Overview:
Digest medicine is the common term used to describe the medications prescribed to aid the breakdown and digestion of food for those whose pancreas cannot make or release enough digestive enzymes. It is used as a supplement or replacement pill containing digestive enzymes. Digest medicine is available as a tablet and as a capsule. The doctor will determine the use and directions.
The active ingredients in digestive medicine are naturally occurring digestive enzymes like amylase, lipase, protease, and others. They are available over-the-counter (do not require a prescription), while some specific others are prescription pills. Avoid taking this medication if symptoms of allergy are experienced, and seek medical help immediately.
Drug Group:
Digest medicine belongs to the class of supplements called digestants or enzymes. The drugs coming under this class are primarily used as remedies to aid digestion in insufficiency of the pancreas, inflammation of the pancreas, cystic fibrosis, or other related conditions. Different strengths are available for this pill based on the composition of the number of digestive enzymes.
What Is Digest Medicine Used For?
The body uses digestive enzymes to break down food's proteins, lipids, and carbs. This is required to ensure nutrition absorption and sustain optimum health. These nutrients in the diet are lost without these enzymes. The main organ responsible for the release of digestive enzymes in the pancreas and the synthesis and release of digestive enzymes are impaired or affected negatively in the following conditions:
-
Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (inability of the pancreas to synthesize digestive enzymes leading to poor nutrition and digestion).
-
Cystic fibrosis (a genetic disorder affecting the digestive system and lungs).
-
Cyst in the pancreas.
-
Pancreatic surgery.
Hence, to supplement the deficiency of these enzymes, digestive medicines are given.
How Does Digest Medicine Work?
The ability of the body to digest food and absorb nutrients is compromised when the pancreas does not naturally generate digestive enzymes. Malnutrition and symptoms like bloating, cramps, gassiness, and diarrhea may result from this.
In place of natural enzymes, replacement digestive enzymes aid in the breakdown of proteins, lipids, and carbohydrates in food. The bloodstream's nutrients are then circulated throughout the body and absorbed through the small intestinal wall. Therefore, the replacement of digestive enzymes can aid in preventing malabsorption and associated gastrointestinal discomforts.
The major constituents of digest medicine are as follows:
-
Amylase: Starches, or carbs, are broken down into sugar molecules by this enzyme. Amylase deficiency can cause diarrhea.
-
Protease: This enzyme is responsible for the digestion of proteins and breaks them down into amino acids.
-
Lipase: Lipase breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol. It functions along with the bile for the digestion of fats.
Onset of Action:
Digest medicines work similarly to naturally occurring enzymes. The onset of action is 20 to 25 minutes post-oral administration, and the pill's effect can last one to 1.15 hours.
Habit-Forming:
Digest medicine contains only natural digestive enzymes, and their use is not associated with habit-forming tendencies.
Expiry Date:
Do not take the pills past their expiry date. The expiry date will be available on the pill packet or at the back of the medication strip.
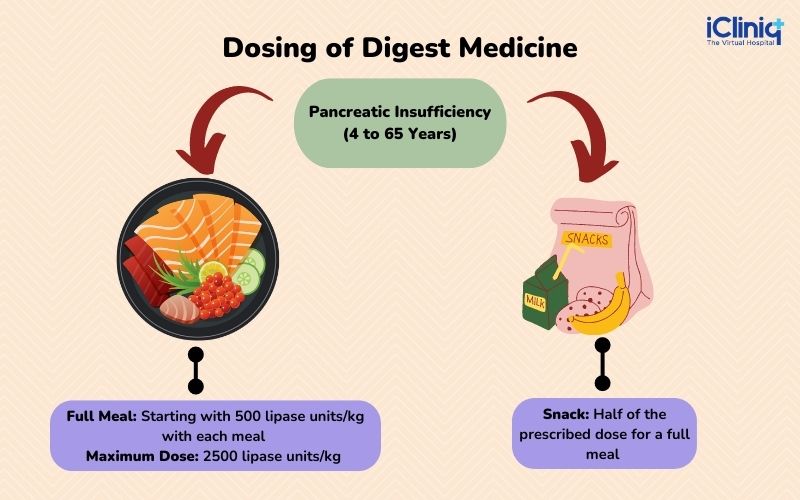
What Is the Dosage of Digest Medicine?
Digest medicines may be purchased over the counter without any prescription. However, the supplementation requires a prescription in case of severe deficiency, pancreatic surgery, or tumors.
The doctor determines the pill dose and adjusts it per the patient's requirements.
How to Use Digest Medicine?
-
Digest medicine must be taken during meals or right before eating.
Tablets:
-
Be careful not to hold it in the mouth for too long because doing so can irritate the cheeks and gums.
-
The drug should be taken with water. Chew the chewable tablets entirely before swallowing them.
Capsules:
-
Swallow the capsule as a whole while taking the meals.
-
If swallowing is a problem and taking the prescription in capsule form, open the capsule and mix the powder with some food or fluids.
General Information:
-
The powder can irritate the inside of the nose or trigger an asthma attack, so take care not to inhale any of it.
-
To get the most out of this drug, take the pill as directed.
-
Do not switch the brands or dosage forms of the pill because the digestive enzymes may be available at varying levels depending on the product. And hence, the effect will be different.
Missed Dose:
In case a dose is missed, do not take double doses for the next meal. Just skip the missed pill and take the next dose as directed.
Overdose:
If the pill is taken greater than the required amount, and if unusual symptoms arise, seek emergency medical help immediately.
What Are the Drug Warnings and Precautions?
The pills should be taken cautiously and only after consulting the doctor under the following conditions:
-
Allergies: History of allergy to the pill or any of the components. Usually, prescription pills contain pork protein. Hence, let the physician know if allergies exist to the active or inactive ingredients of the supplements.
-
Pancreatitis: Notify the doctor if there is a history of inflammation of the pancreas or if symptoms of pancreatic inflammation arise, like swelling or severe abdominal pain.
-
Pregnancy: Consult the doctor before starting the pill. Caution is required.
-
Breastfeeding: Notify the physician before taking the pill.
-
Before Surgery: Inform the physician of taking the pills before any surgical procedures.
What Are the Side Effects of Digest Medicine?
The common side effects include
-
Nausea.
-
Abdominal pain.
-
Vomiting.
-
Cramps.
-
Gas.
-
Flatulence.
These effects usually go on their own. However, if they become persistent or severe, seek medical help.
The serious side effects include
-
Allergy to the pill (swelling, hives, and rashes).
-
Severe abdominal discomfort.
-
Joint pain.
-
Painful urination.
Seek emergency help in case of severe side effects.
What Are the Interactions of Digest Medicine?
It is common for pills to interact with drugs or other supplements. These may result in unwanted side effects. Hence, it is required to check the possible interactions listed below:
1. With Drugs:
-
Antacids.
-
Acarbose.
-
Miglitol.
2. With Alcohol: Digest medicine has not been reported with any interaction with alcohol.
3. With Food: No serious food interaction has been reported. However, there will be diet restrictions while taking the pill. Talk with the physician first. For high doses, the patients are advised to maintain proper hydration.
What Are the Common Brands or Trade Names of Digest Medicine?
-
Tablet Pancreaze.
-
Capsule Zenpep.
-
Capsule Creon.
-
Capsule Pertzye.












