Overview:
Pemigatinib is an anti-cancer medication used to manage adults' bile duct cancer or cholangiocarcinoma. It is specifically used for patients whose cancer has spread rapidly and cannot be removed surgically. Pemigatinib belongs to the class of drugs known as protein kinase inhibitors. This is because the drug explicitly blocks the enzyme known as a protein kinase. These enzymes form a part of the targets or receptors known as the fibroblast growth factor receptors (FGFRs). These receptors are mainly found on the surface of the cancer cells and stimulate the growth and spread of these cells. Pemigatinib blocks the tyrosine kinase in the FGFRs and reduces cancer cells' rapid proliferation and spread. So, this drug is a ray of hope for the ones who have undergone cancer treatments previously but did not achieve the desired results. The doctor would recommend Pemigatinib if they notice a defective FGFR2 gene in the patient's body.
Pemigatinib Development and Approval History:
-
Incyte Corporation originally discovered Pemigatinib for managing previously-treated patients suffering from unresectable locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.
-
An important point to be noted about Pemigatinib is that the drug is not a part of the chemotherapeutic regimen. Instead, it is a targeted therapy for cholangiocarcinoma.
-
Pemigatinib was approved by the United States (US) Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on 17th April 2020 for treating adults with previously treated and unresectable or locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. In addition, the drug can be used in patients with FGFR2 fusion or other rearrangements, as detected in the FDA-approved test.
-
Pemigatinib also received the orphan drug and breakthrough therapy designation in April 2020. The application for the priority review of the drug was accepted in November 2019.
-
The FDA granted accelerated approval to Pemigatinib on 26th August 2022 for treating patients with refractory or relapsed myeloid or lymphoid neoplasms with defects in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1).
Information About Pemigatanib:
How Does Pemigatinib Work to Treat Cholangiocarcinoma or Bile Duct Cancer?
Pemigatinib is one of the most potent, efficacious, minor, and selective inhibitors of the fibroblast growth receptor isoforms 1, 2, and 3. Cholangiocarcinoma, or bile duct cancer, mainly occurs due to defects or mutations in the bile duct's DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). Pemigatinib has marked a revolution in the management of cholangiocarcinoma because the drug directly blocks the phosphorylation and signaling activities of FGFR1, 2, and 3 isoforms. It also reduces the cell viability in cancer cell lines and activates the amplification and fusion of FGFR. This causes constitutive FGFR signaling. During the animal studies, the anti-tumor activities of the drug were noted in mouse xenograft models of human tumors exhibiting alterations in the FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 leading to the activation of FGFR.
Safety and Efficacy of Pemigatinib:
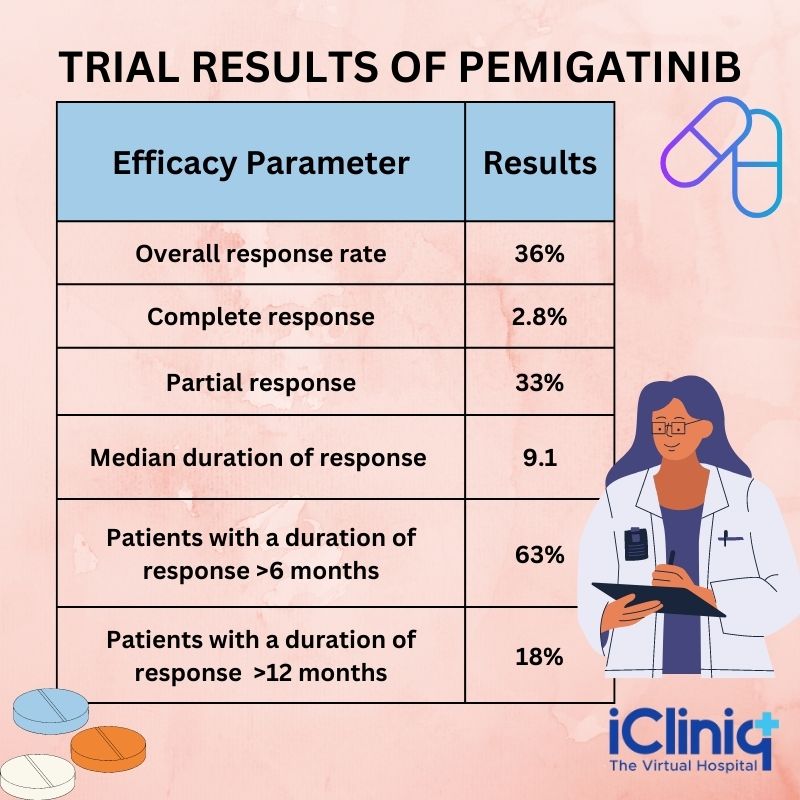
The clinical studies suggest that Pemigatinib effectively manages cholangiocarcinoma. A non-randomized, open-label, multicenter, single-arm, and phase 2 clinical trial named FIGHT-202 was done to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Pemigatinib in previously treated adult patients with metastatic or locally advanced bile duct cancer. The patients also demonstrated FGFR2 gene fusion or non-fusion rearrangement. The trial participants were administered Pemigatinib 13.5 mg oral dose once daily for 14 days, followed by seven days off in a 21 days cycle until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The independent review committee determined the primary outcome measures based on the duration of response and overall response rate. The overall response rate was 36 %, of which 2.8 % of the patients exhibited a complete response and 33 % demonstrated a partial response. In addition, the reaction in 63 % of the patients lasted for more than six months, whereas 18 % had a response for more than 12 months.
What Are the Medical Uses of Pemigatinib?
Pemigatinib is particularly indicated for adults diagnosed with locally advanced or metastatic bile duct cancer having an FGFR2 rearrangement or fusion that has progressed to an advanced stage after at least one line of systemic therapy. In addition, the drug is commonly used in the US to manage refractory or relapsed myeloid or lymphoid neoplasms with FGFR1 rearrangement. Hence, in simple terms, Pemigatinib can be safely used for bile duct cancer that has grown outside the affected organ but has not spread to distant sites of the body or has started spreading to distant organs. In addition, it can also be used for tumors with fusion or rearrangement of the gene called FGFR2.
Dosage and Administration:
Patient Selection:
Patients with locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma who demonstrate the presence of FGFR2 fusion or rearrangement should only be selected for administering Pemigatinib. The FGFR2 fusion and rearrangement can be detected using the FDA-approved test. The FDA-approved test uses a companion diagnostic device, an in vitro imaging tool that grants information about the safety and efficacy of a therapeutic product.
Recommended Dosage:
The recommended dosage of Pemigatinib is 13.5 mg orally once daily for two consecutive weeks. Followed by seven days off therapy during a 21 days cycle. The patient can continue the drug until unacceptable toxicity or disease progression. The drug can be taken with or without food at the same time daily. Make sure the patient swallows the whole tablet without crushing, chewing, splitting, or dissolving it. If the patient misses a dose of Pemigatinib by four hours or more or has vomiting after taking the drug, he can resume the dose as per the following schedule.
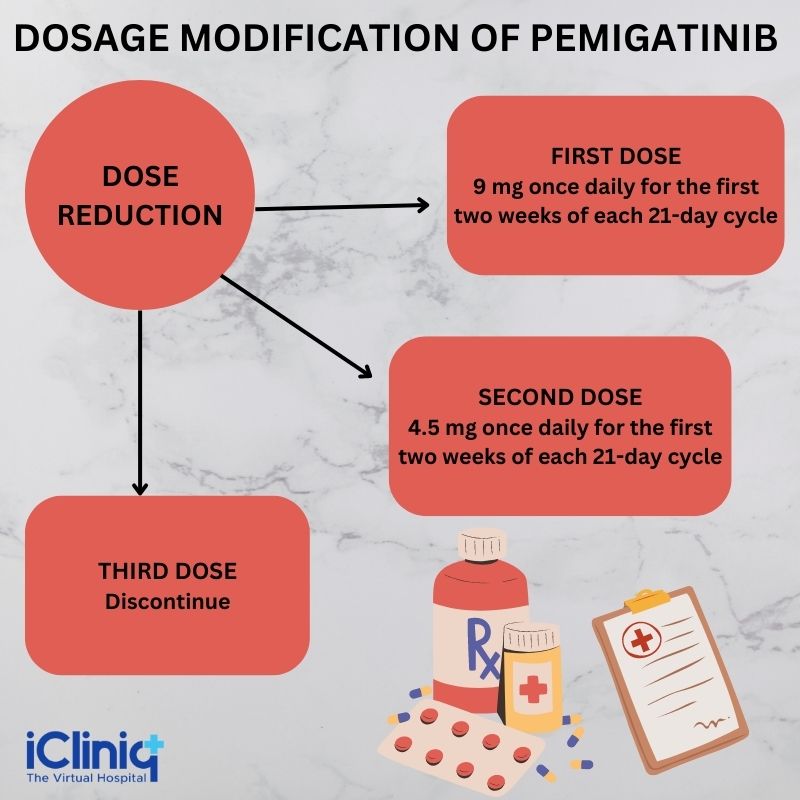
Dosage Modification for Side Effects or Adverse Reactions:
The dose reductions that can be made for the drug are listed in the table below:
Note- The patient must permanently discontinue Pemigatinib if he cannot tolerate 4.5 mg once daily for 14 days in a 21-day cycle.
Dosage Modifications for Pemigatinib Adverse Reactions:
The recommended dosage modifications of the drug according to the adverse reactions are described below:
1) Renal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (RPED):
- If the patient remains asymptomatic and stable during serial examinations, he can continue taking Pemigatinib.
- If the patient is symptomatic or his symptoms worsen over serial examinations, withhold Pemigatinib.
- If the patient becomes asymptomatic and shows improvement in subsequent examinations, resume Permigatinib at a lower dose.
- If the symptoms do not improve or persist even after subsequent examinations, consider permanent discontinuation of the drug based on the patient's clinical status.
2) Hyperphosphatemia:
Severity: Serum phosphate levels more than 7 mg per dL to less than or equal to 10 mg per dL -
- Recommend phosphate lowering therapy for the patient and carefully monitor his serum phosphate levels weekly.
- Withhold Pemigatinib therapy if the levels are not less than 7 mg per dL within two weeks of initiating the phosphate lowering therapy.
- Resume Pemigatinib therapy for the same dose if the phosphate levels are less than 7 mg per dL for the first occurrence.
- Resume the therapy at a lower dose for further recurrences.
Severity: Serum phosphate levels of more than 10 mg per dL -
- Recommend the phosphate lowering therapy for the patient and monitor his phosphate levels every week.
- Withhold Pemigatinib therapy if the levels do not go below 10 mg per dL within one week of starting the phosphate-lowering therapy.
- Resume Pemigatinib therapy only when the levels go below 7 mg per dL.
- Permanently discontinue the drug if serum phosphate levels remain above 10 mg per dL.
Other Adverse Reactions:
-
Severity: Grade 3 -
-
Withhold Pemigatinib therapy until the reactions resolve to grade 1 or baseline.
-
Resume Pemigatinib therapy at a lower dose if the symptoms resolve within two weeks.
-
Permanently discontinue the drug if the symptoms do not resolve within two weeks.
-
Permanently discontinue the drug if the symptoms recur even after dose reductions.
-
-
Severity: Grade 4 - Permanently discontinue the drug.
Dosage Modifications for the Use of Pemigatinib With Strong or Moderate CYP3A Inhibitors: The patient must avoid the concomitant use of Pemigatinib with potent or moderate CYP3A inhibitors.
If the patient cannot avoid the concomitant use of strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitors, the following is recommended:
-
Reduce the dosage of Pemigatininb from 13.5 mg to 9 mg.
-
Reduce the dosage of Pemigatinib from 9 mg to 4.5 mg.
If the patient discontinues the use of CYP3A inhibitors, the dosage of Pemigatinib can be increased to the dosage taken before initiating the therapy with moderate or strong inhibitors.
Recommended Dosage of Pemigatinib for Severe Renal Impairment:
The recommended dosage of Pemigatinib for patients with severe renal impairment and having a GFR (glomerular filtration rate) of 15 mL per min per 1.73 meters square to 29 mL per min per 1.73 meters square is 9 mg as per the schedule.
Recommended Dosage of Pemigatinib for Severe Hepatic Impairment:
The recommended dosage of Pemigatinib for patients with severe hepatic impairment and total bilirubin of more than 3 mg per dL is 9 mg per schedule.
Information About Cholangiocarcinoma:
Bile duct cancer, or cholangiocarcinoma, is a rare condition characterized by the formation of malignant cells or cancer cells in the bile duct. Bile ducts are tube-like structures that carry the digestive juice known as the bile juice to the gallbladder and intestine. Though cholangiocarcinoma mostly affects people above 50, it can occur in anyone. By the time the patient gets diagnosed with cholangiocarcinoma, the cancer has already spread beyond the bile ducts. It is difficult to treat cholangiocarcinoma as the patients usually present with poor prognoses. However, numerous targeted therapies are under clinical trials to treat cholangiocarcinoma.
Symptoms of Cholangiocarcinoma:
The signs and symptoms of cholangiocarcinoma are listed below:
-
The skin and the whites of the eyes become yellow (jaundice).
-
Intense itching and irritation in the skin.
-
Fatigue.
-
Dark urine.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Nausea.
-
Vomiting.
-
Loss of weight without any apparent reason.
-
White-colored stools.
For Patients:
What Is Pemigatinib?
Pemigatinib is a prescription medication used to treat adults with bile duct cancer that has metastasized or cannot be removed by surgery in patients who have already received treatment and have an abnormal FGFR2 gene. In addition, it is also used to treat patients suffering from a type of blood cancer known as myeloid or lymphoid neoplasm. It is specifically used to treat the myeloid neoplasm that recurs, does not respond to the treatment, or has the abnormal FGFR1 gene. The doctor usually tests the patient's cancer for abnormal FGFR1 and FGFR2 genes to ensure the drug is suitable for the patient. Unfortunately, nothing has been known about the safety and efficacy of Pemigatinib in children.
What Should the Patient Inform the Doctor Before Taking Pemigatinib?
Before taking Pemigatinib, the patient must inform the doctor about his medical conditions, including if he or she has:
-
Vision-related issues.
-
Kidney problems.
-
Liver problems.
-
Conceived or planning to become pregnant in the future. Pemigatanib can harm the unborn baby, resulting in pregnancy loss or miscarriage. The patient should not conceive while receiving treatment with Pemigatinib.
-
Breastfed or planning to breastfeed the baby. It is unknown whether Pemigatinib can pass onto the mother's milk. However, the patient must avoid breastfeeding the baby during the therapy and for a week after the last drug dose.
-
Taking or planning to take any prescription or over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, or herbal supplements.
Note - For patients who can become pregnant:
-
The doctor must conduct a pregnancy test before initiating the treatment with Pemigatinib.
-
The patient must use an effective birth control method during the treatment with Pemigatinib or a week after his last dose. The patient can consult his doctor about the most appropriate birth control methods.
For Males Whose Female Partners Can Become Pregnant:
-
Males must use effective birth control methods when sexually active during the treatment and for a week after the last dose of Pemigatinib.
How Should the Patient Take Pemigatinib?
-
Take the drug exactly as per the doctor's recommendation.
-
Pemigatinib must be taken in cycles of 21 days for patients suffering from cholangiocarcinoma. The patient must take the drug once daily for 14 days, followed by a gap of seven days to complete the cycle.
-
Take the drug at the same time every day.
-
The drug can be administered to the patient with or without food.
-
Swallow the tablet without crushing, splitting, or dissolving it.
-
The patient must avoid drinking grapefruit juice or other grapefruit products during the treatment.
-
The doctor might alter the drug dosage or ask the patient to permanently discontinue it if he experiences some adverse reactions.
-
If the patient misses a dose of Pemigatinib, he can take the drug within four hours on the same day. Avoid taking the drug if more than four hours have passed. Take the regular dose of Pemigatinib the next day. Avoid taking more than the prescribed dose of the drug.
-
In case of vomiting, the patient must avoid taking other drug doses. Instead, he must take the drug the next day.
What Are Some of the Most Common Side Effects of Pemigatinib?
Pemigatinib can cause the following serious side effects:
1) Eye Problems - Eye problems are commonly encountered in patients taking Pemigatinib, but they might become serious.
The common eye problems are listed below:
-
Dry eyes.
-
Inflammation of the eyes.
-
Increased tears.
-
Inflammation of the cornea.
-
Increased risk of retinal disorders.
To avoid the above-mentioned side effects, the patient must consult an eye specialist for a complete eye examination before initiating treatment. The eye check-up must be done every three months and every two months for the first six months while taking the drug.
-
The patient can use artificial tears, substitutes, lubricating or hydrating eye gels per the requirement to treat eye problems.
-
The patient must inform the doctor immediately if he develops any changes in his vision during the treatment with Pemigatinib.
2) High Phosphate Levels or Hyperphosphatemia
Hyperphosphatemia is one of the most common side effects of Pemigatinib. Patients with elevated phosphate levels in the blood present with the accumulation of minerals, including calcium, in several other body tissues. The doctor might recommend some dietary modifications for the patient, such as lowering the consumption of phosphate-rich foods. The patient must consult the doctor if he witnesses muscle cramps and numbness or tingling around his mouth.
Some of the most common side effects of cholangiocarcinoma are listed below:
-
Hair loss.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Dry eyes.
-
Dry mouth.
-
Nails might be poorly formed and get separated from the nail bed.
-
Tiredness.
-
Altered taste sensation.
-
Nausea.
-
Constipation.
-
Mouth sores.
-
Loss of appetite.
-
Vomiting
-
Joint pain.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Dry skin.
-
Back pain.
Storage of Pemigatinib:
Pemigatinib must be stored at room temperatures between 68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit. In addition, the medication must be kept out of reach of children.
Safety and Effective Use of Pemigatinib:
Sometimes, a particular drug might be administered for purposes other than those described in the patient information leaflet. However, the patient must note that he must not provide the drug to others, even if they present with similar symptoms. This is because the drug might have harmful effects on some people. The patient must consult the doctor for detailed information about the drug before taking it.
For Doctors:
Description:
Pemigatinib is a commonly used kinase inhibitor having the chemical name 3-(2,6-difluoro-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-ethyl-8-(morpholin-4-ylmethyl)-1,3,4,7-tetrahydro-2H-pyrrolo[3',2':5,6]pyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidin-2-one. The molecular formula of the drug is C24H27F2N5O. In contrast, the molecular mass of the drug is 487.5 g per mole. It is a white or off-white solid that is not hygroscopic. The solubility of Pemigatinib is dependent on the pH. It has been noted that the solubility of the drug decreases with increasing pH. Pemigatinib tablets are meant for oral administration and are usually uncoated.
Indications and Usage:
-
Cholangiocarcinoma: Pemigatinib is particularly indicated for managing adults with previously treated, unresectable, locally advanced, or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma. In addition, these patients demonstrate FGFR2 rearrangement or fusion. This particular usage and indication of the drug come under accelerated approval depending on the overall response rate and time of exposure. Further approval of this indication is subjected to clinical benefits in confirmatory trials.
Contraindications:
There are no absolute or relative contraindications of Pemigatinib.
Clinical Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action:
Pemigatinib is a small molecule kinase inhibitor that targets FGFR1, 2, and 3 with IC50 values less than 2nM. During the in vitro studies, the drug also inhibited FGFR4. However, the concentration was 100 times higher than those that block FGFR1, 2, and 3. Pemigatinib typically inhibits phosphorylation and signaling and demonstrates decreased cell viability in cancer cell lines. The drug also activated FGFR amplifications and fusions, resulting in the constitutive activation of FGFR signaling. This FGFR signaling activity supports the rapid multiplication and survival of malignant cells. The studies on the mouse xenograft model are a piece of extraordinary evidence to evaluate the anti-tumor activity of Pemigatinib. The xenograft model of cholangiocarcinoma expressed an oncogenic FGFR2-Transformer-2 beta homolog (TRA2b) fusion protein.
Pharmacodynamics:
Serum Phosphate:
An increase in serum phosphate levels was observed after Pemigatinib inhibited FGFR. The serum phosphate levels elevated after increasing exposure over the dose range of 1 to 20 mg once daily, resulting in the increased risk of hyperphosphatemia.
Cardiac Electrophysiology:
No modifications are observed in the QTc interval if Pemigatinib is administered at a dose 1.5 times higher than the recommended dose.
Pharmacokinetics:
The geometric steady-state AUC of Pemigatinib was noted to be 2620nM.h (54 %), the maximum concentration (Cmax) was observed to be 236 nM for 13.5 mg of the drug. A proportional increase in the steady state concentrations of Pemigatinib over the dose range of 1 to 20 mg. However, studies report that a steady state could be achieved within four days of drug administration. The median accumulation ratio of Pemigatinib was 1.63 when it was administered once daily.
Absorption:
The mean time to achieve the peak plasma concentration of Pemigatinib was 1.13 hours.
Effect of Food:
No clinically significant effects were observed on the pharmacokinetics of Pemigatinib when it was administered with a high-fat and high-calorie meal containing approximately 1000 calories.
Distribution:
The apparent volume of distribution of Pemigatinib was 235 L after a 13.5 mg oral dose. The estimated protein binding of the drug is 90.6 %, independent of the in vitro concentration.
Elimination:
The geometric mean elimination half-life of the drug was 15.4 hours, with the mean apparent clearance of 10.6 L per hour.
Specific Populations:
No clinically significant modifications were observed in the patients of the following populations-
-
Patients with mild to moderate renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, and on intermittent dialysis.
-
Patients with mild (total bilirubin level is 1.5 mg per dL) to moderate (total bilirubin level is 1.5 to 3 mg per dL) hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies:
Based on Clinical Studies and Model Approaches
-
CYP3A Inhibitors - Itraconazole is one of the strong CYP3A inhibitors that increases the maximum concentration by 17 % when administered after a single oral dose of Pemigatinib 4.5 mg. Hence, it can be concluded that the concomitant use of CYP3A increases the exposure of Pemigatinib by 50 to 80 %.
-
CYP3A Inducers - Rifampin is a potent CYP3A inducer that decreases the maximum concentration of Pemigatinib by 62 % after a single oral dose of 13.5 mg. The concomitant use of this drug is expected to reduce Pemigatinib exposure by approximately 50 %.
-
Other Drugs - No clinically significant differences were noted when Pemigatinib was coadministered with Esomeprazole and Ranitidine. The patient did not exhibit any differences in the glucose levels Pemigatinib was coadministered with Metformin.
Composition of Pemigatinib:
Active Ingredients - Pemigatinib.
Inactive Ingredients - Microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, and sodium starch glycolate.
Non-clinical Toxicology:
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility:
Nothing has been known related to the carcinogenic potential of the drug, as no carcinogenic studies have been conducted yet. Pemigatinib did not demonstrate any mutagenicity in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay. In addition, the drug was not clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay or an in vivo assay in rats. No studies have been conducted to evaluate the effect of Pemigatinib on male or female fertility. However, Pemigatinib did not cause any alterations in the fertility in female and male reproductive organs.
Dosage Forms and Strengths:
Pemigatinib Tablets: The drug is available in the following forms -
-
4.5 mg white to off-white and round tablets with "I" embossed on one side and "4.5" on the other.
-
9 mg white to off-white and round tablets with "I" embossed on one side and "9" on the other side.
-
13.5 mg white to off-white and round tablets with "I" embossed on one side and "13.5" on the other.
Warnings and Precautions:
1) Ocular Toxicity:
- Retinal Pigment Epithelial Detachment (RPED) - Pemigatinib can cause retinal pigment epithelial detachment, resulting in visual floaters, photopsia, and blurred vision. No clinical trials, including optical coherence tomography, were done routinely to monitor or detect asymptomatic RPED. Hence, nothing has been known about the incidences of asymptomatic RPED with Pemigatinib. Out of the 635 patients who received Pemigatinib 13.5 mg during the clinical trial, 11 % of them exhibited RPED, whereas grade 3 to 4 PRED was observed in 1.3 % of patients. The median time of the first onset of RPED was 56 days. The drug's dose reduction and permanent discontinuation were recommended in 1.3 % and 0.2 % of the patients, respectively. RPED improved to grade 1 level in 76 % of the patients who required dosage modifications. The patient must undergo a comprehensive ophthalmological examination before initiating Pemigatinib every two months for the first six months. The patients who develop ocular symptoms must be referred to an eye specialist and kept on follow-up for three weeks.
- Dry Eyes - Out of the 635 patients who received Pemigatinib 13.5 mg during the clinical trials, 31 % of the patients reported dry eyes, including grade 3 to grade 4 in 1.6 % of patients. Such patients can be treated with ocular demulcents if needed.
2) Hyperphosphatemia and Mineralization of the Soft Tissues -
-
Pemigatinib can cause hyperphosphatemia resulting in the mineralization of the soft tissues, cutaneous calcification, nonuremic calciphylaxis, and calcinosis.
-
Elevated phosphate levels are one of the most common side effects of Pemigatinib.
-
Of the 635 patients who received Pemigatinib 13.5 mg during the clinical trials, 93 % reported laboratory values above the normal upper limits.
-
The median time of onset of hyperphosphatemia was noted to be eight days.
-
33 % of the patients required phosphate-lowering therapy after receiving Pemigatinib. Such patients must be carefully evaluated for hyperphosphatemia and given a low-phosphate diet if their serum phosphate levels are more than 5.5 mg per dL.
-
Suppose the serum phosphate levels are more than 7 mg per dL. In that case, the patient must be given a phosphate-lowering therapy and asked to withhold or permanently discontinue the drug based on the duration and severity of the condition.
3) Embryo-Fetal Toxicity - Based on animal studies and the mechanism of action, Pemigatinib can harm the fetus when administered to a pregnant female. This is because when the drug was administered dot pregnant rats at the time of organogenesis, fetal malformations, retardation in fetal growth, and embryo-fetal death were observed. Pregnant females must be counseled about the potential risk of the drug to the fetus. Hence, they must use effective barrier contraceptive methods for one week after the last drug dose.
What Are Some of the Adverse Reactions of Pemigatinib?
The patients presented with the adverse reactions mentioned below during the clinical trials and after the drug was launched in the market:
- Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders:
- Hyperphosphatemia.
- Decreased appetite.
- Dehydration.
- Hypophosphatemia.
-
Dermatologic Disorders:
- Alopecia.
- Nail toxicity includes nail bed inflammation, nail discoloration, nail dystrophy, nail pigmentation, onychalgia, and onycholysis.
- Rash.
- Dry skin.
- Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome.
-
Gastrointestinal Disorders:
- Diarrhea.
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Constipation.
- Stomatitis.
- Dry mouth.
- Abdominal pain.
-
General Disorders:
- Fatigue.
- Peripheral edema.
- Pyrexia.
-
Neurological Disorders:
- Dysgeusia.
- Headache.
- Dizziness.
-
Ocular Disorders:
- Dry eyes.
- Blurred vision.
- Trichiasis.
- Retinal pigment epithelial detachment.
-
Musculoskeletal Disorders:
- Back pain.
- Arthralgia.
- Pain in the extremities.
-
Infestations and Infections:
- Urinary tract infections.
-
Investigations:
-
Weight loss.
-
-
Blood and Lymphatic Disorders:
-
Anemia.
-
-
Respiratory and Thoracic Disorders:
-
Epistaxis.
-
Laboratory Abnormalities:
Hematology: The reductions in the following levels were noted:
-
Hemoglobin.
-
Lymphocytes.
-
Platelets.
-
Leukocytes.
-
Phosphate.
-
Sodium.
-
Albumin.
-
Calcium.
-
Potassium.
The levels of the following hematological indexes were elevated:
-
Alanine aminotransferase.
-
Aspartate aminotransferase.
-
Creatinine.
-
Calcium.
-
Urate.
-
Bilirubin.
Note - In addition to the adverse reactions mentioned above, 16 % of the patients presented with elevations in the prothrombin time (PT)/international normalized ratio (INR). 18 % of the patients presented with elevations in the uric acid levels, whereas 2.9 % had grade three or four elevations.
Possible Drug Interactions:
The following drugs can interact with or change the mechanism of action of Pemigatinib:
-
Amlodipine.
-
Amprenavir.
-
Apalutamide.
-
Armodafinil.
-
Avacopan.
-
Butalbital.
-
Belzutifan.
-
Carbamazepine.
-
Chloramphenicol.
-
Cimetidine.
-
Ciprofloxacin.
-
Clarithromycin.
-
Cyclosporine.
-
Dexamethasone.
-
Erythromycin.
-
Griseofulvin.
Use of Pemigatinib in Specific Populations:
Pregnancy:
According to animal studies and mechanism of action, Pemigatinib can cause fetal toxicity or harm the unborn baby when administered to a pregnant female. However, insufficient data is available about the effect of Pemigatinib on pregnant females. When Pemigatinib was administered to pregnant rats during organogenesis, below the human exposure at the clinical dose of 13.5 mg caused fetal malformations, growth retardation, and embryo-fetal death. Hence, pregnant females must be aware of the drug's possible consequences.
Lactation:
Nothing has been known regarding the presence of Pemigatinib, its metabolites in human milk, or its effects on the breastfed child. However, lactating mothers must avoid feeding the baby a week after the treatment with Pemigatinib.
Males and Females of Reproductive Age Group:
Pemigatinib can harm the fetus, so the patient's pregnancy status must be verified before starting the treatment with the drug. In addition, males and females must use effective contraceptive methods to avoid further complications.
Pediatric Population:
The safety and efficacy of Pemigatinib have not been established in children.
Geriatric Population:
During the clinical trial named FIGHT-202, 32 % of the trial participants were 65 years and above, whereas 8 % of them were 75 years old and above. In the subsequent trial, named FIGHT-203, 44 % of the patients who presented with FGFR1 rearrangement were 65 years old and above, and 2.9 % of them were above 75 years. However, the trial results did not suggest any differences in the safety and effectiveness of the drug in these patients.
Renal Impairment:
The recommended dosage of Pemigatinib can be reduced in patients with severe renal impairment. However, no dosage adjustment is recommended for those with mild to moderate renal impairment, end-stage renal disease, or those receiving intermittent dialysis.
Hepatic Impairment:
The recommended dosage of Pemigatinib can be reduced for the ones suffering from severe hepatic impairment.
Clinical Trial:
A multicenter, open-label, and a single-arm trial named FIGHT-202 was done to evaluate the safety and efficacy of Pemigatinib in 107 patients suffering from metastatic or locally advanced and unresectable cholangiocarcinoma. The disease had progressed even after one year of therapy, and the patients also witnessed FGFR2 fusion or non-fusion rearrangement. These patients received Pemigatinib in a 21-day cycle at 13.5 mg orally once daily for two consecutive weeks. The drug was administered until toxicity or disease progression. The significant outcomes that determined the drug's efficacy included the overall response rate and duration of response.
Trial Results:
The efficacy results are listed in the table below: