What Is a Placenta?
The placenta is an essential organ that is present only during pregnancy. It plays a significant role in the development of the growing fetus. It helps transfer the oxygen, essential nutrients such as calcium and protein, and hormones to the growing baby and remove waste from the baby's blood.
A placenta will usually develop in the third week of pregnancy. It can be visible as early as ten weeks during an ultrasound. The placenta is attached to the baby through an umbilical cord.
The placenta is commonly expelled from the body after the delivery, while in some cases, it is removed manually after vaginal birth. People who have a retained placenta can experience certain post-delivery complications like bleeding or infection.
The placenta is developed when the fertilized egg gets embedded in the uterus. The possible locations of the placenta are:
-
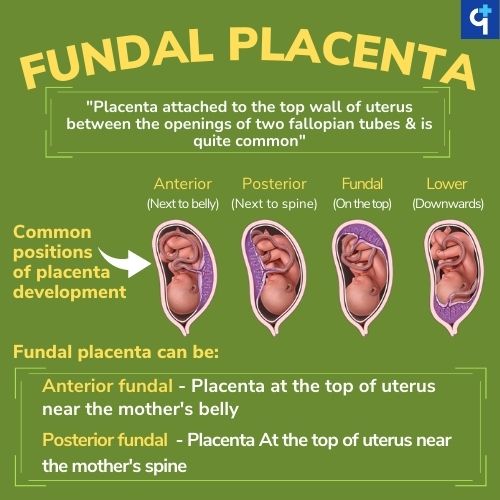
Anterior Position: On the (anterior) front wall of the uterus, which is very close to the belly.
-
Posterior Position: On the back wall of the uterus, which is very close to the spine.
-
Fundal Position: On the top wall of the uterus.
-
Lateral Position: On either side, right or left of the uterus.
-
Low-Lying Placenta: They are present low in the uterus, near or partly covering the internal cervical os (an opening in the uterus).
-
Placenta Previa: The placenta is extending over the internal cervical os. Depending upon how it has blocked the cervix, the treatment is planned, whether vaginal birth or cesarean section. Complications of placenta previa are bleeding from the placenta and preterm birth. If this does occur, close monitoring of both mother and baby should be done in the hospital.
What Is Fundal Placenta?
A fundal placenta, also called the fundic placenta, indicates that the placenta is formed in the top region of the uterus, in between the two fallopian tube openings, also known as the fundus.
The fundal placenta position is common, and the risk is low because the position alone will not pose any complications. As with any placental location, monitoring a fundal placenta's condition is essential to ensure that it provides your baby with the support they need. This will be done during a regular pregnancy ultrasound.
A few people may experience a combination of fundal-anterior or fundal-posterior positions. Placental positioning is usually monitored between 18 and 21 weeks of pregnancy with the help of an ultrasound.
What Are The Types Of Fundal Placenta?
A fundic placenta can be classified as either:
-
An anterior fundal placenta.
-
A posterior fundal placenta.
Anterior Fundal Placenta:
A placenta formed at the top and continues down to the front of the uterus (near the belly) is called the anterior fundal placenta.
Posterior Fundal Placenta:
A placenta that is formed at the top and continues down to the back of the uterus (near the spine) is called the posterior fundal placenta.
Is It Normal To Have A Fundal placenta?
Yes, it is normal to have a fundal placenta because having a fundal placenta seems to be pretty straightforward. It is one of the most familiar placental locations. The placenta usually, while growing, can sufficiently nourish the growing fetus throughout the pregnancy. And as the pregnancy progresses, the placenta may tend to move toward the upper region of the uterus. Unless accompanied by any other signs or symptoms, it is rarely a cause for concern.
Having either anterior and posterior fundal placenta is normal, and it will not affect the growth and development of the growing fetus in the womb. It is better to have a posterior placenta than an anterior placenta because having the placenta on the back wall of the uterus, the mother can feel the baby's movements and kicks early and stronger. Furthermore, the posterior placenta is thought to be the best for the baby because it will allow the baby to grow and come down to the correct position to line up in the birth canal for a vaginal birth. The growing baby will face the mother's spine in the posterior placenta, and the crown will also come down to the birth canal with time.
What Happens If Your Placenta Is In A Bad Position?
If your placenta is in a fundal position, there is no need to be concerned about it because the baby will still get the nourishment unless you have signs and symptoms. Such symptoms may include:
-
Bleeding.
-
Severe back pain.
-
Abdominal pain.
If you have these symptoms, please seek medical attention.
Which Placental Position Is Good For Normal Delivery?
The posterior placenta is often the perfect placental location for birth, but even having a fundal placenta or anterior placenta is not a problem.
The lateral placentas can increase the baby's chances of being in a breech position, leading to complications in the latter stages of pregnancy. The only placental position that requires a cesarean section is the placenta previa. Placenta previa can affect approximately one in 200 pregnancies and can be more likely if the pregnant woman is over 35 years or if it is not their first pregnancy and in women carrying multiples, or underwent previous uterine surgeries, like cesarean section.
The fundal position is the best because it will not get in the way of the labor or delivery process. But placentas covering the cervix can lead to life-threatening complications like bleeding during or before labor and can force the baby into a malpresentation like breech presentation.
Will The Position Of The Placenta Keep Changing?
The position of the placenta keeps changing throughout the pregnancy, either moving upward (as the baby comes down) or rarely downwards if the baby moves to the top. The placenta will take about 50 percent of the area in the uterus during the mid-term of pregnancy. It will take too little space as the baby grows and begins to come down during the later stage.
What Are The Complications Associated With Fundal Placental Position?
The most complicated placental position is called placenta previa. In this condition, the cervix is covered by the placenta during the third trimester of pregnancy. It can lead to severe complications like bleeding, and it requires careful medical attention.
The risk factors for placenta previa are:
-
Previous cesarean delivery.
-
Multiple gestations.
-
Previous placenta previa.












