Introduction:
The face has several bone structures. They are frontal bones, zygomas, orbital bones, nasal bones, maxillary, and mandibular bones. In addition, there are still more bones found deeper into the facial skeleton. In between these bones, there are air spaces called sinuses. The sinuses of the skull are the frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, sphenoid sinus, ethmoid sinus, sigmoid sinus, and superior sagittal sinus. The fractures of these sinuses occur due to blunt trauma to the face leading to severe esthetic deformity and other complications.
Is Facial Fracture a Serious Problem?
Minor fractures are not so severe. But complex fractures may lead to irreversible damage and may be life-threatening. The face is close to the brain and central nervous system and can lead to severe damage to the cranial nerves depending on the location of the fracture. Fractures close to the eyes can cause vision problems. And if the fracture line extends beyond the orbit or jaw, reaching the nose, it can lead to difficulty breathing and speech.
What Is the Anatomy of the Frontal Sinus?
Frontal sinuses are situated within the frontal bone, superior to the orbits. They develop at the age of five to six years, and development is complete around 12 to 20 years of age. The sinuses are supplied blood by supraorbital and supratrochlear arteries. The nerve is from supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves, the branches of the ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve. The sinus drains into the middle meatus of the nose. The frontal bones surrounding the sinus are thicker than the temporal bones; therefore, only a forceful trauma would lead to a frontal sinus fracture.
How Are Frontal Sinus Fractures Classified?
According to Gonty’s classification, frontal sinus fractures are classified as:
-
Anterior table involvement only.
-
Anterior and posterior table involvement.
-
Posterior table involvement only.
-
Comminuted or ‘through and through’ fractures involving the orbits, ethmoids, and nasal bones.
-
Fractures involving the nasofrontal duct.
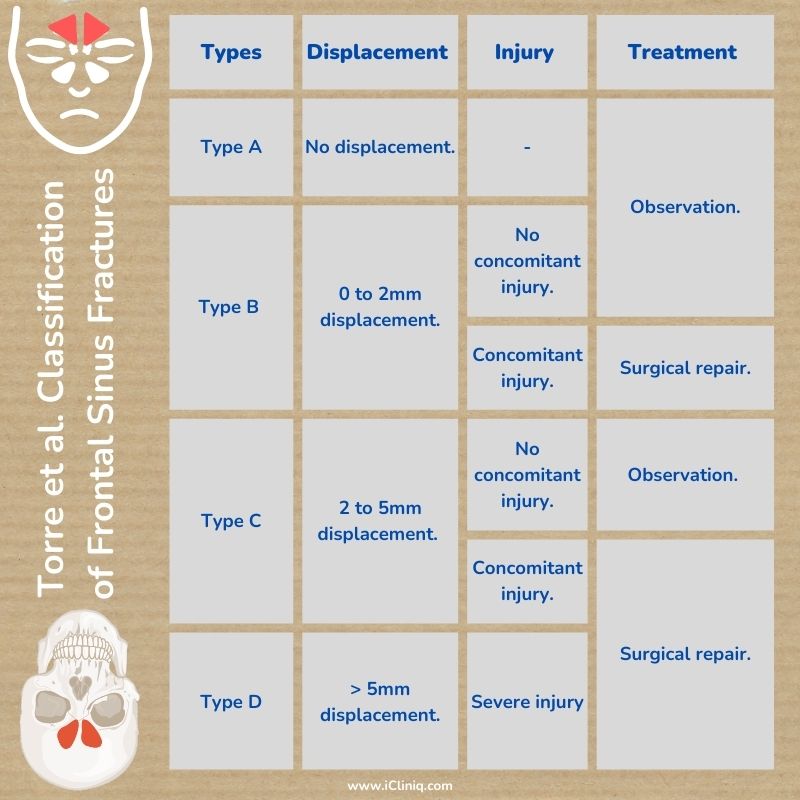
Torre et al. classified frontal sinus fractures based on dislocation, involvement of surrounding structures, and treatment required.
What Are the Causes of Frontal Sinus Fractures?
-
In Adults - Motor vehicle accidents, penetrating trauma, assaults, falls, sports accidents, domestic accidents, and work accidents.
-
In Children - Sports-related injuries, assault, and falls.
What Are the Complications of Frontal Sinus Fracture?
The complications may occur within six weeks (acute) or greater than six weeks (chronic). The common complications of a frontal sinus fracture are:
-
Frontal headaches.
-
Diplopia.
-
Blindness.
-
Facial deformities.
-
Brain abscess (puss-filled cavity in the brain).
-
Mucocele (a non-cancerous fluid-filled cavity).
-
Meningitis (swelling of the membranes of the brain).
-
Frontal sinusitis.
-
Osteomyelitis (bone infection).
-
Paresthesia (tingling or prickling sensation) of the ophthalmic nerves.
How Are Facial Fractures Diagnosed?
-
The individual is checked for any life-threatening injuries. The conditions, including blockage of air passage, size and reactions of the pupil, and any brain damage, are initially assessed before a complete examination of the face.
-
The patient's complete history of trauma and medical problems will be recorded.
-
A complete physical examination of the face for symmetry and motor activities is encountered.
-
Palpation of different face areas is done to assess tenderness and fractures.
-
Taking an X-ray is necessary if the individual cannot breathe through the nose and if there is any blood clot in the nasal septum.
-
If the physician suspects a fracture, they recommend a computed tomography (CT) scan to determine the exact type and location of the fracture. CT scans are recommended for correct diagnosis and planning of facial reconstruction.
How to Manage Frontal Sinus Fracture?
-
Observation With Close Follow-Up: For minimally displaced fracture of the anterior table without a frontonasal injury, a surgical repair is not required. A patient under observation with a scheduled follow-up is sufficient.
-
Closed Fracture Reduction: Closed repair of the fractures provides a more favorable esthetical outcome. Fractures can be reduced using percutaneous screws and inflating a Foley catheter into the sinus.
-
Open Reduction With Internal Fixation: The procedure is indicated if the individual has a forehead deformity due to displacement of the anterior table fracture without the involvement of the nasofrontal recess. The procedure can be performed endoscopically or open, depending upon the fracture extent. This procedure involves using screws and plates to secure the bone fragments.
-
Frontal Sinus Obliteration: Frontal sinus obliteration is indicated if patients have anterior table fractures without nondisplaced posterior table fractures. It can also be used to manage the mucosal disruption of the sinus. This process involves the removal of sinus mucosa, occlusion of the nasofrontal duct, and filling of the cavity with bone grafts. The graft materials commonly used for this procedure are hydroxyapatite, adipose tissue, glass ionomer, and pericranial flaps. The complication of this procedure is the formation of a mucocele. If left untreated, it can lead to bone destruction.
-
Cranialization: Cranialization is performed in patients with posterior table fractures with intracranial injury and comminution. The process involves the removal of the mucosa, external debris, bone fragments, and the posterior table of the frontal sinus. Defects in the anterior table can be reconstructed to protect the brain.
How to Prevent Face Fractures?
-
Wear protective equipment such as a helmet while driving a two-wheeler, and fasten your seatbelt if you drive a car.
-
Wear a protective face shield or mask in a sport.
-
Follow the safety guidelines to prevent accidents.
When Should One Seek Medical Help?
-
If the person has open wounds with the bones visible outside.
-
If the person has a bloody discharge from the nose.
-
If the person has blurred vision.
-
If the person has trouble breathing and swallowing.
-
If the person has a displaced nose or jaw.
-
If the person experiences pain while moving the jaw.
-
If the affected person loses teeth.
-
If there is pain and swelling in the face.
Conclusion:
A frontal sinus fracture can be managed comprehensively with an interprofessional team based on the injury's extent and severity. Under an emergency situation, the patient will be handled by the emergency team, whereas the surgical repair can be carried out only by a specialized surgeon.












