Overview:
Esketamine is the generic name of the S-Ketamine and has been newly approved by the United States FDA in 2019 for the treatment of TRD (treatment-resistant depression) in adults. The drug relieves pain, produces dissociative anesthesia (affects sensory perception and feelings), and induces sedation. It is potentially effective and immediately affects the brain to offer rapid relief from depressive symptoms in days or even hours. Esketamine is an analgesic, twice as effective as Ketamine, and is often prescribed for post-operative pain management.
This nasal spray is available only under a restricted risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (REMS) program owing to its potential for abuse and misuse. The liquid is sprayed into the nose, usually twice a week, for up to four weeks to treat the major depressive disorder. Long-term use of Ketamine can also cause irreversible damage to the urinary tract leading to renal failure. So, Esketamine must always be taken under the direct supervision of a health professional.
Drug Group:
Esketamine belongs to a class of medications called NMDA receptor antagonists. These drugs affect the brain-derived neurotransmitters and decrease stress and depression. Unlike conventional oral medicine, Esketamine acts more on the glutamate chemical messengers in the brain. This improves communication between the brain cells, creating a positive mood and fewer depressive symptoms. The easy administration of this drug and fast action sets it apart from others in this group.
What Is Esketamine Used For?
Treatment-Resistant Depression:
The drug is used to treat depression. It is given with oral anti-depressants to manage conditions like treatment-resistant depression (TRD) in adults. TRD is a condition where the person fails to respond to standard doses of antidepressants continuously for at least six weeks. It is associated with an increased risk of relapse, hospitalization, and suicide.
Major Depressive Disorder:
Esketamine is also used in treating major depressive disorder (MDD).
Suicidal Thoughts:
Furthermore, it reduces suicidal thoughts and behavior. Suicidal behavior is a state where one has thoughts of self-harm with or without an action plan that might cause one's death. Therefore, it can be given to people who have a major depressive disorder with acute suicidal ideation.
How Does Esketamine Work?
Intranasal Esketamine is a noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NDMA) glutamate antagonist with multiple benefits compared with other routes of administration. It is one of the two molecules of Ketamine (S enantiomer) and has a higher affinity to NMDA receptors.
The drug stimulates brain-derived neurotrophic factors (BDNF) production in the brain to improve brain plasticity. The drug has a more direct stimulation effect on the BDNF than oral antidepressants. This resulted in rapid onset and continued effect even after the drug was eliminated from the body.
Esketamine acts more on glutamate and increases its levels in the brain. This results in improved availability of glutamate and better communication between the brain cells.
What Is Its Onset of Action?
Esketamine has a rapid antidepressant effect in patients with major depressive disorder, suicidal ideation, and treatment-resistant depression.
Drug absorption occurs in two pathways - an immediate pathway and a slower pathway. 70 % of the drug is absorbed directly in the pulmonary circulation from the alveoli, while the remaining 30 % is absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract, oropharynx, or pulmonary tissues.
The expected time taken by the drug to reach a peak plasma concentration is 20 to 40 minutes after the last spray. The drug is actively metabolized and rapidly enters the body's systemic circulation with a mean bioavailability of approximately 48 % following nasal administration.
Habit-Forming:
Repeated use of drugs can lead to drug-seeking behavior and dependency. The drug produces tolerance, and repeated use is often associated with a recognized withdrawal syndrome like poor appetite and anxiety fatigue.
Expiry Date:
Avoid taking this medicine after it expires. The expiry date will usually be printed on the back of the pack.
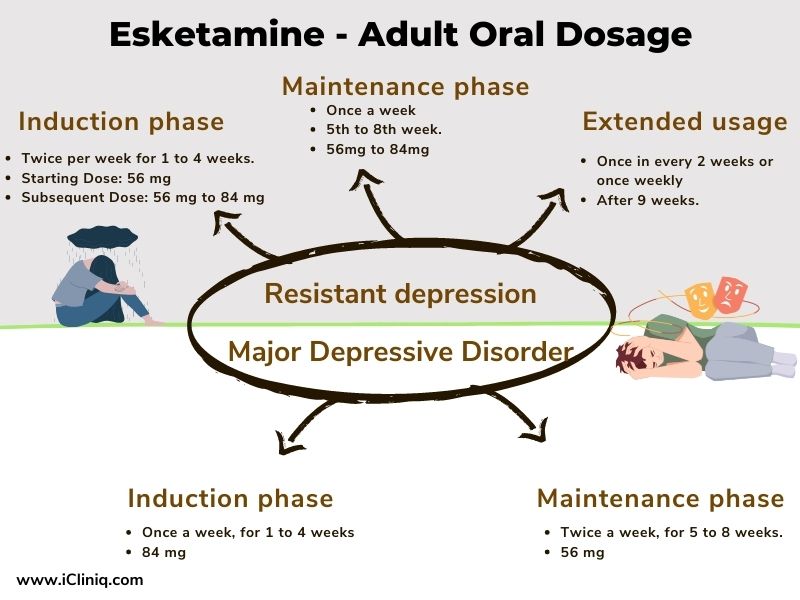
What Is the Dosage of Esketamine?
The nasal drug is available as a solution and with a spray device. Each nasal spray delivers two sprays containing 28 mg of Esketamine. It is supplied as a 56 mg kit (two 28 mg nasal spray devices) or an 84 mg kit (three 28 mg nasal spray devices).
Esketamine is given in conjunction with an oral antidepressant in adults with TRD and MDD.
Recommended Dosage for Treatment-Resistant Depression:
How to Use Esketamine?
Esketamine must always be administered under the direct supervision of a health professional. The patient must be enrolled in the REMS program (Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies) before the administration of the drug. The drug is available only in the spray. Each nasal spray device provides two sprays (one in each nostril). It is advised not to prime the device to avoid loss of the medicine.
The dose can be adjusted based on efficacy and tolerability. To maximize the effect, a five-minute rest is advised before administering the drug. Also, it is advised to avoid intake of food two hours before drug administration. The drug should be administered in a semi-reclined position. In case you have other health conditions or are under medications, your doctor will alter your dosage accordingly.
IMPORTANT: It is advised to assess the blood pressure before the S Ketamine dose as the drug administration can further elevate it.
Missed Dose:
If there is no worsening of the symptoms after missing a session of treatment, then he should continue the current dose schedule. Patients who miss the sessions during the maintenance treatment and develop worsening symptoms then they should return to the previous dose schedule. e.g., if doses are missed during weekly dosing, return to twice weekly dosing.
What Are the Drug Warnings and Precautions?
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding - Esketamine is not recommended in pregnant and breastfeeding women. If a woman becomes pregnant during the treatment, the drug should be discontinued and the patient should be counseled about the risk to the fetus. Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment. If you are planning to conceive, are pregnant, or breastfeeding your child, inform your doctor beforehand.
-
High Blood Pressure - This drug increases systolic and diastolic blood pressure at all recommended doses. There can be an increase in blood pressure within 40 minutes of administration. Getting your blood pressure checked before administering the nasal dose is recommended.
-
Ulcerative or Intestinal Cystitis - Long-term use causes intestinal ulcers, so monitoring of the urinary tract and bladder during the treatment is required.
-
Memory Impairment - Repeated ketamine misuse results in long-term cognitive and dementia (memory loss).
-
Sedation - Because of the possibility of delayed or prolonged sedation, patients must be monitored by a health provider for at least two hours during the treatment session. The patient is allowed to leave the health facility after he is considered clinically stable.
-
Dissociation - The most common effect of Esketamine is dissociation or disorientation of time-space and other perception changes.
-
Impaired Ability to Drive and Operate Machines - Once taken, patients should not engage in activities requiring mental alertness and motor coordination until the next day.
-
Abuse and Misuse - Patients should be monitored for the development of this behavior, including drug-seeking behavior, while on therapy. Esketamine is available only through a restricted program under REMS. The healthcare provider must ensure every patient is enrolled before starting the treatment.
-
Other Medications - It is advised to administer other nasal medications 1 hour before.
The drug is available in a black box warning by the FDA for its high relative incidence of sedation and dissociation.
What Are the Side Effects of Esketamine?
The most common side effects of Esketamine are
The more severe side effects include
-
Vertigo.
-
Dizziness.
-
Hypoesthesia.
-
Euphoric mood.
-
Dissociation.
-
Feeling drunk.
-
Blurred vision.
-
Pounding in neck and ears.
-
Hallucinations.
-
Painful urination.
-
Chest pain.
IMPORTANT: The side effects above are not the only effects you will experience. In addition, there can be various other side effects. If you experience any of the side effects listed above or discomfort, call your doctor immediately. Always let your doctor know if you notice any unusual symptoms.
What Are the Interactions of Esketamine?
With Medicines:
-
CNS Depressants - Benzodiazepines, Opioids, and alcohol can increase the risk of sedation.
-
Psychostimulants - Amphetamines, Methylphenidate, Modafinil, and Armodafinil can result in high BP.
-
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) - If these drugs are used with Esketamine, it may increase blood pressure.
-
Rifampicin.
-
Ticlopidine.
With Alcohol:
Avoid consuming alcohol when taking this drug, as it may increase side effects like confusion, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and drowsiness.
With Food:
Caffeine-containing food and beverages with Esketamine may increase blood pressure.
With Diseases:
-
Heart Diseases - Do not use this medicine if you have heart and heart vessel diseases.
-
Psychosis - Patients with psychosis must be assessed before administering this drug.
-
Hepatic Impairment - Patients with hepatic impairment need to be monitored for adverse reactions.
-
Drug Abuse - Individuals with prior history of drug abuse or dependency may be assessed before the administration of Esketamine.
Conclusion:
Esketamine is a potentially effective nasal spray used for the treatment of depression in adults who have not benefitted from other antidepressants. Repeated use of the drug is associated with recognized withdrawal syndrome and should be used judiciously.












