What Is Aging?
Aging denotes the process of becoming old and refers to humans, animals, fungi, or the tiniest organisms. The term aging is not only confined to the organisms but also refers to the cells that divide to form the tissues. Some cells are immortal, whereas some continue to increase throughout life. Hence aging is a normal physiologic process experienced by every individual born on this planet. People have been observed to live longer, so the average expected lifespan of individuals has been noted to be beyond 60 years. When the population of a particular country progresses toward aging, it is known as population aging. Molecular studies reveal that aging results from molecular and cellular damage over time. As a result, the physical and mental activities of an individual get reduced to a large extent. Hence, the person becomes more vulnerable to diseases and, ultimately, death. Aging is not only associated with biological changes but also with other transitions like retirement and relocating to a convenient place.
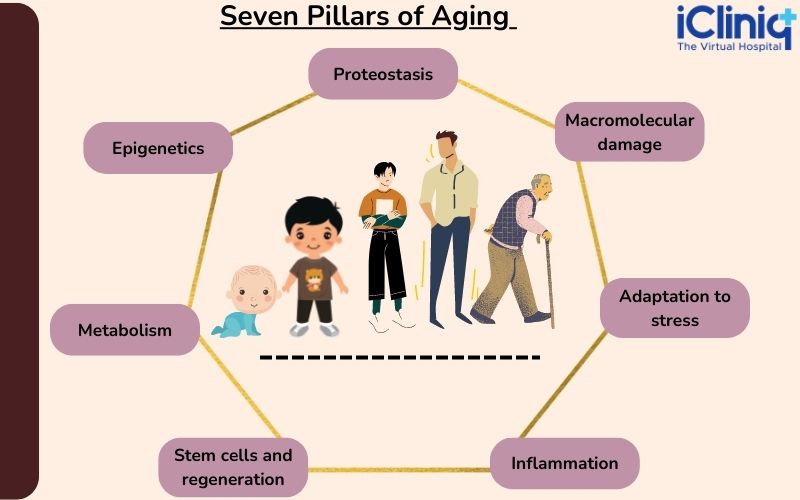
What Are the Seven Pillars of Aging?
Aging is a continuous process, and people have different perspectives on aging. For example, some people believe that age is just a number, whereas some accept the fact that changes occur in the body over time. The seven pillars of aging are listed in the diagram below:
-
Pillar 1 - Epigenetics - In simple terms, epigenetics is a study that determines the influence of human behavior and environment on genes. These changes are usually reversible and do not change the manner in which the body reads a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence.
-
Pillar 2 - Metabolism - Metabolism is a normal physiologic process by which the body converts food and drink into energy. Usually, metabolism decreases with aging.
-
Pillar 3 - Macromolecular Damage - Macromolecules are the building blocks of the body that provide structural support and energy and play a significant role in the body's biological reactions. Macromolecular damage is more likely to increase with a person’s age.
-
Pillar 4 - Inflammation - A long-standing inflammation in the absence of infection is one of the significant features of aging. It is a risk factor for mortality (death) in the elderly population.
-
Pillar 5 - Adaptation to Stress - Aging can alter an individual’s response to stress. People who adapt to stress do respond strongly to it.
-
Pillar 6 - Stem Cells and Regeneration - The ability of the stem cells to divide into several other types of cells gets diminished with aging.
-
Pillar 7 - Proteostasis - Proteostasis or protein balance gets disturbed with aging. As a result, the misfolded and damaged proteins accumulate in the body resulting in reduced cellular activities.
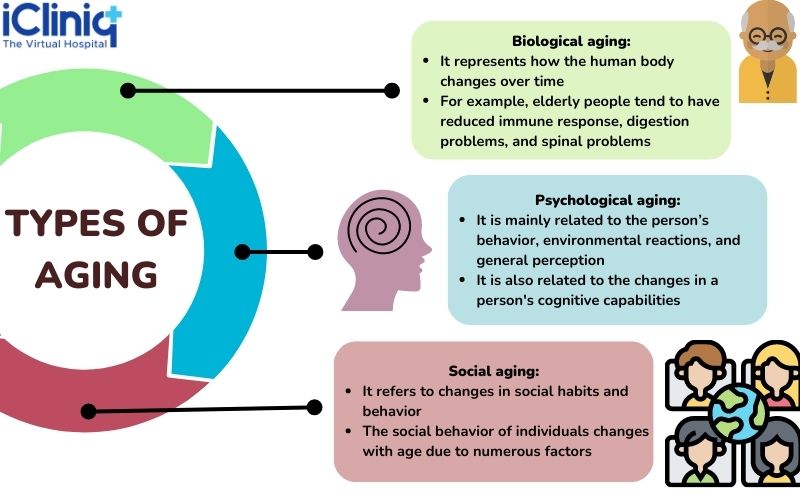
What Are the Different Types of Aging?
The different types of aging are listed in the table below:
What Are the Seven Signs of Aging?
Skin is a vital body organ that acts as a barrier against various microorganisms and other harmful allergens. It is indeed a fact that beautiful and wrinkle-free skin signifies youth. In contrast, the one with fine lines and wrinkles signifies old age. The seven significant signs of aging are listed below:
-
Wrinkles and Fine Lines - Fine lines and wrinkles appear when the collagen and elastin fibers that make the skin taut or firm become weak. As a result, the skin becomes loose and presents with wrinkles.
-
Uneven Skin Tone - The skin tone or the complexion might become uneven because of the difference in melanin levels.
-
Skin Dullness - The moisture levels in the deeper layers of the skin start depleting with age. As a result, the skin appears dull or dark with aging.
-
Dry Skin - The skin appears dry with age because it loses its ability to retain moisture.
-
Age Spots or Blotches - The skin becomes thin with age, accompanied by reddish-brown spots due to exposure to ultraviolet rays.
-
Rough Texture - The smooth and baby-soft skin becomes rough textured because the number of dead cells outgrows the number of healthy cells.
-
Skin Pores - The skin pores become enlarged due to loss of skin elasticity.
How Does Aging Impact Other Body Organs?
Aging is typically associated with only one perspective, which is the wrinkling and graying of hair. However, the effects of aging on the different body organs are listed below:
-
Cardiovascular System - The peculiar age-related changes that occur in the cardiovascular system include the hardening of the blood vessels and arteries. The heart rate remains the same at rest but would not increase much during physical activities. As a result, elderly people are more likely to have heart attacks, hypertension, and cardiac diseases.
-
Muscles, Bones, and Joints - Bones tend to shrink, lose their density and become weak with age due to the lack of calcium. Similarly, muscles lose their flexibility and elasticity with age.
-
Digestive System - Elderly people are more likely to have constipation due to problems in the large intestine. The risk factors for these problems include lack of exercise, diabetes, not staying hydrated, and a low-fiber diet.
-
Urinary Tract - With aging, the urinary bladder loses its elasticity resulting in urinary incontinence or urine leakage. The person might have to pass urine frequently because the pelvic floor muscles and bladder muscles become weak.
How Can a Person Stay Healthy in His Old Age?
Aging affects not only the physical appearance of an individual but also the functioning of the internal organs. A person can do the following to keep his organs healthy:
-
Go for a walk daily for 30 to 45 minutes.
-
Stay active and exercise regularly to keep the heart healthy.
-
Maintain a healthy body weight to lower the risk of heart disease.
-
Avoid smoking as it elevates the risk of heart and lung diseases.
-
Yoga and meditation can be done to overcome stress and anxiety.
-
Sleep for seven to eight hours at night to stay fresh and healthy.
-
Consume adequate amounts of calcium-containing foods to maintain bone strength and density.
-
Limit the consumption of alcohol.
-
Consume adequate vitamins and minerals.
-
Do not hold urine for prolonged periods to avoid the risk of urinary tract infections.
-
Maintain healthy bowel and bladder habits.
-
Do pelvic floor muscle exercises or Kegel exercises daily to keep the urinary tract healthy.
-
Avoid carbonated drinks, caffeine, and acidic foods as they are bladder irritants and increase the risk of urologic diseases.
-
Read books, novels, or magazines to stay active mentally.
-
Interact with people and spend time with other family members to overcome age-related depression and anxiety.
Conclusion:
Aging is a normal phenomenon experienced by every individual born on this planet. The body undergoes several changes with aging. Hence, an individual must get adapted to these changes and stay healthy. Consult a doctor to learn more about age-related changes.












