Drug Overview:
Salicylic acid acts as a keratolytic or a peeling agent that helps shed the outer layer of skin to clear the pores. It is topically applied over the skin to treat acne, seborrhea, dandruff, or psoriasis and remove calluses, corns, and warts. Salicylic acid contains beta hydroxy acid. It can work best for mild acne-like blackheads and whiteheads by exfoliating the affected skin and clearing the pores. Salicylic acid can also help prevent future breakouts. Read the article to know more about the indications, contraindications, side effects, and uses of the drug.
What Is Salicylic Acid?
Salicylic acid is a phenolic and beta hydroxy acid obtained from the willow bark tree. It has exfoliant, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties. Salicylic acid products are available through prescription or over the counter, depending on the skin type and condition.
-
Face washes.
-
Gels.
-
Creams.
-
Shampoo to treat dandruff.
For Patients:
How Does Salicylic Acid Work?
When the hair follicles get obstructed or clogged with dead skin cells and oil, whiteheads (closed clogged pores), blackheads (open clogged pores), or pimples (pustules) often appear. Salicylic acid can penetrate the skin and dissolve the dead skin cells clogging the pores. It may take several weeks to get the full effects of it. If there is no result after six weeks of usage, check with the dermatologist.
What Should One Avoid Before Using Salicylic Acid?
-
Do not use it on sunburned, open wounds, irritated, windburned, or dry skin.
-
Rinse thoroughly with water if topical salicylic acid touches the eyes or mouth.
-
Salicylic acid may be flammable, so do not use it near high heat or open flame.
-
Wash the medicine from the hands before going near a stove or handling a hair styling appliance like a curling or straightening iron because high heat can cause the medicine to ignite and may burn the skin.
-
Avoid smoking until the gel gets wholly dried on the skin.
-
Avoid using other topical medications on the area treated with salicylic acid unless the doctor instructs individuals to use them.
Things to Inform the Doctor Before They Prescribe Salicylic Acid:
Inform the healthcare provider if one has the following conditions:
-
Chickenpox (varicella).
-
Flu (influenza).
-
Inform the doctor of any allergies to any drug or its composition.
-
Inform the doctor if one is pregnant, breastfeeding, or planning pregnancy.
-
Inform the doctor if on any medications for any medical conditions.
-
Inform the doctor if any underlying medical condition is present, like liver disease, kidney disease, blood vessel disease, and diabetes.
Look Out for the Side Effects:
-
Salicylic acid is usually considered safe overall, but sometimes it may cause skin irritation when used for the first time.
-
It may also remove too much oil and lead to dryness and irritation.
-
Skin tingling or stinging.
-
Itching.
-
Hives.
-
Peeling skin.
-
Feeling light-headed.
-
Swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Things to Do After Using:
-
Inform the doctor in case of any side effects of the drug.
-
Keep track of the improvement in the symptoms and inform the doctor during the follow-up visits.
-
In case of worsening symptoms, inform the doctor immediately.
How to Use Salicylic Acid Products?
-
Use as directed on the label or as prescribed by the doctor.
-
Do not take it orally; it should be used only topically.
-
Apply a very small amount of the topical agent as a test dose to one to two small skin areas daily for three days.
-
If one does not react to that medicine, use the full prescribed amount on the fourth day.
-
Salicylic acid topical is available in many forms, like lotion, cream, liquid, gel, soap, shampoo, ointment, foam, cloth pads, and skin patches.
-
Read and carefully follow the instructions provided on the label.
-
Shake the medicine before use.
-
It may take many days for the symptoms to disappear.
-
Call the healthcare provider if symptoms do not disappear.
For Doctors:
Pharmacology:
Mechanism of Action: Salicylic acid works by inhibiting both COX1 and COX 2 inhibitors (cyclooxygenase enzymes) irreversibly and thereby reducing the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins precursors.
Pharmacodynamics: By the dose of 160 to 325 mg of Aspirin, COX inhibition can be maintained at over 9 percent. These effects typically continue for seven to ten days, which is the same amount of time as a platelet lives. It is possible to block prostate cyclin by using greater doses. The blood vessel's endothelial cells experience this inhibition.
What Are the Indications of Salicylic Acid?
Salicylic acid treats skin and hair problems like:
-
It reduces acne blemishes.
-
It prevents blackheads and whiteheads from causing breakouts.
-
Exfoliates the skin.
-
Reduces inflammation.
-
Reduces uneven skin tone.
-
Decreases dandruff.
-
Reduces age spots.
-
Angina pectoris (sudden pain in the chest).
-
Myocardial infarction (blockage of blood flow to the heart).
-
Colorectal cancer (cancer of the colon and rectum).
-
Fever.
What Are the Contraindications for Salicylic Acid?
-
Genitals.
-
Eyes.
-
Hypersensitivity.
-
Moles.
-
Birthmarks.
-
Warts with hair growing from them.
-
Infected, reddened, or irritated skin.
-
Facial warts or warts on mucous membranes.
What Are the Warnings and Precautions of Salicylic Acid?
Talk with the doctor before using salicylic acid, even though it is available over the counter.
-
Allergies: Inform the healthcare provider if one has been allergic to salicylic acid or other topical medications.
-
Children: Children's skin can absorb and get irritated more than adults. Therefore, it should be avoided in children under two years of age.
-
Drug Interactions: Certain medications do not interact well with salicylic acid. Let the doctor know what medications one is currently taking.
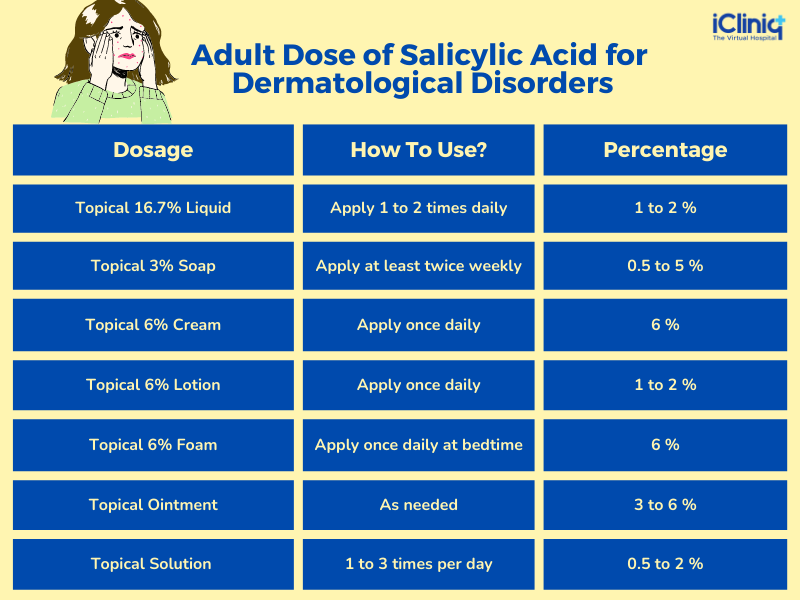
Salicylic Acid Dosage and Forms For Acne:

Adult Dose of Salicylic Acid for Dermatological Disorders:
What Are the Drugs That Interact With Salicylic Acid?
Medicine commonly used on the skin will not be affected by other topical drugs. But many drugs can interact with each other. Therefore, tell the health care provider about all medicines, including over-the-counter and prescription medications, vitamins, and herbal products.
Ingredients
Active Ingredient: Salicylic acid is the only active ingredient present.
Inactive Ingredients:
-
Purified water.
-
Tea tree oil.
-
Glycerine.
-
Tocopheryl acetate.
-
Shea butter.
-
White willow extract.
-
Stearic acid.
-
Argan oil.
-
Sesame seed oil.
Salicylic Toxicity
The toxicity level of salicylic acid is around 300 mcg per mL.
Salicylic acid toxicity can rarely occur from topical application of salicylic acid. To avoid this:
-
Do not apply salicylic acid products to large body areas.
-
Do not use it for a long time.
-
Do not use it under air-tight dressings like plastic wrap.
Stop using salicylic acid and consult the healthcare provider if symptoms or signs like:
-
Vomiting exists.
-
Nausea.
-
Headache.
-
Lethargy.
-
Confusion.
-
Ringing or buzzing in the ears, called tinnitus.
-
Diarrhea.
-
Increase in breathing depth (hyperpnea).
-
Minor skin irritation, rash, or peeling.
-
The color of the treated skin is changed, usually white.
-
Problems with hearing.
-
Thinking about problems.
Drug Interactions:
-
Salicylic acid decreases Abacavir's excretion rate, resulting in toxicity.
-
Salicylic acid, when combined with Acarbose, increased the hypoglycemic activities of Acarbose.
-
Salicylic acid, when combined with Acebutolol, increases the antihypertensive activities of the drug.
-
The toxic effects of salicylic acid are increased when it is combined with Acemetacin.
-
The risk of bleeding increases when the salicylic drug acid is combined with Acenocoumarol.
Food Interactions: Salicylic acid does not interact with food products.
Technical Profile of Salicylic Acid:
-
Boiling Point: The boiling point of the drug is 20 millimeters of mercury.
-
Melting Point: The melting point of the drug is around 158 to 161 degrees Celsius.
-
PH: The pH of the drug is 2.4.
-
Solubility: It is easily soluble in water, acetone, benzene, and ether.
-
Therapeutic Drug Levels of Aspirin: Therapeutic drug levels of salicylic acid are around 150 to 300 mcg per mL.
-
Time to Steady State: It is around five to seven days.
Plasma Concentration: The average plasma concentration of Aspirin is around two to ten mg per dL.
Distribution: The average distribution volume of salicylic acid is 170 mL per kg body weight.
Metabolism: At a minimum dose, around 80 percent of salicylic acid is metabolized in the liver.
Elimination: About 10 percent of salicylic acid is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Protein Binding: Salicylic acid binds to almost 90 percent of the plasma protein.
Can Salicylic Acid Be Used in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women?
Salicylic acid for acne should be used cautiously during pregnancy only if the benefits outweigh the risks. There is no proper information on using salicylic acid for acne while breastfeeding. Still, pregnant or breastfeeding patients should get advice from a healthcare provider before using over-the-counter (OTC) drugs.
Missed Dose
Topical salicylic acid is used only when needed; therefore, one may not be on a dosing schedule. If it is time for the next dose, skip any missed dose, and do not use two doses simultaneously.
Salicylic Acid Overdose:
Salicylic acid overdose is not considered to be dangerous. But seek emergency medical attention if it is swallowed accidentally.
Storage:
Store it at room temperature and away from moisture and heat. Keep out of reach of children. Place the medicine in its original packaging when not in use. Keep the foam away from open flame or high heat because it may explode if it gets too hot. Do not puncture or burn an empty aerosol canister.
Other Specifications:
-
Salicylic Acid in Pregnant and Lactating Women: Salicylic drug acid should be used cautiously in pregnant and lactating women. The safety and efficacy of the drug for use in pregnant and lactating mothers are yet not established.
-
Salicylic Acid in Pediatric Patients: Salicylic acid in a child patient with flu can result in Reye’s syndrome, a fatal condition. Therefore the salicylic drug acid should be used cautiously in pediatric patients.
-
Salicylic Acid in Geriatric Patients: The use of a topical form of salicylic acid in the elderly has not yet been established. It should be used very cautiously in elderly patients with blood-related disorders.












