Tezepelumab-ekko is 147 kDa. The injection used was sterile and had no preservatives. It appears as a clear, colorless, or light yellow-colored solution. The single dose of Tezepelumab is available as a vial or prefilled syringe. Each dose contains a 1.91 mL solution (210 mg Tezepelumab, 3 mg glacial acetic acid, 50 mg L-Proline, 0.20 mg of Polysorbate, trace amount of sodium hydroxide, and water). pH was recorded as 5.2.
Clinical Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action:
Tezepelumab-ekko binds to the antibody present in the human with a dissociation constant of 15.8 pM. It interferes with the binding of heterodimeric receptors. Tezepelumab-ekko is a cytokine obtained from epithelial cells. It occupies the inflammatory reactions produced during asthma exacerbations.
Inflammatory reactions of asthma take place in the bronchi or airways. Cells involved in inflammation include mast cells, white blood cells, and ILC2 cells. Mediators like histamines, leukotrienes, and cytokines are also involved. Blocking the receptors reduces the markers and inflammatory mediators, including IgE, IL-5, and IL-13. The mechanism of Tezepelumab is not thoroughly studied.
Pharmacodynamics:
Administration of Tezepelumab 210 mg in the subcutaneous route for a month (n=528) showed a decreased number of eosinophils, IL-5, and IL-13 compared with clinical trials (n=531) after drug administration for two weeks followed by the administration for 52 weeks. Tezepelumab resulted in a slow and step-by-step reduction of serum IgE for the entire 52 weeks. Similar results were also observed in PATHWAY studies.
Pharmacokinetics:
To determine the pharmacokinetics, 2.1 mg to 420 mg (twice the recommended dose) of Tezepelumab-ekko were administered. It is given in a single dose. The dosing regimen was changed once every 4 weeks. A steady state was observed after 12 weeks with a Ctrough of 1.86-fold.
-
Absorption - After drug administration through the subcutaneous route, serum concentration of Tezepelumab reached a maximum in seven to 10 days. Bioavailability was about 77 % in the analysis. It remains the same for different injection sites like the abdomen, thigh, or arm.
-
Distribution - Pharmacokinetics was recorded in population analysis. For an elderly patient above 65 years of age, central and peripheral distribution was found to be 3.9 L and 2.2 L, respectively.
-
Elimination - Tezepelumab-ekko is cleared by intracellular catabolism. Target-mediated clearance does not take place in Tezepelumab-ekko. The recorded result for clearance was 0.17 L/d for an individual weighing above 70 kg. The half-life of Tezepelumab is 26 days.
-
Metabolism - Proteolytic enzymes break down the Tezepelumab and distribute the drug widely. It is not degraded by hepatic enzymes.
-
Age - Individuals between the age of 12 to 80 years had no impact during the pharmacokinetic analysis.
-
Sex - No significant changes were determined in male and female patients.
-
Race - White, Black, or Asian people had no clinical effects of Tezepelumab.
-
Body Weight - Less drug exposure was associated with increased body weight. But population analysis showed that body weight is not related to the safety and efficacy of Tezepelumab. So the dosage need not be modified according to the body weight.
-
Patients With Renal Impairment - There are no proven clinical studies for determining the influence of Tezepelumab in patients with renal impairment. Population analysis was performed among 320 people (23 % subjects) observed with mild renal impairment and 38 individuals (3 % subjects) observed with moderate renal impairment. Individuals with mild renal impairment had a creatinine clearance of 60 to 89 mL/min. The individuals with moderate renal impairment had a creatinine clearance of 30 to 59 mL/min. People with normal kidney function had an average creatinine clearance of 90 mL/min or more. The individuals with severe renal impairment had a creatinine clearance of less than 30 mL/min.
-
Patients With Hepatic Impairment - Interaction of Tezepelumab-ekko in individuals with hepatic impairment was not studied clinically. Since hepatic enzymes are not involved in the metabolism, the hepatic impairment does not affect the clearance of Tezepelumab.
-
Clinical Studies on Drug Interactions - During the population analysis, studies were conducted to determine the interaction of Tezepelumab and other medications used to treat asthma. It includes the drug administered through oral or inhalation routes such as Theophylline, corticosteroids, and leukotriene antagonists. These drugs did not influence the clearance of Tezepelumab-ekko.
Nonclinical Toxicology:
-
Carcinogenesis - Studies conducted in monkeys could not determine the carcinogenic effect of Tezepelumab-ekko. Malignant effects of antibodies interfering with the thymic stromal lymphopoietin are not determined.
-
Mutagenesis - Mutation of human cells did not occur after the administration of a recommended dose of Tezepelumab. However, increasing the dose in monkeys during the animal study produced mutagenesis.
-
Reduced Fertility - Histopathological studies were conducted in sexually matured monkeys to determine the effect of Tezepelumab on the reproductive organs. There were no adverse effects on male and female fertility, menstrual cycle, and semen analysis. The cynomolgus monkeys were administered 300 mg/kg/week of Tezepelumab through subcutaneous injection for about 26 weeks. It is 134 times more than the recommended dose for humans.
Clinical Studies:
The efficacy of Tezepelumab is determined in randomized trials, double-blind studies, parallel groups, and placebo-controlled trials for about 52 weeks. It comprised 1610 pediatric patients 12 years and above with severe asthma. PATHWAY trials were conducted on 550 adult patients with asthma for 52 weeks. They received Tezepelumab-ekko 70 mg once every four weeks, Tezepelumab 210 mg once every four weeks through subcutaneous injection, or Tezepelumab-ekko 280 mg once every two weeks. All those patients had a history of asthma exacerbations twice and required management using oral or injectable corticosteroids or patients with a history of one asthma exacerbation and hospitalization in the past year.
NAVIGATOR trials were conducted on 1060 patients (both adult and pediatric patients above 12 years of age) with asthma exacerbations and received Tezepelumab 210 mg through a subcutaneous route once every four weeks or a placebo once every four weeks. The patients are noted with a history of two asthma attacks receiving oral or injectable corticosteroids or being hospitalized in the past year.
In PATHWAY and NAVIGATOR trials, screening and lung function tests are conducted. The forced expiratory volume (FEV1) results are predicted to be 80 % in adults and 90 % in adolescents. These patients were managed with medium or high-dose inhaled corticosteroids, including an asthma controller and oral corticosteroids. Usual medications for controlling asthma were continued throughout the trials. Both trials do not require the baseline of eosinophils and FeNO (fractional exhaled nitric oxide).
Exacerbations:
Asthma exacerbations indicate the worsening of asthmatic episodes in individuals using oral or injectable corticosteroids for three days or a single dose of corticosteroid injection or the patients admitted to the emergency room for treating severe asthma attacks. The patients significantly reduced exacerbations and hospitalizations after the administration of Tezepelumab.
PATHWAY and NAVIGATOR trials showed reduced asthma exacerbation rates compared to placebo.
Lung Function:
Change from FEV1 was examined, and there is an improvement after administration of Tezepelumab for two weeks and continued till 52 weeks.
Clinical Outcomes in Asthmatic Patients:
Standardized asthma quality of life was determined using PATHWAY and NAVIGATOR. More pediatric patients treated with Tezepelumab had an improvement in ACQ-6 and AQLQ (S)+12. The score was obtained as 0.5 or more during the clinical trials. NAVIGATOR analysis for Tezepelumab showed ACQ-6 had an improvement up to 86 %, but the placebo had only 77 %. AQLQ (S)+12 for Tezepelumab was 78 % but the placebo was 72 %. These results were obtained from PATHWAY.
Additional Trial:
A clinical trial is conducted on randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled subjects to evaluate the Tezepelumab 210 mg effect through a subcutaneous route once every four weeks after evaluating the OCS. The trial comprised 150 patients affected by severe asthma and required OCS (7.5 mg to 30 mg) treatment daily as an adjunct therapy to high-dose ICS and long-acting Beta-agonist. In the 48th week, the final OCS dose was observed as a 90 % reduction, 75 % to 90 % reduction, 50 % to 75 % reduction, 0 to 50 % reduction, or no change during the maintenance phase of asthma. Tezepelumab did not participate in the reduction of the OCS dose when compared to the placebo (OR = 1.28 and 95 % CI 0.69, 2.35).
Tezepelumab Supply:
Tezepelumab-ekko injection appears as an opalescent solution. It is available in a single-dose syringe with a needle measuring 27-gauge half inch with a cap. The stopper of the vial and cap is not made of natural rubber latex.
Recommended Dose of Tezepelumab:
Storage:
Tezepelumab is refrigerated at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). It can also be stored at room temperature of 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C) for a month. If the Tezepelumab has attained room temperature, do not restore it to the refrigerator. If the Tezepelumab is taken from the refrigerator, use it within a month or discard it. Do not replace the original carton of the Tezepelumab drug. It prevents light access into the carton. The carton should not be freezed. Avoid shaking the Tezepelumab drug. Avoid excess heat exposure to the Tezepelumab drug.
Patient Counseling Information
Ask the patient to gain knowledge about the FDA-approved information on patient labeling.
-
Hypersensitivity Reactions - Inform the patient about the rashes and allergies caused by long-term Tezepelumab. Ask the patient to consult their medical professional if they undergo any adverse effects or symptoms of the Tezepelumab drug.
-
Worsens Asthma - The patients should stop using Tezepelumab if it worsens asthma after the initiation of treatment.
-
Corticosteroids - The patients taking corticosteroids must be carefully monitored.
-
Vaccine Administration - Patients should not take potential vaccinations during the treatment phase with Tezepelumab. Ask them to inform their physician.
For patients:
What is Tezepelumab?
-
The physician prescribes Tezepelumab-ekko injection as an adjunct therapy to other medications used to control asthma in pediatric patients above 12. Tezepelumab is used when other medications cannot control asthma.
-
Tezepelumab prevents exacerbations or severe asthmatic attacks. It also helps to improve the breathing mechanism.
-
Tezepelumab cannot be used to manage the acute or sudden onset of breathing issues. Inform your physician about the prognosis or adverse effects after initiating the treatment with Tezepelumab.
-
The safety and efficacy of Tezepelumab in children under 12 years of age are not proven.
Avoid Tezepelumab Through Subcutaneous Route:
Patients should avoid Tezepelumab if they are allergic to Tezepelumab itself or the ingredients of Tezepelumab. Patients should observe the ingredients carefully and clear their doubts regarding Tezepelumab injection.
What Are the Instructions to Follow Before Receiving a Tezepelumab Injection Through a Subcutaneous Route?
Before obtaining a Tezepelumab injection through a subcutaneous route, inform your medical professional about,
-
Your underlying systemic diseases and medical conditions.
-
Medicines, vitamins, herbal extracts, mineral supplements, or vitamin supplements that are taken daily. You should include both the prescribed drugs and over-the-counter (OTC) drugs.
-
Any history of surgery or cardiac issues.
-
History of hypersensitivity or severe allergic reaction for Tezepelumab injection.
-
Recent history of severe parasitic or helminth infection for many days.
-
Recent history of receiving live attenuated vaccines or scheduled for receiving live attenuated vaccines. Tezepelumab should not be co-administered with live attenuated vaccines.
-
If you are pregnant, doubt about pregnancy, or have a plan to become pregnant. However, the Tezepelumab injection is not proven harmless for unborn or newborn babies.
-
Suppose you are breastfeeding or have a plan to breastfeed the newborn. However, there is no precise study about transferring Tezepelumab dosage to the newborn through breast milk. Discuss with your medical professional about breastfeeding and the best time for breastfeeding after receiving the Tezepelumab dose.
-
Avoid changing or stopping the corticosteroids without the knowledge of your medical professional. Follow the instructions given by your medical professional.
What Is the Procedure for Receiving Tezepelumab Injection Through a Subcutaneous Route?
-
Your medical professional will deliver a Tezepelumab injection in the healthcare or hospital setting.
-
Tezepelumab is injected under the skin through the subcutaneous tissue. It is administered once every four weeks.
-
Follow the appointment schedule every month for receiving the complete dose of Tezepelumab.
-
If you missed an appointment with your medical professional, ask him or her to reschedule your next appointment to receive a Tezepelumab injection.
What Are the Possible Adverse Effects Caused by Tezepelumab Injection?
Tezepelumab causes serious health issues. It includes the following;
-
Severe allergy or hypersensitivity.
-
Long-term use of Tezepelumab injection results in breathing issues.
-
Skin rashes with redness.
-
Hives.
-
Itching, swelling, or inflammation of the skin around the eyes.
Consult your physician if you notice any of the above adverse effects.
The most common adverse effects observed after the administration of the Tezepelumab dose include;
-
Pharyngitis (inflamed pharynx).
-
Arthralgia or joint pain.
-
Back pain.
All the adverse effects need not occur in every patient. Always seek medical advice from medical professionals and report the adverse effects to the FDA.
General Information About the Efficacy and Safety of Tezepelumab:
Your medical professional may prescribe Tezepelumab for other medical conditions that are not mentioned here, depending on the underlying systemic diseases. You can ask the pharmacist or medical professional to read more information about Tezepelumab provided for health professionals.
What Are the Ingredients Present in Tezepelumab Injection?
Both active and inactive ingredients are present in the Tezepelumab drug.
-
Active Ingredient - Tezepelumab-ekko is the only active ingredient present in the Tezepelumab injection.
-
Inactive Ingredient - Various inactive ingredients in the Tezepelumab injection include glacial acetic acid, L-Proline, Polysorbate 80, trace amounts of sodium hydroxide, and water.













