Introduction:
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is considered the most common type of heart disease. Coronary arteries are the major vessels supplying the heart. CAD occurs primarily when the arteries of the heart get blocked, resulting in decreased or insufficient blood supply. This block in the arteries is also known as plaque. The plaque gradually builds over time and is composed mainly of fat (cholesterol) and calcium.
Initially, the plaque is a soft material; gradually, as they deposit in the blood vessels, they get calcified and occlude the blood vessel either completely or partially. This is also known as atherosclerosis. This would impede the blood flow, and the heart would be deprived of oxygen-rich blood. This would result in chest pain, shortness of breath, or a complete block that may also cause a heart attack.
Another consequence of the plaque buildup would be the rupture of the plaque resulting in a blood clot. This clot can block the blood flow resulting in heart attack, unstable angina, or myocardial infarction. Hence early detection of this plaque can be helpful in the management of CAD.
What Is a Coronary Calcium Scan?
A coronary calcium scan, also known as a heart scan, is a specialized imaging scan that uses computed tomography (CT) to evaluate the calcified plaque in the coronary arteries of the heart. It is a non-invasive procedure used to determine the presence, extent, and site of the calcified plaque. Based on the results, the doctors can advise medications, lifestyle changes, or further interventions to prevent any complications.
What Are the Uses of Coronary Calcium Scans?
A coronary calcium scan is mostly indicated in low or medium-risk patients. It is done so that individuals diagnosed with moderate risk can make certain lifestyle changes to prevent coronary artery disease and its consequences. The risk factors associated with CAD are as mentioned below:
-
Patients with a familial history of heart disease.
-
Patients with a history of smoking and drinking alcohol.
-
Patients with a history of high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
-
Patients with a sedentary lifestyle.
What Are the Instructions Before the Procedure?
-
Patients will be advised to avoid caffeine for 4 hours before the procedure.
-
Patients would be asked to refrain from smoking for 4 hours before the procedure.
-
Patients should wear loose, comfortable clothes while going for the procedure.
-
They should remove all metallic accessories and jewelry.
-
Eyeglasses, hearing aids, body piercings, removable dental appliances, and wallets should be removed before the procedure.
-
Female patients will be advised to remove bras with the metal underwire.
-
Ladies should inform the doctor if they are pregnant or could be pregnant.
-
The patient should keep the doctor informed regarding all the prescription medicines, supplements, and over-the-counter medications taken by them.
How Is the Procedure Done?
-
A coronary calcium scan is done on an outpatient basis. The entire procedure would take 10 to 15 minutes.
-
The patient will be given a hospital gown to wear before the procedure.
-
Three small areas on the chest will be shaved, cleaned, and sterilized. Small sticky electrodes will be stuck on these areas in the chest and will be connected to the electrocardiograph machine (ECG). This helps the doctor to analyze the heart activity and facilitate the process of taking the images when the heart is relaxed and not contracting.
-
The patient will be made to lie on a table that slides into the CT scanning machine. The CT scanner is a hollow tunnel-like device.
-
Patients might be given medication that could slow down heart activity, thus enabling better images.
-
Patients will be asked to hold their breath for a few seconds when the images are being acquired.
-
These images are then processed in the computer and visible as two-dimensional images.
How Are the Results Interpreted?
The results are most likely available on the same day or the next day. It is broadly described as a negative cardiac CT scan and a positive cardiac CT scan.
-
Negative Scan: Absence of any calcification suggestive of minimal or no CAD.
-
Positive Scan: Calcifications are present suggestive of CAD irrespective of the presence or absence of any signs and symptoms.
The calcium present is quantified as the calcium score, also known as the Agatston score. The scoring is as given below:
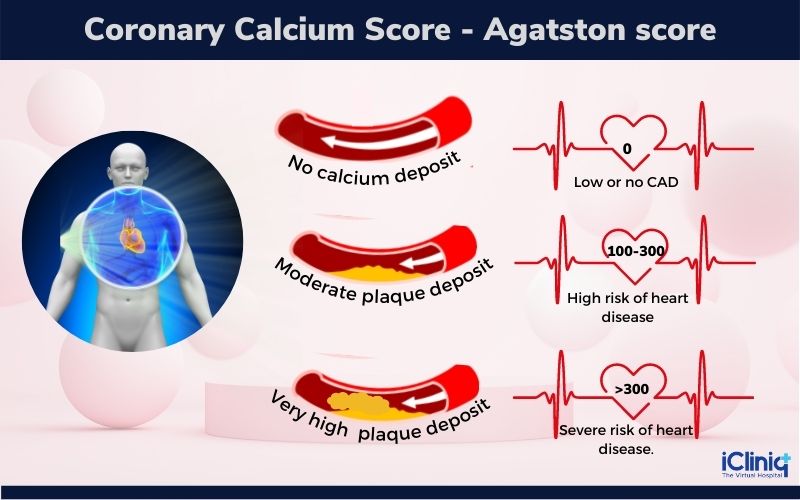
-
A high score cannot be taken as an individual predictor of heart health. However, a high score is indicative of lifestyle changes, medications, and supplementary tests to prevent major cardiac issues.
-
The doctor may suggest a revised diet plan, new exercises, weight loss regime, or certain medications based on the scoring. Additional diagnostic tests and follow-ups may also be advised.
What Instructions Should Be Followed by the Patient After the Procedure?
There are no special instructions required post-procedure. It is a simple and easy procedure, and patients can carry on with their routine activities after the procedure is done.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of the Procedure?
Advantages:
-
Detecting heart diseases at the earliest stage.
-
Non-invasive, fast, and painless.
-
Extremely convenient.
-
Well tolerated by the patients.
-
No injection of any contrast material or dye.
Disadvantages:
-
Limited radiation exposure.
-
Not indicated in pregnant ladies.
-
Other diagnostic tests may be required in patients with high scores, which may or may not corroborate clinical results.
What Are the Limitations of the Procedure?
-
This test may not be vital to the patient associated with low-risk factors as there will be no calcium deposit present.
-
Patients with proven CAD, under treatment for CAD, or with suspicious symptoms of heart disease are not ideal candidates for this test.
-
Soft or early stages of plaque formation may also not be visible in the scan.
-
Obese patients or those weighing over 450 pounds may not be accommodated in the CT machine.
-
An increased heart rate may hinder the test.
What Are the Advances in Coronary Calcium Scans?
-
A conventional CT can be replaced with electron beam computed tomography (EBCT) in a coronary calcium scan.
-
It is considered extremely fast to create 20 images per second.
-
The entire scanning procedure takes only a few seconds.
-
It can be used even when the heartbeat is rapid, as it causes no blurring.
-
The major limitation of EBCT is that it is not commonly available and is less versatile.
Conclusion:
A coronary calcium scan is an easy, convenient and effective way to diagnose heart problems at their earliest stage. Heart diseases, when identified at an early stage, can be easily treated with lifestyle modifications and medical management. It would help avoid surgical interventions and other complications too. Certain blood tests and cardiac markers also provide vital information on cardiac health. However, a heart scan is considered more precise and may prove extremely beneficial in individuals with high risk.












