What Is Ejaculation?
Ejaculation is the release of semen from the male reproductive organ. It occurs due to extreme sexual arousal or orgasm at the end of sexual intercourse.
What Is an Ejaculation Disorder?
Any condition that causes a disturbance in the normal ejaculatory pathway and sexual response cycle of a male.
Who Is Affected by Ejaculation Disorders?
Males of most ages (18 to 59 years commonly) can be affected by ejaculation disorders. However, it is more common in older men, for natural, biological reasons of age. Younger men experiencing issues with ejaculation may exhibit symptoms for reasons that are often reversible with counseling or medication.
What Are the Types of Ejaculations?
Ejaculations can be of five types:
- The standard orgasm or ejaculatory.
- Retrograde or dry orgasm, as seme enters the bladder and very little is ejaculated out through the penis, but a person still reaches the climax.
- Pelvic, which can be achieved by a technique known as edging, which is done by masturbating continuously until a person comes.
- Wet dreams occur as an involuntary orgasm during sleep.
- Prostrate orgasm is achieved by stimulating the male G-spot, which is the prostate gland.
What Are the Types of Ejaculation Disorders?
Ejaculation disorders are classified into four types:
- Premature ejaculation.
- Delayed ejaculation.
- Retrograde ejaculation.
- Anejaculation.

What Is Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is when a male ejaculates sooner than expected or normal during sexual intercourse. The average time to ejaculation for healthy males has been estimated at 5.5 minutes, give or take a couple of minutes. However, the experience differs for different individuals, and this value should not be accepted as concrete. What does matter is when the instances of premature ejaculation are frequent and take away from the pleasure of the sexual experience for both partners.
What Are Some Other Names for Premature Ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation may also be referred to as:
-
Premature climax.
-
Rapid ejaculation.
-
Early ejaculation.
How Is Premature Ejaculation Categorized?
Premature ejaculation is categorized into two types, based on the time of onset:
-
Primary Premature Ejaculation (Lifelong): Consistently experienced since the first sexual experience.
-
Secondary Premature Ejaculation (Acquired): Recently developed, the patient will usually have a history of normal ejaculation during previous sexual experiences.
What Are the Causes of Premature Ejaculation?
1. Physical Factors:
-
Inflammation of the prostate gland.
-
Inflammation of the urethra.
-
Underactive or overactive thyroid gland.
-
Substance abuse (use of recreational drugs or alcohol).
-
Abnormal levels of hormones like testosterone.
-
Abnormal neurotransmitter (chemicals produced by the nerve cells) levels.
2. Psychological and Emotional Factors:
- Anxiety.
- Stress.
- Depression.
- Poor self-esteem.
- Body image issues.
-
History of sexual abuse can also cause premature ejaculation both in the accused or culprit and the victims.
- Relationship or marital troubles.
- Performance anxiety is caused by worrying about sexual experience or performance and being unable to ejaculate due to anxiety.
- Individuals with a strict upbringing are discouraged from sexual intimacy.
- The sexual beliefs of people may psychologically influence them to the extent that they experience premature ejaculation during sexual intercourse.
3. Physiological Factors:
-
Older age groups.
4. Biological Factors:
-
Sensitive Penis: Rarely, men may complain of extreme sensitivity in the penis.
How Is Premature Ejaculation Treated?
Treatment options available depend on individual needs, the needs of the couple, and the causative factors for premature ejaculation, but generally fall under one of four categories:
1. Self-help:
-
Masturbation: Patients are advised to masturbate an hour or two before having sex. This may help hold off on ejaculation for at least a little while.
-
Avoid Intercourse: Trying out non-penetrative sexual activities or games for a short period could alleviate performance anxiety.
-
Condom Usage: Using a thick condom with or without a numbing agent would cause a mild reduction in sensation.
-
Ejaculatory Reflex Shutdown: Taking deep breaths would shut down the reflex that causes ejaculation to occur and prevent rapid ejaculation.
-
Take Breaks: Short breaks during intercourse would distract from the focus on ejaculation.
2. Counseling and Therapy:
-
Couples Therapy: Couples therapy will benefit couples struggling with issues within their relationship that may be contributing to psychologically-mediated premature ejaculation.
3. Exercises:
Exercises that couples can perform together may be attempted without any outside help. They may also learn them from a therapist. The most popular methods are:
-
Squeeze Technique: The partner masturbates or stimulates the penis until ejaculation is almost achieved, then stops immediately to squeeze the penis for 10-20 seconds until the erection weakens. The process is repeated several times, with 30-second breaks in between. This can lead to the development of better control over climaxing.
-
Stop-Go Technique: The process is precisely the same as the squeeze technique for the stop-go technique, except that the penis is not squeezed. The partner stops stimulating the penis just before the point of ejaculation and waits till the affected partner is in control again. Then they repeat the process at least three more times, with actual ejaculation occurring during the final attempt.
Apart from these exercises, patients may also attempt pelvic floor exercises or Kegel maneuvers, which focus on tightening the pelvic floor muscles to develop better control.
4. Medications:
Drugs available for treatment are not generally marketed as medication specific to premature ejaculation. Drugs marketed as antidepressants or medication for erectile dysfunction are prescribed instead - they are known to delay ejaculation.

What Is Delayed Ejaculation?
Delayed ejaculation occurs when the stimulation period required for a male to achieve climax is excessively long. In some cases, ejaculation is not achieved at all. The sexual stimulation time required to ejaculate may be as long as 30 minutes.
What Are Some Other Names for Delayed Ejaculation?
-
Impaired ejaculation.
-
Retarded ejaculation.
-
Inhibited ejaculation.
How Is Delayed Ejaculation Classified?
Delayed ejaculation is symptomatically classified as:
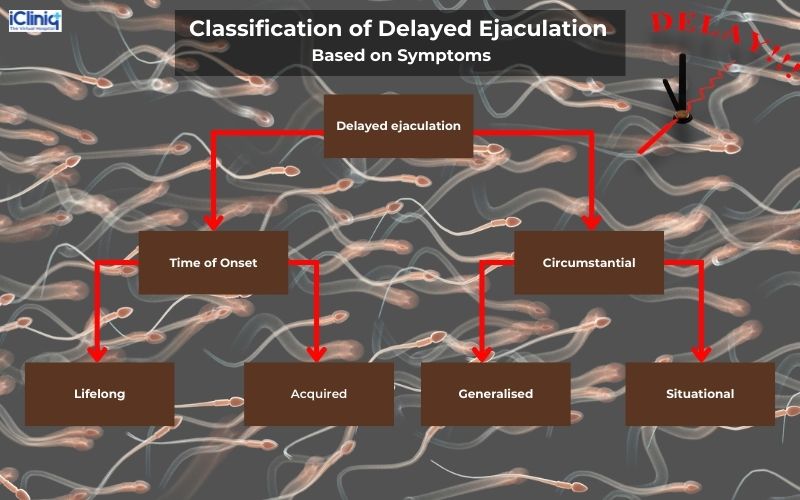
-
Lifelong: Present since attaining sexual maturity.
-
Acquired: Develops at some point in life, before which normal ejaculation was present.
-
Generalized: Generalized delayed ejaculation applies to all sexual partners and any form of stimulation.
-
Situational: Situational delayed ejaculation occurs specific to particular circumstances, partners, or forms of stimulation.
What Are the Causes of Delayed Ejaculation?
1. Physical Factors:
-
Pelvic nerve injuries.
-
Infections.
-
Hormonal disorders such as low levels of thyroid hormone, and low levels of testosterone.
Neurological diseases such as stroke and spinal damage.
2. Psychological and Emotional Factors:
-
Stress.
-
Anxiety.
-
History of sexual trauma and abuse.
-
Relationship or marital issues.
-
The conflict between sexual fantasies and the reality of sexual experiences.
3. Medications:
-
Antidepressants and antipsychotics.
-
Anti-epileptics (seizure medications).
-
Antihypertensives (medications for high blood pressure).
-
Muscle relaxants.
-
Strong painkillers.
4. Physiological Factors:
-
Older age groups.
5. Other Factors:
-
Substance abuse (alcohol and drug use).
How Is Delayed Ejaculation Treated?
Treatment depends on the causative factor for delayed ejaculation.
-
Sex Therapy: When the underlying cause is psychological, sex therapy will provide two services - counseling for psychological or mental health issues and sex advice to help implement changes to the sexual routine of the patient.
-
Reduction of Drug Dosage or Substitution of Drug: If the cause is a drug, reducing the dosage or switching to an alternative drug will often help rectify the problem.
-
Addressing Substance Abuse: Avoiding alcohol and drugs or reducing the amount consumed.
-
Medications: Drugs used, as in the case of premature ejaculation, are not strictly targeted at delayed ejaculation - they are marketed for various other purposes.

What Is Retrograde Ejaculation?
Retrograde ejaculation also known as dry orgasm occurs when semen travels backward into the urinary bladder rather than forwards and through the urethra. The muscle that controls the movement of semen and pushes it out through the urethra while preventing it from entering the bladder fails to perform this function. This results in little to no ejaculate being released.
What Are the Causes of Retrograde Ejaculation?
Retrograde ejaculation can be attributed solely to physical causes. The mechanism involves damage to the nerves or muscles around the neck of the urinary bladder.
The causes for this damage may include:
-
Surgery: Prostate gland surgery or bladder surgery.
-
Diseases: Multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, diabetes.
-
Medications: Certain antihypertensives (drugs for blood pressure treatment) and antidepressants.
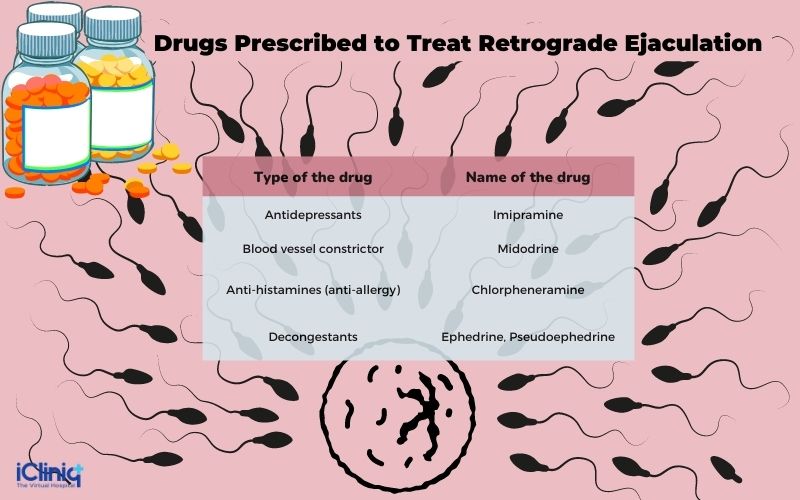
How Is Retrograde Ejaculation Treated?
Retrograde ejaculation does not generally interfere with sexual pleasure and does not require treatment unless the patient's infertility is a matter of concern. It is challenging to treat since it is a nerve disorder.
-
Medication Change or Termination: If the issue has occurred as a result of any particular medication, then changing the drug will help. Stopping the drug will also reverse the situation but should never be attempted unless the physician in charge agrees.
-
Medications: As with all other ejaculation disorders, drugs recommended for other conditions are prescribed for retrograde ejaculation.
In case of irreversible damage to the nerves or muscles, treatment is usually impossible. However, if the patient would like to father children at some point through artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization (IVF), the sperm present in the urine can be collected for this purpose.
What Is Anejaculation?
Anejaculation happens when there is absolutely no emission of ejaculate by the male partner during sexual intercourse. Although sperm may be produced and sexual satisfaction achieved to a degree, semen is not released. Anejaculation may or may not be accompanied by orgasmic dysfunction.
How Is Anejaculation Classified?
-
Primary Anejaculation: The inability to ejaculate right from the first sexual experience.
-
Secondary Anejaculation: Developed at some point after being able to ejaculate normally.
What Are the Causes of Anejaculation?
1. Physical Factors:
-
Diseases: Diabetes mellitus, infections, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis.
-
Surgeries: Lymph node dissection (retroperitoneal), prostate surgery.
-
Medications: Antidepressants.
-
Injuries: Spinal cord injuries, pelvic injury.
2. Psychogenic Factors:
-
Psychological Factors: Performance anxiety could contribute to an inability to ejaculate.
-
Relationship Issues: Marital or relationship issues, including lack of sexual attraction to the partner, communication issues, or non-sexual problems that affect the sexual life.
-
Behavioral Factors: Preference for masturbation and sexual fantasy over the reality of sexual intimacy with one's partner; sexual proclivities that do not align with the partner's interests.
How Is Anejaculation Treated?
-
Vibrostimulation: Application of a vibrator to the penis that stimulates an ejaculation response.
-
Electroejaculation: Electric stimulation of the prostate nerves by inserting an electric probe into the rectum that delivers current and stimulates ejaculation.
-
Sex Therapy: In case of psychological issues and relationship problems.
-
Medication Changes: Changing or reducing medication such as antidepressants which act as causative factors for anejaculation.
-
Insemination: Using insemination to address the patient's need to procreate, thereby relieving anxiety.
Conclusion:
Ejaculatory disorders are not easy to face, but they are not all untreatable and the solutions employed have found satisfaction in almost all recorded cases. Partner support, good communication, open discussion with physicians, and willingness to go the extra mile to achieve mutual satisfaction will give the best results. Therefore, if a person is experiencing any type of ejaculatory issues, they should consult the doctor for proper assistance and treatment.













