Introduction:
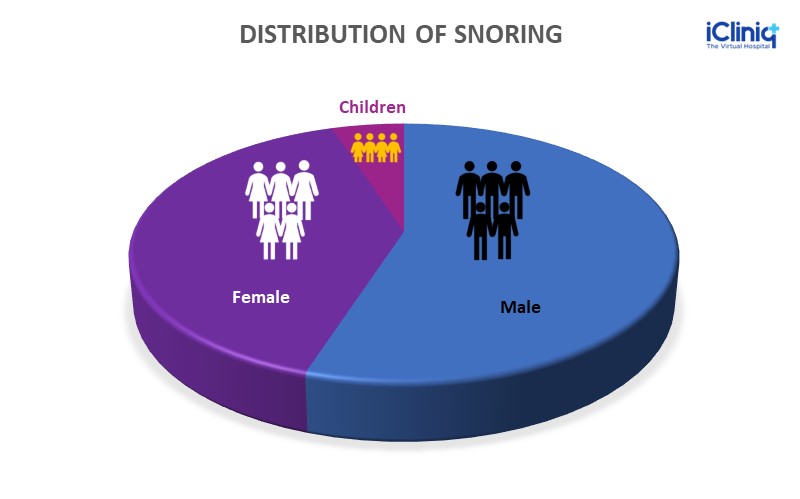
Snoring is a sleep disturbance occurring in mostly middle-aged individuals, which may turn into a serious health issue called obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Everyone who snores does not mean they have obstructive sleep apnea, but people with obstructive sleep apnea tend to have to snore. The occurrence of snoring is approximately 50 to 55 % in the male population, 35 to 40 % in females, and around two to five percent among children.
What Is Snoring?
Snoring occurs due to obstruction in the airflow while breathing during sleep. While snoring, the muscle tone of the upper airway tract decreases, causing the tongue to fall back and relax other soft tissues as well, leading to the narrowing of the airway resulting in a noise which is called snoring.
What Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is more distinct when there is a partial or complete narrowing of the respiratory lumen causing continuous interruption while breathing in during sleep resulting in sleep disturbances and louder snoring.
What Are the Causative Factors for Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome?
-
Weight gain.
-
Sedentary lifestyle.
-
Underlying health conditions (like hypothyroidism).
-
Increased alcohol consumption.
-
Smoking.
-
Enlarged tonsils.
-
Broad tongue.
-
Nasal blockage.
-
Overdose of sedative drugs.
-
Daytime fatigue.
How to Diagnose and Differentiate Snoring from Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
The first picture that comes to mind is figuring out how severe the snoring habit has become.
Like many people, due to various underlying factors, we tend to get into the habit of snoring. To rule out how serious a health issue it has become, early diagnosis and management of the underlying cause are very crucial. For the initial intervention, making appointments with the doctors and discussing the symptoms with them helps to flag relevant symptoms useful in the diagnosis of the health condition and investigate them accordingly.
Various questions that draw a significant margin between snoring and obstructive sleep apnea diagnosis are:
-
How was the snoring detected?
-
What is the frequency of snoring?
-
Feeling tired every morning, even after a long sleep?
-
Any recent weight gain?
-
If having a sedentary lifestyle?
-
Any change in the body mass index (BMI) over the last six months?
These questions help to reach an accurate diagnosis and run the necessary investigations according to the diagnosed condition. Polysomnography (PSG) and the Eworth sleepiness scale are other diagnostic tools used to confirm obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
How to Get Rid of Snoring and Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome?
-
Say No to Sedentary Lifestyle: Many people often undergo a sedentary lifestyle because of various reasons. Changes or modifications in the lifestyle help to maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being fat or obese is one of the main contributing factors to snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, so adding a healthy diet and exercise to the daily routine helps in maintaining a healthy weight and protecting against risk factors of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Maintaining Body Mass Index (BMI): Body mass index is the ratio of weight divided by height in meters square. Weight loss helps in normalizing the body mass index to a normal range acting as one of the precautionary measures against snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Avoiding or Moderating Use of Alcohol: Increase in the frequency and duration of alcohol intake, especially before bedtime, further aggravates snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. As alcohol acts as a muscle relaxant, it relaxes the muscle and soft tissues of the upper respiratory tract, causing the narrowing of the airway and further deteriorating snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Avoid Overdose of Sedatives: Sedative drugs further lead to the compromised airway as it tends to relax the respiratory tract muscles resulting in further worsening of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome.
-
Change Sleeping Positions: Try to prefer more of a lateral sleep position than lying on the back, as sleeping on the back results in gravitational forces drawing the muscles of the upper airway downwards, leading to narrowing of the upper airway column, thereby aggravating snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Treat Nasal Congestion: Runny nose due to bacterial or viral infections or allergies also causes difficulty in breathing due to obstruction of air through the nasal passage. Nasal decongestant drugs can be used under a physician’s prescription to treat nasal congestion.
-
Aging: As age advances, the muscles of the upper airway tract lose their tone, causing the weakening of muscles. Various jaw and neck exercises can be done to decrease muscle laxity and prevent snoring.
-
Hypothyroidism: It is a condition in which the thyroid gland functions abnormally and does not secrete enough thyroid hormone as needed by the body. If undiagnosed, it can lead to snoring. Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment of hypothyroidism should be made.
-
Myofunctional Appliances: Many oral appliances have become reliable and cost-effective in the management of obstructive sleep apnea, such as palatal lift appliances for the elevation of the soft palate and improvement in the upper airway column. These appliances are constructed by dental professionals after diagnosing the underlying cause of snoring and clinical examination of oral structures.
-
Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): Continuous positive airway pressure is the minimally invasive and best therapy to maintain patent upper respiratory airways, especially for people who are not compliant to undergo surgical treatment. This device is used during sleep hours as a nasal or oral-nasal mask after setting the recommended positive pressure in the machine. Continuous positive airway pressure therapy is mostly recommended in people with an apnoea-hypopnoea index (AHI) of more than 15.
What Are the Surgical Treatment Modalities Performed for Snoring or Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome?
-
Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: It is a surgical procedure done to remove extra tissues surrounding the throat to increase the patency of the upper airway.
-
Septoplasty: It is a surgical procedure done to correct deviated nasal septum, which further corrects the problem of snoring and obstructive sleep apnea.
-
Tonsillectomy: Removal of enlarged tonsils is done to increase the patency of the upper airway.
Conclusion:
Snoring has become one of the most common symptoms that are always ignored or remain undiagnosed. It becomes serious when it turns to obstructive sleep apnea. As various treatment modalities are available nowadays, early diagnosis and treatment by doctors at the earliest is the best solution.